2024 federal income tax brackets for head of household are a crucial aspect of financial planning for individuals who qualify for this filing status. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the tax brackets, standard deduction, and key credits and deductions available to head of household filers in 2024.
Understanding these factors is essential for maximizing tax savings and ensuring compliance with federal tax regulations.
Navigating the tax system can be complex, especially for those filing as head of household. This guide aims to demystify the process by providing clear explanations and practical tips. We’ll explore the eligibility requirements for head of household status, examine the specific tax brackets and deductions, and offer strategies for minimizing tax liability.
Contents List
- 1 Understanding Head of Household Filing Status
- 2 2024 Federal Income Tax Brackets for Head of Household
- 3 Key Tax Credits and Deductions for Head of Household Filers
- 4 Tax Planning Tips for Head of Household Filers
- 5 Resources for Head of Household Filers
- 6 Wrap-Up: 2024 Federal Income Tax Brackets For Head Of Household
- 7 Common Queries
Understanding Head of Household Filing Status
The Head of Household (HOH) filing status is a tax filing option available to unmarried individuals who pay more than half the costs of keeping a home for a qualifying child or dependent. This status often offers lower tax rates and a higher standard deduction than the Single filing status, making it beneficial for many taxpayers.
If you’re looking to contribute to a traditional 401k, you might be wondering about the contribution limits for 2024. The What are the 401k contribution limits for 2024 for traditional 401k can help you plan your savings strategy.
Eligibility Criteria for Head of Household
To qualify for Head of Household filing status, you must meet the following criteria:
- Be unmarried at the end of the tax year.
- Pay more than half the costs of keeping up a home for a qualifying child or dependent.
- Have a qualifying child or dependent living with you for more than half the year.
- Be able to claim the qualifying child or dependent as a dependent on your tax return.
Benefits of Head of Household Filing Status
The Head of Household filing status offers several benefits, including:
- Lower Tax Rates:The tax rates for Head of Household are generally lower than the Single filing status, resulting in lower tax liability.
- Higher Standard Deduction:The standard deduction for Head of Household is higher than the Single filing status, which reduces your taxable income.
- Access to Other Tax Credits and Deductions:You may be eligible for various tax credits and deductions, such as the Child Tax Credit, which can further reduce your tax liability.
Potential Drawbacks of Head of Household Filing Status
While Head of Household offers benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Limited Eligibility:The specific requirements for qualifying for Head of Household status can be restrictive, and not everyone who is unmarried and has a child or dependent will qualify.
- Tax Implications:If you are close to the income threshold for a particular tax bracket, choosing Head of Household status could potentially push you into a higher tax bracket, increasing your tax liability.
Comparison to Single and Married Filing Separately Statuses
The Head of Household filing status provides advantages over the Single filing status, offering lower tax rates and a higher standard deduction. However, it’s crucial to compare the benefits and drawbacks of Head of Household against the Married Filing Separately status, as the most advantageous option will depend on your individual circumstances.
- Single Filing Status:This status is for unmarried individuals who are not eligible for Head of Household. While it offers simplicity, it often results in higher tax liability compared to Head of Household.
- Married Filing Separately Status:This status is for married couples who choose to file their taxes separately. It may be beneficial in some situations, but it often results in higher tax liability than filing jointly.
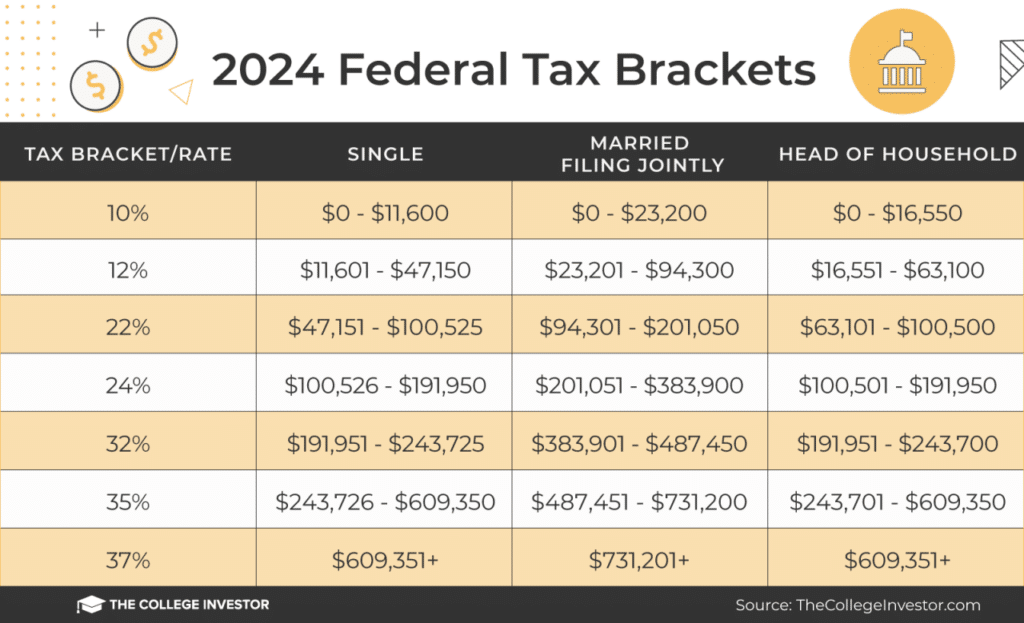
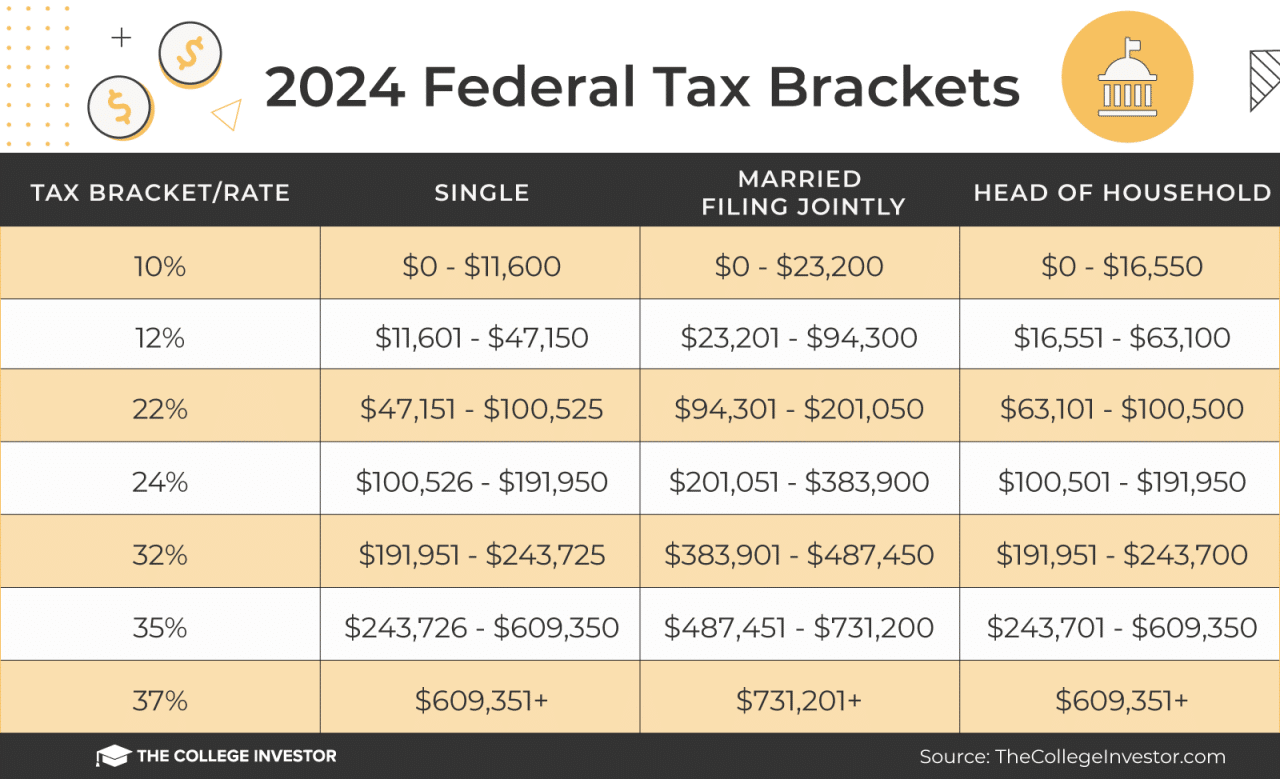
2024 Federal Income Tax Brackets for Head of Household
The 2024 federal income tax brackets for Head of Household filers determine the tax rate applied to different income levels. These brackets are designed to ensure a progressive tax system, where higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes.
The how much can I contribute to a Roth IRA in 2024 is a great question to ask if you’re considering contributing to a Roth IRA. This amount can help you plan your savings strategy.
Understanding these brackets is crucial for Head of Household filers to accurately estimate their tax liability and plan their finances accordingly.
The Tax extension deadline October 2024 for estates and trusts is a crucial date for those responsible for managing these entities.
2024 Federal Income Tax Brackets for Head of Household
The following table summarizes the 2024 tax brackets for Head of Household filers:
| Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0
You might be wondering if you can contribute more than the 401k limit in 2024. The answer is, it depends. Check out this article for more information: Can I contribute more than the 401k limit in 2024.
|
10% |
$10,751
|
12% |
$45,001
|
22% |
| $110,001
The standard deduction amount for 2024 tax year is important to know when you’re filing your taxes.
|
24% |
$210,001
|
32% |
| $550,001
If you’re planning a move in October 2024, you’ll want to know the latest mileage rate for moving expenses. The October 2024 mileage rate for moving expenses can help you calculate the deductible expenses for your relocation.
|
35% |
| $1,000,001+ | 37% |
Standard Deduction for Head of Household Filers in 2024
The standard deduction amount for Head of Household filers in 2024 is $20,800. This amount is subtracted from a filer’s adjusted gross income (AGI) before calculating their taxable income. The standard deduction helps reduce the amount of income subject to taxation, potentially lowering the overall tax liability.
Tax Brackets and Standard Deduction Impact on Tax Liability
The tax brackets and standard deduction significantly influence the tax liability of Head of Household filers.
Wondering how much you can contribute to your IRA in 2024? The How much can I contribute to my IRA in 2024 can help you plan your retirement savings.
The standard deduction reduces the amount of taxable income, which directly impacts the tax rate applied to the remaining income.
For example, if a Head of Household filer has an AGI of $50,000, their taxable income would be $29,200 ($50,000$20,800). This income falls within the 12% tax bracket, meaning they would pay 12% on the first $10,750 of taxable income and 22% on the remaining amount.
Understanding the interplay between tax brackets and the standard deduction is crucial for Head of Household filers to optimize their tax planning strategies and minimize their tax burden.
If you’re wondering about the standard deduction for the 2024 tax year, you can find the information on the How much is the standard deduction in 2024 page.
Key Tax Credits and Deductions for Head of Household Filers
Head of Household filers can take advantage of various tax credits and deductions that can significantly reduce their tax liability. Understanding these benefits can help you maximize your tax savings and keep more money in your pocket.
Tax Credits
Tax credits directly reduce your tax liability, dollar for dollar. Here are some of the major tax credits available to Head of Household filers in 2024:
- Child Tax Credit:The Child Tax Credit is a fully refundable credit that can be claimed for each qualifying child under 17 years old. The credit amount for 2024 is $2,000 per qualifying child. The credit begins to phase out for taxpayers with adjusted gross income (AGI) above certain thresholds.
The What is the 401k contribution limit for 2024 is a great question to ask if you’re planning your retirement savings strategy.
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC):The EITC is a refundable credit for low- and moderate-income working individuals and families. The credit amount depends on your income, filing status, and the number of qualifying children. The EITC can provide a significant tax refund, especially for those with qualifying children.
Thinking about your retirement savings? The What is the 401k contribution limit for 2024 can help you determine how much you can contribute to your 401k plan in the coming year.
- American Opportunity Tax Credit:This credit is available for the first four years of post-secondary education. The credit is worth up to $2,500 per eligible student and is phased out for taxpayers with AGI above certain thresholds.
Tax Deductions, 2024 federal income tax brackets for head of household
Tax deductions reduce your taxable income, which in turn reduces your tax liability. Here are some of the common tax deductions applicable to Head of Household filers:
- Homeownership Deduction:This deduction allows you to deduct the interest paid on your mortgage and property taxes on your primary residence. The deduction can be a significant benefit for homeowners.
- Charitable Contributions:You can deduct cash and non-cash contributions to qualified charities. The amount of the deduction is generally limited to 60% of your AGI.
- Medical Expenses:You can deduct medical expenses exceeding 7.5% of your AGI. This deduction can be helpful if you have high medical costs.
- State and Local Taxes (SALT):The SALT deduction allows you to deduct up to $10,000 in state and local taxes paid. This deduction can be beneficial for taxpayers in states with high property taxes or income taxes.
Impact of Tax Credits and Deductions
The impact of tax credits and deductions on your overall tax liability depends on your individual circumstances. For example, a taxpayer with a high income and multiple qualifying children may benefit significantly from the Child Tax Credit and the EITC.
The deadline for filing your W9 Form in October 2024 might be on your mind. You can find the W9 Form October 2024 deadline for filing here.
On the other hand, a taxpayer with a lower income and no qualifying children may not benefit as much from these credits. It’s important to carefully consider all available credits and deductions and to seek professional advice to determine which benefits are most beneficial for your situation.
Tax Planning Tips for Head of Household Filers
Being a Head of Household filer comes with unique tax benefits. However, there are many ways to further optimize your tax situation and potentially lower your tax burden. Here are some strategic tax planning tips designed to help you navigate the complexities of Head of Household filing in 2024.
The What are the 401k contribution limits for 2024 for different ages can help you understand the different contribution limits based on your age.
Maximizing Deductions and Credits
Understanding available deductions and credits is crucial for Head of Household filers. Utilizing these tax benefits can significantly reduce your tax liability.
- Child Tax Credit:This credit is worth up to $2,000 per qualifying child under 17. The credit is fully refundable, meaning you can receive a refund even if you don’t owe any taxes.
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC):The EITC is a refundable tax credit for low-to-moderate income working individuals and families. The credit amount depends on your income and number of qualifying children.
- American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC):The AOTC is a tax credit for qualified education expenses for the first four years of post-secondary education. It is worth up to $2,500 per student.
- Student Loan Interest Deduction:You can deduct up to $2,500 in interest paid on qualified student loans.
- Medical Expense Deduction:You can deduct medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI).
- State and Local Tax (SALT) Deduction:The SALT deduction allows you to deduct up to $10,000 in state and local taxes paid, including property taxes, income taxes, and sales taxes.
- Homeownership Deductions:If you own a home, you can claim deductions for mortgage interest and property taxes.
- Charitable Contributions:You can deduct cash contributions up to 60% of your AGI, and non-cash contributions up to 30% of your AGI.
Avoiding Common Tax Pitfalls
While tax benefits can be beneficial, it’s equally important to avoid common tax pitfalls that can lead to penalties and additional tax liabilities.
Corporations might need to file for a tax extension in October 2024. The Tax extension deadline October 2024 for corporations is a crucial date to remember.
- Failing to File on Time:The deadline for filing your federal income tax return is April 15th each year. Filing late can result in penalties.
- Incorrectly Claiming the Head of Household Filing Status:To qualify for Head of Household status, you must meet specific requirements, such as paying more than half the costs of keeping up a home for a qualifying child.
- Not Keeping Accurate Records:Maintaining detailed records of income, expenses, and deductions is essential for accurate tax reporting.
- Overlooking Tax Credits:Many taxpayers miss out on valuable tax credits due to lack of awareness or incorrect eligibility requirements.
- Not Understanding Tax Implications of Major Life Events:Significant life events, such as marriage, divorce, birth of a child, or job changes, can impact your tax situation.
- Not Taking Advantage of Tax Planning Strategies:Proactive tax planning can help you minimize your tax burden and maximize your financial benefits.
Tax Planning Strategies for Head of Household Filers
Proactive tax planning can make a significant difference in your tax liability.
The Ira contribution limits for 2024 vs 2023 can help you understand the changes in contribution limits for the upcoming year.
- Maximize Your Retirement Contributions:Consider contributing to a 401(k) or Roth IRA to reduce your taxable income and save for retirement.
- Make Tax-Advantaged Investments:Explore investment options that offer tax benefits, such as municipal bonds or tax-loss harvesting strategies.
- Review Your Withholding:Ensure your withholding is accurate to avoid underpayment penalties or large tax bills at the end of the year.
- Consider a Tax Professional:Consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice and guidance on complex tax situations.
Resources for Head of Household Filers
Navigating the complexities of tax laws and regulations can be overwhelming, especially for Head of Household filers. Fortunately, there are several resources available to provide guidance and support throughout the tax season.
Government Websites
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the primary source of information for all tax-related matters. Their website offers a wealth of resources, including:
- Tax Forms and Publications:Downloadable forms, instructions, and publications covering various tax topics.
- Taxpayer Assistance Center (TAC):Contact information for local IRS offices and phone numbers for assistance with tax questions.
- IRS Free File:Free online tax preparation services for eligible taxpayers with adjusted gross income (AGI) below a certain threshold.
- Interactive Tax Assistant (ITA):A tool that answers tax-related questions based on individual circumstances.
Tax Preparation Services
Tax preparation services can provide valuable assistance, especially for those who find tax filing challenging or time-consuming. Reputable services offer:
- Professional Expertise:Experienced tax professionals can help navigate complex tax situations and ensure compliance with tax laws.
- Software and Tools:Utilize advanced software and tools to streamline tax preparation and maximize deductions.
- Personalized Advice:Receive tailored recommendations and strategies based on individual circumstances and financial goals.
Tax Professional Consultation
Consulting with a qualified tax professional can provide personalized advice and guidance specific to your unique situation. They can help you:
- Determine Your Filing Status:Ensure you are filing under the correct status, including Head of Household, to maximize your tax benefits.
- Identify Deductions and Credits:Explore eligible deductions and credits that can reduce your tax liability.
- Develop a Tax Planning Strategy:Create a plan to minimize your tax burden and achieve your financial objectives.
Wrap-Up: 2024 Federal Income Tax Brackets For Head Of Household
By understanding the intricacies of the 2024 federal income tax brackets for head of household, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their financial planning. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the relevant information, including tax brackets, deductions, credits, and planning strategies.
However, it’s important to consult with a tax professional for personalized advice and guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Common Queries
What are the eligibility requirements for filing as head of household?
To file as head of household, you must be unmarried and pay more than half the costs of keeping up a home for a qualifying child or dependent relative. This qualifying child or dependent must live with you for more than half the year.
There are specific requirements for the qualifying child or dependent, so it’s important to consult with the IRS guidelines.
What are the benefits of filing as head of household?
Filing as head of household typically results in lower tax liability compared to filing as single. This is because the tax brackets for head of household are more favorable than those for single filers. Additionally, the standard deduction amount for head of household is higher than for single filers.
How do I know if I should file as head of household or single?
The best filing status for you depends on your individual circumstances. If you meet the eligibility requirements for head of household and your income falls within the lower tax brackets, filing as head of household will likely result in lower taxes.
However, if your income is high, the difference in tax liability between the two filing statuses may be minimal. It’s best to consult with a tax professional to determine the most advantageous filing status for your situation.
What are some common tax deductions for head of household filers?
Head of household filers can claim a variety of deductions, including the standard deduction, homeownership deductions (mortgage interest and property taxes), charitable contributions, medical expenses (above a certain percentage of adjusted gross income), and student loan interest. The specific deductions you can claim depend on your individual circumstances.
Where can I find more information about 2024 federal income tax brackets for head of household?
For the most up-to-date information and detailed guidance, consult the IRS website (www.irs.gov). You can also find valuable resources from reputable tax preparation services and financial advisors.