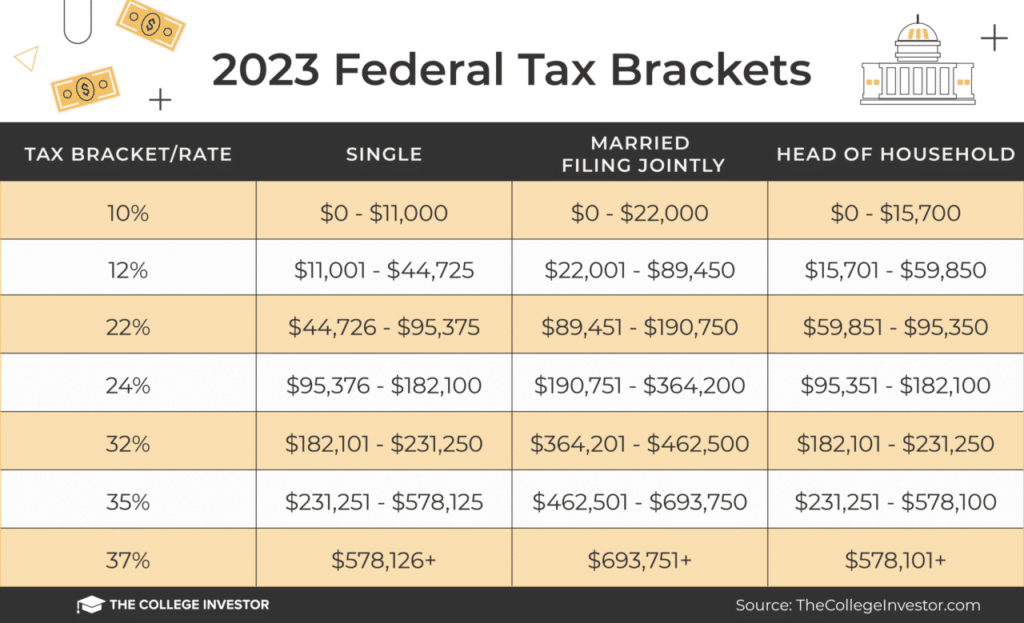
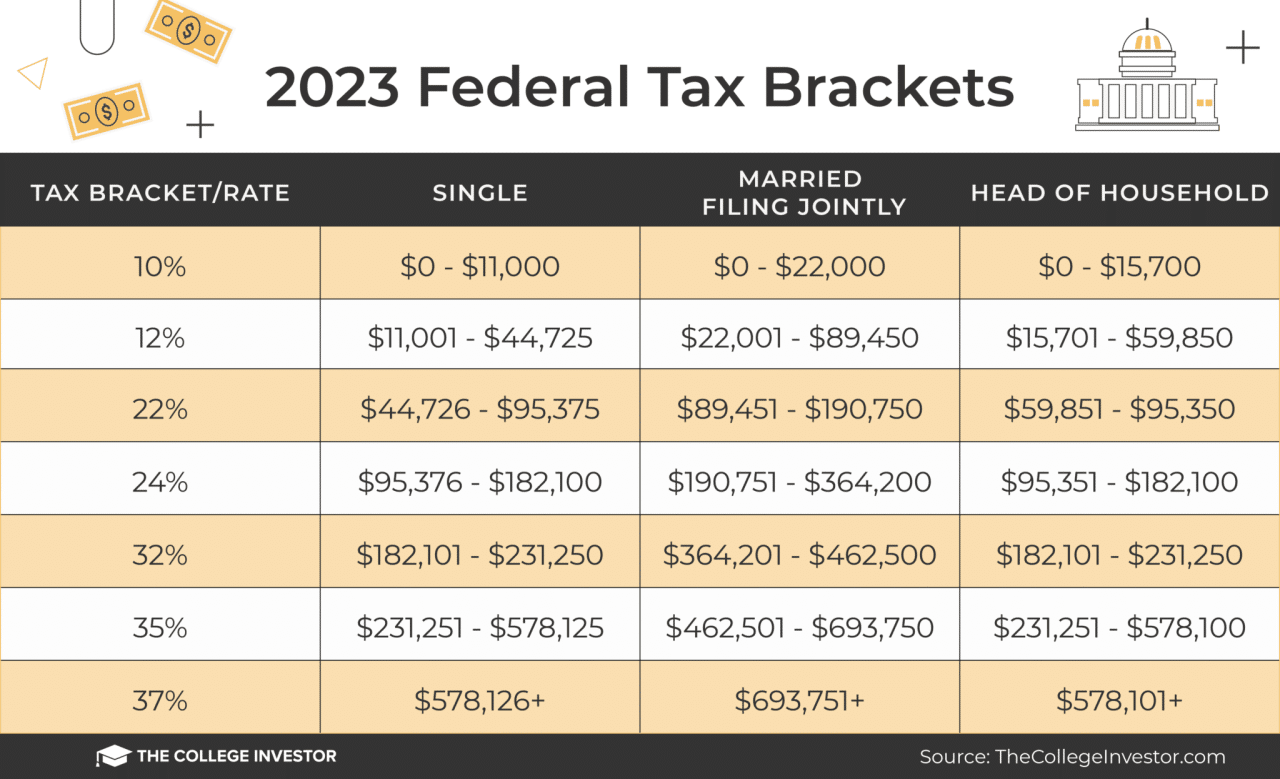
2024 Federal Tax Brackets are a crucial aspect of financial planning, determining how much tax you owe on your income. Understanding these brackets can help you make informed decisions about your finances, from saving for retirement to managing your investments.
The tax brackets are designed to be progressive, meaning that higher earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. This year, several factors, including inflation and potential legislative changes, may impact the tax brackets.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the 2024 Federal Tax Brackets, covering key concepts like taxable income, deductions, and credits. We’ll explore the different filing options available and offer strategies for minimizing your tax liability. Whether you’re a seasoned tax filer or a first-time taxpayer, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the tax landscape with confidence.
Contents List
- 1 Understanding Federal Tax Brackets
- 2 2024 Federal Tax Brackets
- 3 4. Standard Deduction and Itemized Deductions: 2024 Federal Tax Brackets
- 4 5. Tax Credits
- 5 6. Tax Filing Options
- 6 7. Tax Planning for 2024
- 7 Impact of Tax Brackets on Financial Decisions
- 8 Resources for Tax Information
- 9 Final Thoughts
- 10 Key Questions Answered
Understanding Federal Tax Brackets
The federal tax system in the United States uses a progressive tax system, meaning that individuals with higher incomes pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. The foundation of this system is built upon tax brackets, which are income ranges with specific tax rates.
This guide delves into the concept of federal tax brackets, how they work, their historical evolution, and the impact of inflation on them.
How Federal Tax Brackets Work
Federal tax brackets are defined by income ranges and corresponding tax rates. For each bracket, a different tax rate applies to the income earned within that range. To illustrate, let’s assume a simplified tax system with two brackets: * Bracket 1:Income up to $50,000 taxed at 10%.
Bracket 2
Income above $50,000 taxed at 20%.An individual earning $60,000 would pay 10% on the first $50,000 and 20% on the remaining $10,000. This means they would pay $5,000 (10% of $50,000) + $2,000 (20% of $10,000) = $7,000 in total federal income tax.
History of Federal Tax Brackets in the United States
The federal income tax system in the United States has undergone significant changes since its inception. The 16th Amendment, ratified in 1913, granted Congress the power to levy an income tax. Initially, the tax rates were relatively low and applied only to a small portion of the population.
“The Sixteenth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States was adopted in 1913. It gave Congress the power to levy an income tax without apportionment among the states.”
During World War II, the government increased tax rates to fund the war effort. After the war, tax rates gradually decreased, but the basic structure of the progressive tax system remained in place.
Impact of Inflation on Tax Brackets
Inflation can erode the purchasing power of income, leading to a situation known as “bracket creep.” This occurs when inflation pushes individuals into higher tax brackets, even if their real income (adjusted for inflation) has not increased.For example, if an individual earns $100,000 in 2023 and their income remains the same in 2024, but inflation is 3%, their real income has decreased by 3%.
Looking for financial assistance? The California Stimulus Check October 2024 Eligibility Requirements outline the criteria you need to meet to qualify for this payment.
However, due to inflation, their income may fall into a higher tax bracket in 2024, resulting in a higher tax burden.
“Bracket creep refers to the phenomenon where individuals are pushed into higher tax brackets due to inflation, even if their real income remains the same.”
To address this issue, policymakers may adjust tax brackets to account for inflation. This process is called “indexing” and ensures that individuals are not paying higher taxes simply because of inflation.
2024 Federal Tax Brackets
The 2024 federal tax brackets represent the different income ranges and corresponding tax rates that individuals and households will be subject to. Understanding these brackets is crucial for accurate tax planning and maximizing tax savings.
2024 Federal Tax Brackets
The 2024 federal tax brackets are based on your filing status and taxable income. Here is a detailed table outlining the 2024 federal tax brackets for different filing statuses:
| Filing Status | Income Range | Tax Rate | Maximum Tax |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single | $0
|
10% | $1,095 |
| Single | $10,951
|
12% | $5,054.50 |
| Single | $46,276
|
22% | $17,985.50 |
| Single | $101,751
|
24% | $37,895.50 |
| Single | $208,351
|
32% | $141,815.50 |
| Single | $578,126 or more | 37% | $197,673.50 + 37% of amount over $578,125 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $0
|
10% | $2,190 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $21,901
|
12% | $9,366 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $82,551
|
22% | $29,970 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $172,751
|
24% | $63,780 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $345,501
|
32% | $167,620 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $656,251 or more | 37% | $214,340 + 37% of amount over $656,250 |
| Married Filing Separately | $0
|
10% | $1,095 |
| Married Filing Separately | $10,951
|
12% | $4,683 |
| Married Filing Separately | $41,276
Planning a road trip? It’s helpful to know the latest 2024 Mileage Rate for your tax deductions. This rate can fluctuate, so it’s best to stay informed about current regulations.
|
22% | $14,985 |
| Married Filing Separately | $86,376
|
24% | $31,890 |
| Married Filing Separately | $172,751
|
32% | $83,810 |
| Married Filing Separately | $328,126 or more | 37% | $107,170 + 37% of amount over $328,125 |
| Head of Household | $0
|
10% | $1,835 |
| Head of Household | $18,351
|
12% | $6,603 |
| Head of Household | $61,701
Saving for retirement is a smart move! The Max 401k Contribution 2024 has been adjusted, so you can potentially contribute more to your future financial security.
|
22% | $22,963 |
| Head of Household | $138,201
|
24% | $48,863 |
| Head of Household | $282,101
|
32% | $120,903 |
| Head of Household | $578,126 or more | 37% | $171,673.50 + 37% of amount over $578,125 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | $0
|
10% | $2,190 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | $21,901
Mark your calendars! The 2024 Tax Deadline is approaching. Make sure you file your taxes on time to avoid any penalties.
|
12% | $9,366 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | $82,551
|
22% | $29,970 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | $172,751
|
24% | $63,780 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | $345,501
Want to improve your audio quality? Acoustic Foam Youtube 2024: Elevate Your Audio offers a guide to choosing the right acoustic foam for your recording setup.
|
32% | $167,620 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | $656,251 or more | 37% | $214,340 + 37% of amount over $656,250 |
Potential Changes to 2024 Federal Tax Brackets
The 2024 federal tax brackets are subject to change based on various economic and political factors. For example, inflation, economic growth, and political agendas can influence the tax rates and income thresholds.
It’s important to stay informed about any potential changes to the tax brackets as they can impact your tax liability.
4. Standard Deduction and Itemized Deductions: 2024 Federal Tax Brackets
The standard deduction and itemized deductions are two ways to reduce your taxable income. Understanding the differences between these options can help you maximize your tax savings.
Thinking about retirement? The Annuity King Sarasota 2024: Your Guide to Secure Retirement provides valuable insights and resources to help you plan for a comfortable future.
Comparing and Contrasting the Standard Deduction and Itemized Deductions
The standard deduction is a fixed amount that you can subtract from your taxable income, while itemized deductions allow you to deduct specific expenses, such as medical expenses, charitable contributions, and mortgage interest.
Key Differences
- Standard Deduction:A fixed amount that you can deduct from your taxable income, regardless of your expenses. It’s a simplified way to reduce your tax liability.
- Itemized Deductions:Allow you to deduct specific expenses that exceed certain thresholds. This can potentially result in a larger deduction than the standard deduction, but it requires more documentation and calculation.
Benefits and Drawbacks
- Standard Deduction:
- Benefit:Easy to claim, no need to track specific expenses.
- Drawback:May result in a smaller deduction than itemizing.
- Itemized Deductions:
- Benefit:Potentially larger deduction than the standard deduction.
- Drawback:Requires more paperwork and calculation, and not all expenses are deductible.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Standard Deduction | Itemized Deductions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A fixed amount deducted from taxable income. | Specific expenses exceeding certain thresholds that can be deducted. |
| Eligibility Criteria | All taxpayers are eligible. | Eligibility depends on the specific expense being deducted. |
| Calculation Method | Fixed amount determined by the IRS. | Calculated based on specific expenses and applicable deductions. |
| Potential Benefits | Simplified tax preparation, no need to track specific expenses. | Potentially larger deduction than the standard deduction. |
Common Itemized Deductions
Itemized deductions allow you to deduct certain expenses that exceed specific thresholds.
Medical Expenses
- Eligibility Requirements:You can deduct medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income (AGI). This means you can only deduct the amount that exceeds 7.5% of your AGI.
- Deductible Percentage:The deductible percentage for medical expenses is 7.5% of your AGI. This means you can only deduct the portion of your medical expenses that exceeds this threshold.
- Limitations:There are certain limitations on what qualifies as a medical expense. For example, cosmetic surgery is generally not deductible. You should consult with a tax professional for specific guidance on what expenses qualify.
Mortgage Interest
- Eligibility Requirements:You can deduct interest paid on a qualified mortgage loan, which includes loans used to acquire, construct, or improve a primary residence. This deduction is limited to interest on the first $750,000 of debt for a loan acquired after December 15, 2017.
- Maximum Deductible Amounts:The maximum deductible amount for mortgage interest is limited to $750,000 of debt for loans acquired after December 15, 2017. This means you can only deduct interest on the first $750,000 of your mortgage debt.
- Limitations:There are limitations on the types of mortgages that qualify for the deduction. For example, home equity loans generally do not qualify. It’s essential to consult with a tax professional to determine if your mortgage qualifies for the deduction.
Charitable Contributions
- Types of Contributions:You can deduct contributions to qualified charities, including cash, property, and volunteer services. The types of contributions you can deduct will vary depending on the charity and the type of donation.
- Limitations:There are limitations on the amount of charitable contributions you can deduct. The maximum deduction for cash contributions is generally 60% of your AGI. For non-cash contributions, the deduction is limited to 30% of your AGI.
- Required Documentation:You must have documentation to support your charitable contributions. This documentation may include a receipt from the charity or a written acknowledgement of the donation.
Choosing Between Standard and Itemized Deductions
The best option for you will depend on your individual circumstances.
Factors to Consider
- Total Itemized Deductions:If your total itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction, you should itemize.
- Specific Expenses:If you have significant medical expenses, charitable contributions, or mortgage interest, you may benefit from itemizing.
- Complexity:Itemizing requires more paperwork and calculation, so it may be more time-consuming. If you prefer a simpler tax preparation process, the standard deduction may be a better choice.
Examples of Scenarios
- Scenario 1:If you have high medical expenses, you may benefit from itemizing because the medical expense deduction can significantly reduce your taxable income.
- Scenario 2:If you have a large mortgage and significant charitable contributions, you may also benefit from itemizing.
- Scenario 3:If you have few deductible expenses, the standard deduction may be the best option for you.
Flowchart
[image of flowchart]
5. Tax Credits
Tax credits are a powerful tool for reducing your tax liability, offering direct reductions to the amount of taxes you owe. They differ from deductions, which only lower your taxable income, leading to a smaller tax bill.
California residents, keep an eye out! The California Stimulus Check October 2024: Amount and Payment Schedule has been released, so check if you qualify for this financial assistance.
Understanding Tax Credits and Deductions
Tax credits and deductions are both valuable tools for reducing your tax burden, but they work in distinct ways.
Tax deductionslower your taxable income, which in turn reduces your tax liability. Think of it as reducing the size of the pie you’re being taxed on.
Tax creditsdirectly reduce the amount of taxes you owe. This is like getting a discount on your tax bill.
Retirement planning is crucial! The 401k Limits 2024 have been updated, so make sure you’re aware of the maximum contributions you can make this year.
To illustrate the difference, imagine you have a taxable income of $50,000, and your tax rate is 15%. You’re looking at a tax bill of $7,500.Now, let’s see how a tax deduction and a tax credit would affect your tax bill:
Tax deduction
Tax season is around the corner! It’s important to know the Tax Brackets 2024 to understand how your income will be taxed. This information can help you plan your finances and potentially reduce your tax liability.
Let’s say you claim a $5,000 tax deduction. This reduces your taxable income to $45,000. Your tax bill would then be $6,750 (15% of $45,000). You’ve saved $750 in taxes.
Tax credit
If you claim a $5,000 tax credit, your tax liability directly decreases by $5,000. Your tax bill would be $2,500. You’ve saved $5,000 in taxes.As you can see, a tax credit offers a more significant reduction in your tax liability than a tax deduction.
Child Tax Credit
The Child Tax Credit provides financial assistance to families with qualifying children.
- Eligibility Requirements:
- The child must be under 17 years old at the end of the tax year.
- The child must be your dependent, meaning you provide more than half of their support.
- The child must be a U.S. citizen, national, or resident alien.
- The child must have a valid Social Security number.
- There are income limitations for the Child Tax Credit, which vary based on your filing status.
- Credit Amount:
- The Child Tax Credit for 2024 is $2,000 per qualifying child.
- The credit is phased out for taxpayers with higher incomes.
- The amount of the credit that is refundable depends on your income and other factors.
- Examples:
- A single parent with an adjusted gross income (AGI) of $40,000 and two qualifying children could claim a Child Tax Credit of $4,000.
- A married couple with an AGI of $100,000 and three qualifying children might have their Child Tax Credit reduced due to the phase-out.
Earned Income Tax Credit
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income working individuals and families.
- Eligibility Requirements:
- You must have earned income and meet certain income limits.
- You must have a valid Social Security number.
- You must meet specific work requirements.
- You must file a tax return, even if you don’t owe any taxes.
- Credit Amount:
- The maximum amount of the EITC for 2024 depends on your filing status and number of qualifying children.
- The credit is phased out for taxpayers with higher incomes.
- Examples:
- A single individual with no children and an AGI of $20,000 could claim a significant EITC amount.
- A married couple with three children and an AGI of $50,000 could also be eligible for the EITC.
Other Notable Tax Credits
There are several other tax credits available in 2024 that can benefit individuals and families in specific situations.
- American Opportunity Tax Credit:This credit helps offset the cost of college tuition and fees.
- Purpose:To help make college more affordable for families.
- Eligibility:The student must be enrolled at least half-time in a qualified educational institution. The student must be pursuing a degree or other recognized educational credential. There are income limitations for the credit.
- Credit Amount:The credit is worth up to $2,500 per eligible student, and it’s phased out for taxpayers with higher incomes.
- Example:A family with a student enrolled full-time at a community college could claim the American Opportunity Tax Credit, reducing their tax liability.
- Premium Tax Credit:This credit helps offset the cost of health insurance purchased through the Affordable Care Act’s marketplace.
- Purpose:To make health insurance more affordable for individuals and families.
- Eligibility:You must purchase health insurance through the marketplace. Your income must fall within certain limits.
- Credit Amount:The amount of the credit depends on your income and the cost of your health insurance plan.
- Example:An individual with an income below the eligibility threshold could receive a significant Premium Tax Credit to help cover the cost of their health insurance premiums.
6. Tax Filing Options
Filing your federal income taxes can be a complex process, but you have several options to choose from, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore the different ways to file your taxes in the United States.
Using Tax Software
Tax software has become increasingly popular in recent years, offering a convenient and user-friendly way to file your taxes. These programs guide you through the process, help you claim all eligible deductions and credits, and ensure your return is accurate.
The auto industry is seeing significant changes! The EV Tax Credits Impact on the Auto Industry in 2024 is shaping the market and driving innovation in the electric vehicle sector.
- TurboTax: One of the most popular tax software options, TurboTax offers a range of plans for different income levels and tax situations. Its features include personalized guidance, expert advice, and audit support. Pricing varies based on the plan you choose, with options starting from free for simple returns.
- H&R Block: Another well-known tax software provider, H&R Block offers a similar range of plans to TurboTax, with features such as tax preparation assistance, audit support, and access to tax professionals. Pricing is comparable to TurboTax, with options starting from free for simple returns.
- TaxAct: TaxAct is a more affordable option compared to TurboTax and H&R Block, offering a variety of plans for different income levels and tax situations. Its features include personalized guidance, tax preparation assistance, and audit support. Pricing is typically lower than TurboTax and H&R Block, with options starting from free for simple returns.
Hiring a Tax Professional, 2024 Federal Tax Brackets
If you find tax filing overwhelming or have a complex tax situation, hiring a tax professional can provide peace of mind and ensure your return is accurate. There are different types of tax professionals you can choose from, each with its own qualifications and expertise.
- Certified Public Accountants (CPAs): CPAs are highly qualified professionals who have passed rigorous exams and met specific experience requirements. They can provide comprehensive tax services, including tax preparation, financial planning, and auditing.
- Enrolled Agents (EAs): EAs are tax professionals who are licensed by the IRS to represent taxpayers before the agency. They have expertise in federal tax law and can provide tax preparation, tax planning, and representation services.
- Tax Preparers: Tax preparers are not required to have specific qualifications or licenses, but they can assist with preparing your tax return. They may have expertise in certain areas of tax law, but they may not be able to provide comprehensive tax advice or representation.
Filing by Mail
You can still file your federal income taxes by mail, although this method is becoming less common. Filing by mail involves obtaining the necessary forms from the IRS, completing them manually, and sending them by mail.
- Obtaining Forms: You can obtain the necessary forms from the IRS website or by contacting the IRS directly.
- Completing Forms: You will need to complete all the required sections of the forms, providing accurate information about your income, deductions, and credits.
- Sending Forms: Once you have completed the forms, you will need to mail them to the IRS address listed on the forms.
7. Tax Planning for 2024
Proactive tax planning is essential for minimizing your tax liability and maximizing your financial well-being. It involves making informed financial decisions throughout the year, not just during tax season, to optimize your tax situation.
Wondering how much you can deduct from your taxes? The Standard Deduction 2024 amount can significantly impact your tax bill. It’s a good idea to review your options and choose the deduction that benefits you most.
Strategies for Minimizing Tax Liability
Strategic tax planning can help you reduce your tax burden and keep more of your hard-earned money. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Maximize Retirement Contributions:Contributions to traditional 401(k) and IRA accounts are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income. For 2024, the maximum contribution limit for 401(k) plans is $22,500, and $7,500 for traditional IRAs.
- Utilize Tax-Advantaged Accounts:Consider using Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) for healthcare expenses, as contributions are tax-deductible and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. Also, explore the benefits of 529 college savings plans, which offer tax-free growth and withdrawals for qualified education expenses.
- Explore Charitable Giving Options:Charitable contributions can reduce your taxable income. Consider making donations to qualified charities to receive a tax deduction. For 2024, the standard deduction for single filers is $13,850, and $27,700 for married couples filing jointly. Donating appreciated assets, like stocks or real estate, can result in a capital gains tax deduction.
- Take Advantage of Deductions:Familiarize yourself with deductions applicable to your situation, such as home mortgage interest, property taxes, medical expenses, and state and local taxes.
- Claim Available Tax Credits:Tax credits directly reduce your tax liability. Research credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), Child Tax Credit, and American Opportunity Tax Credit, which can provide significant tax savings.
Importance of Proactive Tax Planning
Engaging in ongoing tax planning throughout the year offers numerous benefits. It allows you to:
- Track Income and Expenses:Keeping accurate records of your income and expenses helps you make informed financial decisions and ensure you claim all eligible deductions and credits.
- Make Strategic Financial Decisions:Proactive tax planning enables you to make tax-efficient decisions regarding investments, real estate, and retirement planning.
- Minimize Tax Liability:By identifying potential tax savings opportunities throughout the year, you can reduce your overall tax burden.
- Seek Professional Advice:Consulting with a qualified tax professional can provide personalized guidance and ensure you take advantage of all available tax benefits.
Tax-Efficient Financial Decisions
Making tax-efficient financial decisions can significantly impact your overall financial well-being. Here are some key areas to consider:
Investing
- Taxable vs. Tax-Advantaged Accounts:When investing, consider the tax implications of different account types. Taxable accounts, like brokerage accounts, subject investment gains to capital gains tax, while tax-advantaged accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, offer tax deferral or tax-free growth.
- Tax-Loss Harvesting:Selling losing investments to offset capital gains can reduce your tax liability.
Real Estate
- Homeownership Deductions:Homeowners can deduct mortgage interest and property taxes on their primary residence.
- Capital Gains Exclusion:When selling a primary residence, you may be eligible for a capital gains exclusion of up to $250,000 for single filers and $500,000 for married couples filing jointly.
Retirement Planning
- Maximize Retirement Contributions:Contributing the maximum amount to your 401(k) and IRA accounts can significantly reduce your taxable income.
- Roth IRA Conversions:Converting traditional IRA assets to a Roth IRA can provide tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
Additional Considerations
Anticipated Tax Law Changes in 2024
While no major tax law changes are anticipated for 2024, it’s essential to stay informed about any potential developments that could affect your tax situation.
Tax Implications for Specific Situations
- Self-Employment:Self-employed individuals are responsible for paying self-employment tax, which includes Social Security and Medicare taxes.
- Freelancing:Freelancers should track their income and expenses carefully to claim deductions for business expenses.
- Small Business Ownership:Small business owners have access to various deductions and credits, such as the home office deduction and the Qualified Business Income Deduction (QBI).
- Retirement Planning:Retirement planning strategies, such as Roth IRA conversions and withdrawals, have tax implications that should be considered.
- College Savings:529 college savings plans offer tax advantages for funding education expenses.
Key Tax Deductions and Credits in 2024
| Deduction/Credit | Description ||—|—|| Standard Deduction | Deductible amount based on filing status. || Itemized Deductions | Specific expenses, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, and medical expenses. || Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) | Tax credit for low- and moderate-income working individuals and families.
|| Child Tax Credit | Tax credit for each qualifying child. || American Opportunity Tax Credit | Tax credit for qualified education expenses. |
Looking to boost your retirement savings? The IRA Contribution Limits 2024 have been updated, so check out how much you can contribute this year.
Disclaimer:This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute professional tax advice. Please consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice.
Impact of Tax Brackets on Financial Decisions
Tax brackets play a significant role in shaping financial decisions, influencing how individuals approach investment strategies, retirement planning, and charitable giving. Understanding how tax brackets work is crucial for making informed financial choices that maximize benefits and minimize tax liabilities.
Tax Brackets and Investment Strategies
Tax brackets can influence investment strategies by impacting the after-tax returns on different investments. For example, individuals in higher tax brackets may prefer investments with lower tax implications, such as tax-advantaged retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs, where earnings grow tax-deferred.
Conversely, individuals in lower tax brackets might find it more beneficial to invest in taxable accounts, where they can potentially benefit from lower capital gains tax rates.
Tax Brackets and Retirement Planning
Tax brackets are a key consideration for retirement planning. Individuals in higher tax brackets might prefer to contribute to Roth IRAs, where contributions are made with after-tax dollars and withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. Conversely, individuals in lower tax brackets might prefer to contribute to traditional IRAs, where contributions are tax-deductible, but withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
Tax Brackets and Charitable Giving
Tax brackets can also influence charitable giving. Individuals in higher tax brackets may benefit more from itemized deductions for charitable contributions, as they can deduct a larger portion of their donation from their taxable income. Conversely, individuals in lower tax brackets may find it more advantageous to make charitable donations through a donor-advised fund, which allows them to claim a tax deduction in the year of the donation while spreading out the charitable giving over time.
Pitfalls of Making Decisions Solely Based on Tax Brackets
While tax brackets are an important factor in financial decision-making, it’s crucial to consider other factors as well. Focusing solely on tax brackets can lead to suboptimal decisions. For instance, investing solely in tax-advantaged accounts without considering risk tolerance and investment goals might not be the best strategy for everyone.
Additionally, tax laws are subject to change, so relying solely on current tax brackets can lead to unexpected tax liabilities in the future.
Resources for Tax Information
Navigating the complexities of federal taxes can be daunting, but access to accurate and reliable information is crucial for making informed financial decisions. There are several resources available to help you understand your tax obligations and ensure you’re taking advantage of all eligible deductions and credits.
Retirement planning is essential! Knowing the Ira Limits 2024 can help you make informed decisions about your savings goals.
Official Government Websites
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the primary source for official tax information. The IRS website provides comprehensive guidance on all aspects of federal taxation, including:
- Tax brackets and rates
- Deductions and credits
- Tax filing instructions
- Forms and publications
- Taxpayer assistance resources
The IRS website is a valuable resource for anyone seeking accurate and up-to-date tax information. You can find answers to frequently asked questions, download tax forms, and access a variety of publications and guides.
Tax Preparation Software
Tax preparation software offers a user-friendly and efficient way to file your taxes. These programs guide you through the filing process, help you identify eligible deductions and credits, and ensure your return is accurate and complete. Some popular options include:
- TurboTax
- H&R Block
- TaxAct
- FreeTaxUSA
These software programs are designed for individuals with varying levels of tax knowledge and can be a helpful tool for both simple and complex tax situations. They often offer free versions for basic returns and paid versions with additional features and support.
Tax Professional Organizations
If you prefer personalized assistance, consider consulting a tax professional. Tax professionals are qualified individuals who specialize in tax preparation and planning. You can find reputable tax professionals through organizations like:
- The National Society of Tax Professionals (NSTP)
- The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA)
- The National Association of Enrolled Agents (NAEA)
These organizations offer resources and support for tax professionals, ensuring they maintain the highest standards of knowledge and ethical conduct. When selecting a tax professional, it’s important to verify their credentials and experience.
Other Resources
In addition to these primary sources, there are other resources available for tax information, including:
- Tax advocacy groups
- Financial advisors
- Libraries and community centers
These organizations and resources can provide valuable insights and support for navigating the complexities of federal taxation.
Final Thoughts
Navigating the complexities of federal tax brackets can feel overwhelming, but understanding the fundamentals and available strategies can empower you to make informed financial decisions. By taking advantage of deductions, credits, and tax-efficient planning, you can potentially reduce your tax liability and optimize your financial well-being.
Remember to consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice and guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between a tax deduction and a tax credit?
A tax deduction reduces your taxable income, while a tax credit directly reduces your tax liability. For example, a deduction for charitable contributions lowers the amount of income you’re taxed on, while a tax credit for child care expenses directly reduces the amount of taxes you owe.
How can I determine which tax filing option is best for me?
The best tax filing option depends on factors such as your income level, tax situation, time constraints, comfort with taxes, and budget. Consider using tax software if you have a straightforward tax situation, hiring a tax professional if you have complex finances, or filing by mail if you prefer a traditional approach.
What are some common tax deductions that I might be eligible for?
Common tax deductions include the standard deduction, itemized deductions for medical expenses, mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and state and local taxes. The specific deductions you can claim will depend on your individual circumstances.
Are there any changes to the Child Tax Credit in 2024?
The Child Tax Credit is subject to change, so it’s important to stay updated on any potential adjustments to eligibility requirements, credit amounts, and phase-outs. Consult the IRS website or a tax professional for the most current information.
Where can I find more information about federal tax brackets and filing?
The IRS website is a valuable resource for information on federal tax brackets, filing requirements, deductions, credits, and other tax-related topics. You can also consult reputable tax preparation software or seek advice from a qualified tax professional.