Navigating the complexities of federal taxes can be daunting, especially with the ever-changing landscape of tax laws. Understanding the 2024 federal tax brackets and standard deduction is crucial for taxpayers to accurately calculate their tax liability and maximize potential deductions.
This guide aims to provide clarity and insight into these key aspects of the federal tax system.
The 2024 federal tax brackets are designed to progressively tax income, meaning higher earners pay a greater percentage of their income in taxes. The standard deduction, on the other hand, offers a fixed amount that can be deducted from taxable income, simplifying the tax filing process for many individuals.
Contents List
Understanding 2024 Federal Tax Brackets
The federal income tax system in the United States uses a progressive tax system, where individuals pay a higher percentage of tax on higher levels of income. This is achieved through tax brackets, which categorize income levels and assign a specific tax rate to each bracket.
Businesses often need to file for tax extensions. If you’re a business owner and need to file for an extension, you can find information about the tax extension deadline for businesses in October 2024 here: Extension Tax Deadline October 2024 for Businesses.
Tax Brackets and Tax Liability
Tax brackets define the income ranges that are subject to different tax rates. Each bracket has a specific marginal tax rate, which is the rate applied to the income earned within that bracket. The tax liability for an individual is calculated by applying the corresponding marginal tax rate to the income earned within each bracket.
Non-profit organizations also need to fill out a W9 form. If you’re working with a non-profit organization, you can find information about the W9 form for October 2024 in this article: W9 Form October 2024 for non-profit organizations.
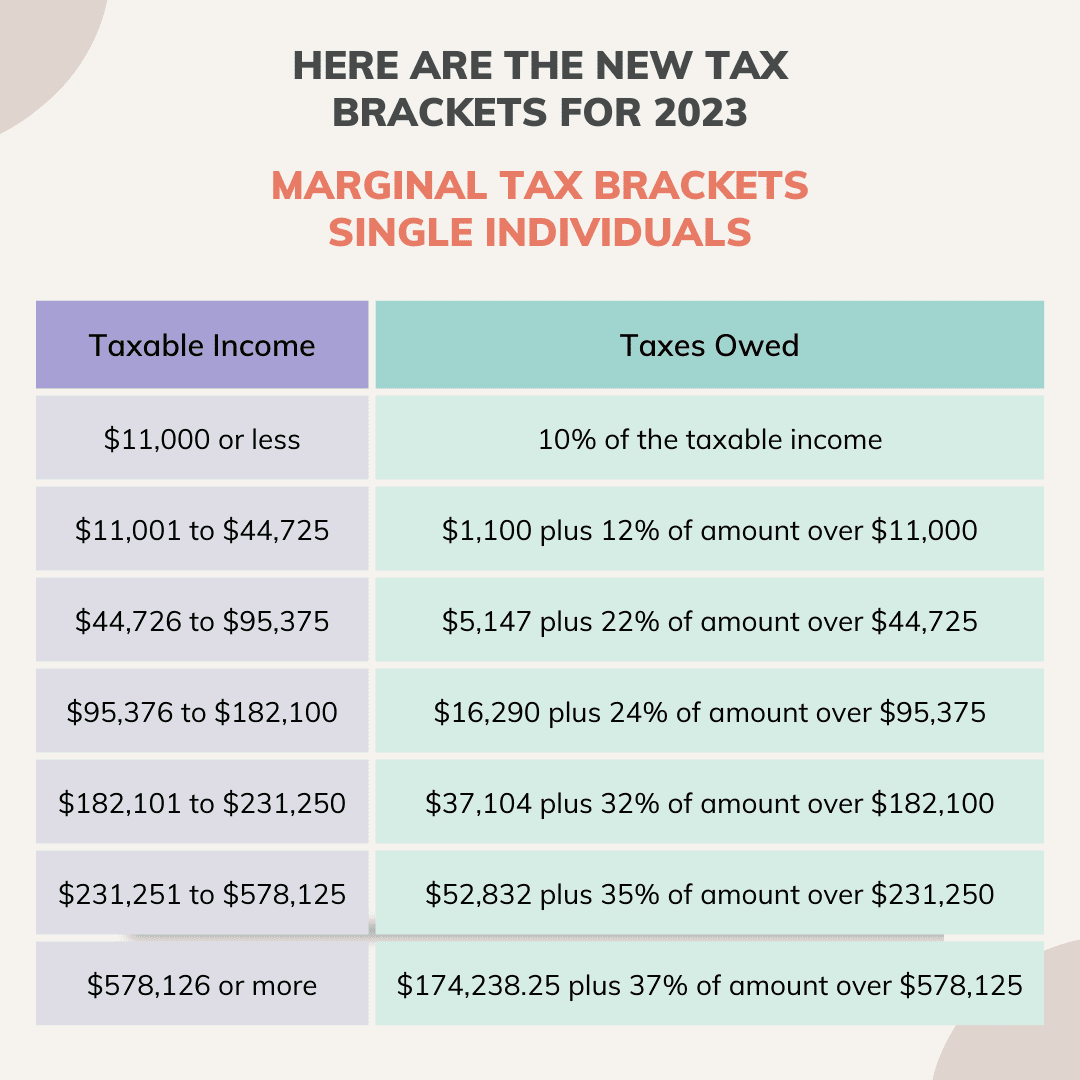
2024 Federal Tax Brackets
The 2024 federal tax brackets for different filing statuses are as follows:
| Filing Status | Tax Bracket | Marginal Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single | 10% | 10% | $0
|
| 12% | 12% | $10,951
If you’re planning on contributing to a Roth 401k in 2024, you’ll want to know the contribution limits. The good news is that the IRS has set a limit for how much you can contribute each year. You can find the exact limits for 2024, including any changes, on the IRS website or by checking out this helpful article: 401k contribution limits for 2024 for Roth 401k.
|
|
| 22% | 22% | $46,276
|
|
| 24% | 24% | $101,751
|
|
| 32% | 32% | $192,151
The 401k contribution limits can vary based on your age. To learn more about the contribution limits for different age groups in 2024, you can check out this article: What are the 401k contribution limits for 2024 for different ages.
|
|
| 35% | 35% | $577,101
If you’re a head of household, you may be eligible for a higher contribution limit for your Roth IRA. To learn more about the Roth IRA contribution limit for head of household filers in 2024, you can check out this article: Roth IRA contribution limit 2024 for head of household.
|
|
| 37% | 37% | $1,000,001+ | |
| Married Filing Jointly | 10% | 10% | $0
|
| 12% | 12% | $21,901
|
|
| 22% | 22% | $82,551
Freelancers often need to fill out a W9 form. If you’re a freelancer, you can find information about the W9 form for October 2024 in this article: W9 Form October 2024 for freelancers.
|
|
| 24% | 24% | $172,751
|
|
| 32% | 32% | $344,301
You might be wondering if it’s possible to contribute more than the 401k limit in 2024. While there are some exceptions, in most cases, the limit is set for a reason. To learn more about the 401k contribution limits for 2024, check out this helpful resource: Can I contribute more than the 401k limit in 2024.
|
|
| 35% | 35% | $614,201
|
|
| 37% | 37% | $1,000,001+ | |
| Married Filing Separately | 10% | 10% | $0
|
| 12% | 12% | $10,951
|
|
| 22% | 22% | $41,276
|
|
| 24% | 24% | $86,376
|
|
| 32% | 32% | $172,151
|
|
| 35% | 35% | $307,101
|
|
| 37% | 37% | $500,001+ | |
| Head of Household | 10% | 10% | $0
|
| 12% | 12% | $18,551
|
|
| 22% | 22% | $82,551
|
|
| 24% | 24% | $172,751
|
|
| 32% | 32% | $344,301
|
|
| 35% | 35% | $614,201
|
|
| 37% | 37% | $1,000,001+ | |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | 10% | 10% | $0
|
| 12% | 12% | $21,901
|
|
| 22% | 22% | $82,551
|
|
| 24% | 24% | $172,751
|
|
| 32% | 32% | $344,301
|
|
| 35% | 35% | $614,201
|
|
| 37% | 37% | $1,000,001+ |
Marginal Tax Rates
The marginal tax rate is the rate applied to the portion of income that falls within a specific bracket. For example, if a single filer earns $50,000, the first $10,950 would be taxed at 10%, the income between $10,951 and $46,275 would be taxed at 12%, and the remaining income above $46,275 would be taxed at 22%.
Taxation Within Each Bracket
Income is taxed incrementally within each bracket. This means that only the income within a specific bracket is taxed at the corresponding marginal tax rate. For instance, if an individual earns $150,000, the first $10,950 would be taxed at 10%, the income between $10,951 and $46,275 would be taxed at 12%, and so on.
The entire income is not taxed at the highest marginal tax rate.
Retirees may have different tax obligations than other taxpayers. To learn more about the tax deadline for retirees in October 2024, you can check out this article: October 2024 tax deadline for retirees.
Standard Deduction for 2024
The standard deduction is a fixed amount that taxpayers can choose to deduct from their taxable income instead of itemizing their deductions. This deduction simplifies the tax filing process and reduces the amount of taxes you owe. The standard deduction is designed to provide a basic level of tax relief for all taxpayers, regardless of their individual circumstances.
Standard Deduction Amounts for 2024
The standard deduction amount varies depending on your filing status. Here are the standard deduction amounts for 2024:
| Filing Status | Standard Deduction Amount |
|---|---|
| Single | $13,850 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $27,700 |
| Head of Household | $20,800 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | $27,700 |
| Married Filing Separately | $13,850 |
Comparison with Itemized Deductions
Taxpayers can choose to either take the standard deduction or itemize their deductions. Itemized deductions include expenses such as medical expenses, state and local taxes, mortgage interest, and charitable contributions. You can only choose one method—either the standard deduction or itemized deductions—not both.
If your itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction amount, you should itemize to lower your taxable income. However, if your itemized deductions are less than the standard deduction, you should claim the standard deduction.
Benefits of Claiming the Standard Deduction
The standard deduction simplifies the tax filing process and reduces the amount of taxes you owe. It benefits taxpayers who:* Have limited itemized deductions.
Tax calculators are a great tool for getting a better understanding of your tax situation and potentially saving money. If you’re wondering how to use a tax calculator for the October 2024 deadline, you can find helpful information in this article: How to use a tax calculator for October 2024.
- Find itemizing their deductions to be time-consuming and complex.
- Want to avoid the risk of making errors when itemizing their deductions.
The standard deduction provides a convenient way to reduce your tax liability and simplifies the tax filing process for many taxpayers.
Factors Influencing Tax Liability
Your tax liability, the amount of income tax you owe, isn’t simply determined by your income. Several factors come into play, shaping how much you pay to the government. Understanding these factors can help you plan and potentially reduce your tax burden.
Income
Your income is the foundation of your tax liability. The more you earn, the more tax you’ll generally pay. However, the way your income is taxed isn’t linear. The US tax system uses a progressive tax structure, meaning your tax rate increases as your income rises.
Non-profit organizations may also need to file for tax extensions. If you’re working with a non-profit organization, you can find information about the tax extension deadline for non-profit organizations in October 2024 here: Tax extension deadline October 2024 for non-profit organizations.
This is done through tax brackets.
- Each tax bracket has a different tax rate. For example, in 2024, income between $11,000 and $46,275 is taxed at 12%, while income above $594,750 is taxed at 37%.
- You only pay the higher rate on the portion of your income that falls within that specific bracket. For example, if you earn $50,000, you won’t pay 37% on your entire income. You’ll pay 10% on the first $11,000, 12% on the portion between $11,000 and $46,275, and so on.
Dependents, 2024 federal tax brackets and standard deduction
Having dependents, like children or other qualifying individuals, can significantly impact your tax liability. The government provides tax credits and deductions for dependents, reducing your overall tax burden.
Taxes can be a bit overwhelming, especially when you’re trying to figure out how to file by the deadline. But don’t worry, there are resources available to help you navigate the process. You can find helpful tips and advice on how to file your taxes by the October 2024 deadline in this article: How to file taxes by the October 2024 deadline.
- The Child Tax Credit offers a significant credit for each qualifying child. The amount of the credit depends on the child’s age and your income.
- The Dependent Care Credit helps offset the cost of childcare for qualifying dependents, including children and adults. The credit amount is based on your income and the amount you spend on care.
Deductions
Deductions are expenses you can subtract from your taxable income, reducing your tax liability. There are several types of deductions, including:
- Standard Deduction: This is a fixed amount you can choose to deduct instead of itemizing your deductions. The amount varies based on your filing status.
- Itemized Deductions: These are specific expenses you can deduct if they exceed the standard deduction. Common itemized deductions include mortgage interest, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and medical expenses.
Scenario: Impact of Income and Filing Status
Imagine two individuals:
- Person A: Single, earns $60,000 per year.
- Person B: Married filing jointly, earns $120,000 per year.
Person A, being single, has a lower standard deduction than Person B. While both individuals may have similar deductions for expenses like charitable contributions, Person A’s lower standard deduction and lower income will result in a lower tax liability compared to Person B.
This highlights how both income and filing status can influence tax liability.
If you’re a single filer, you may be wondering about the Roth IRA contribution limit for 2024. You can find the specific limit for single filers in this article: Roth IRA contribution limits for 2024 for single filers.
Impact of Tax Changes on 2024 Filings
The 2024 tax season will see a few changes that could impact your tax liability. While these changes may not be dramatic, understanding them is essential for accurate filing.
Changes to the Standard Deduction
The standard deduction amount, which is the amount you can deduct from your taxable income without itemizing, is adjusted annually for inflation. For 2024, the standard deduction amounts are:
- Single filers: $13,850
- Married filing jointly: $27,700
- Head of household: $20,800
- Qualifying widow(er): $27,700
This adjustment could affect your tax liability, depending on your income level and filing status. For example, if your income falls near the threshold of a higher tax bracket, the increased standard deduction might push you into a lower tax bracket, resulting in lower taxes.
The standard deduction is a valuable tax benefit that can reduce your tax liability. There are often changes to the standard deduction each year. To learn more about the standard deduction changes for 2024, check out this article: Standard deduction changes for 2024.
Changes to the Child Tax Credit
The Child Tax Credit, which can reduce your tax liability by up to $2,000 per qualifying child, has seen some changes in recent years. For 2024, the credit remains at $2,000 per child, but the amount of the credit that is refundable (meaning you can receive a refund even if you don’t owe taxes) has been adjusted.
- The refundable portion of the Child Tax Credit is $1,500 per child for 2024.
This means that even if your tax liability is less than $2,000, you can still receive a refund of up to $1,500 per qualifying child.
Changes to the Earned Income Tax Credit
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a tax credit for low- and moderate-income working individuals and families. The EITC amount varies depending on your income, filing status, and the number of qualifying children. For 2024, the EITC has been adjusted to reflect inflation.
- The maximum EITC amount for 2024 is $7,430 for qualifying individuals with three or more qualifying children.
These changes to the EITC could result in a larger tax credit for eligible individuals, potentially leading to a larger refund.
Changes to the Deduction for State and Local Taxes (SALT)
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 placed a $10,000 limit on the deduction for state and local taxes (SALT). This limit remains in place for 2024.
- The $10,000 limit applies to the combined amount of state and local income taxes, property taxes, and sales taxes that you can deduct.
This limit could impact taxpayers in high-tax states, as they may be unable to deduct all of their state and local taxes.
Changes to the Deduction for Medical Expenses
The deduction for medical expenses is available if your medical expenses exceed a certain percentage of your adjusted gross income (AGI). For 2024, the threshold for this deduction remains at 7.5% of your AGI.
- This means that you can only deduct the amount of medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of your AGI.
This threshold can be a significant factor for taxpayers with high medical expenses, as it could affect the amount of their deductible expenses.
The maximum 401k contribution limit can vary depending on your age and other factors. To learn more about the maximum 401k contribution limit for 2024, check out this article: What is the maximum 401k contribution for 2024.
Resources for Taxpayers: 2024 Federal Tax Brackets And Standard Deduction
Navigating the complexities of federal taxes can be challenging, but numerous resources are available to assist taxpayers in understanding their obligations and maximizing their tax benefits. This section provides a comprehensive guide to accessing and utilizing these valuable resources, ensuring a smooth and informed tax filing experience.
Preparing your taxes can feel like a daunting task, but with the right tips and strategies, it can be a smoother process. There are lots of resources available to help you understand your tax obligations and make sure you’re prepared.
Check out these helpful tax preparation tips for the October 2024 deadline: Tax preparation tips for the October 2024 deadline.
Official Government Websites
Official government websites are the most reliable sources for accurate and up-to-date information on federal taxes. These websites provide comprehensive guidance on tax laws, regulations, forms, and procedures.
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS):The IRS website, www.irs.gov, is the primary source for all federal tax information. It features a wealth of resources, including:
- Tax publications and forms
- Tax law changes and updates
- Interactive tax tools and calculators
- Information on tax credits and deductions
- Contact information for IRS assistance
- Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS):The TAS is an independent organization within the IRS that helps taxpayers resolve tax problems. The TAS website, www.taxpayeradvocate.irs.gov, provides information on:
- Filing an appeal with the TAS
- Assistance with IRS audits and collections
- Guidance on resolving tax disputes
Reputable Third-Party Resources
In addition to official government websites, several reputable third-party resources can provide valuable insights and support for taxpayers. These resources often offer user-friendly explanations, tax calculators, and expert advice.
- Tax Preparation Software:Tax preparation software programs, such as TurboTax, H&R Block, and TaxAct, simplify the tax filing process. These programs provide:
- Step-by-step guidance through the tax filing process
- Tax calculators and estimates
- Access to tax forms and publications
- Electronic filing options
- Financial Institutions:Many financial institutions offer resources and tools to help taxpayers understand their tax obligations. For example, banks and credit unions may provide:
- Tax planning guides and calculators
- Information on tax-advantaged accounts
- Access to financial advisors
- Tax Professionals:Certified Public Accountants (CPAs), Enrolled Agents (EAs), and tax attorneys can provide expert tax advice and preparation services. These professionals are knowledgeable about tax laws and can help taxpayers:
- Develop tax planning strategies
- Prepare accurate tax returns
- Resolve tax disputes
Accessing and Utilizing Resources Effectively
To maximize the benefits of these resources, taxpayers should follow these steps:
- Start Early:Begin gathering tax information and exploring resources well in advance of the tax filing deadline. This allows for ample time to research tax laws, understand deductions and credits, and seek professional assistance if needed.
- Utilize Official Government Websites:The IRS website is the primary source for accurate and up-to-date tax information. Regularly visit the IRS website for tax law updates, publications, and forms.
- Explore Reputable Third-Party Resources:Supplement official government resources with information from reputable third-party sources, such as tax preparation software, financial institutions, and tax professionals. Use these resources to gain a comprehensive understanding of your tax obligations.
- Seek Professional Advice:If you are unsure about your tax obligations or need assistance with complex tax matters, consult a qualified tax professional. A CPA, EA, or tax attorney can provide expert advice and support.
- Keep Records Organized:Maintain organized records of all income, expenses, and other tax-related documents. This will simplify the tax filing process and facilitate any future tax audits.
- Stay Informed:Stay informed about tax law changes and updates. Subscribe to IRS email alerts or follow reputable tax news sources to stay current on tax developments.
Closing Notes
Understanding the 2024 federal tax brackets and standard deduction is essential for individuals and families to navigate the tax filing process effectively. By carefully considering income levels, filing status, and eligible deductions, taxpayers can optimize their tax liability and ensure compliance with federal tax regulations.
Staying informed about tax changes and utilizing available resources can empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their tax obligations.
Q&A
What is the difference between the standard deduction and itemized deductions?
The standard deduction is a fixed amount that can be deducted from taxable income, while itemized deductions allow taxpayers to deduct specific expenses, such as medical expenses, mortgage interest, and charitable contributions. Taxpayers choose the deduction method that results in the lower tax liability.
Who benefits most from claiming the standard deduction?
Individuals with relatively low income and fewer deductible expenses generally benefit most from claiming the standard deduction. It simplifies the tax filing process and can often result in a lower tax liability.
What are the key factors that influence an individual’s tax liability?
Key factors include income level, filing status (single, married filing jointly, etc.), dependents, and eligible deductions. These factors interact with tax brackets and the standard deduction to determine an individual’s tax obligation.