Tax calculator for income from rental properties in October 2024 can be a valuable tool for landlords navigating the complexities of property income taxation. Understanding how to calculate your tax liability and identify potential deductions is crucial for maximizing your rental income and minimizing your tax burden.
This guide will delve into the key factors influencing rental income tax, providing a step-by-step approach to using a tax calculator and exploring effective tax planning strategies.
The tax landscape for rental properties can be intricate, with numerous factors impacting your tax liability. From depreciation and interest expenses to property taxes and different income levels, understanding these nuances is vital for accurate tax calculations. This guide will provide insights into these factors and demonstrate how a tax calculator can streamline the process of determining your tax obligations.
Contents List
- 1 Introduction to Rental Property Income Taxation: Tax Calculator For Income From Rental Properties In October 2024
- 2 Understanding the Tax Calculator
- 3 Key Factors Affecting Rental Income Tax
- 4 Steps to Use a Tax Calculator
- 5 Tax Planning Strategies for Rental Property Owners
- 6 Resources and Tools for Rental Property Tax Calculations
- 7 Legal and Ethical Considerations
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 FAQ Compilation
Introduction to Rental Property Income Taxation: Tax Calculator For Income From Rental Properties In October 2024
Rental property income is considered taxable income in the United States. This means that the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires you to report your rental income and expenses on your tax return. The IRS considers rental income to be any money you receive from renting out a property, including rent payments, security deposits, and late fees.
IRA contribution limits can change from year to year. You can find out what the IRA contribution limits are for 2024 at What are the IRA contribution limits for 2024.
You can deduct certain expenses related to your rental property from your rental income, which can reduce your overall tax liability.
The mileage rate for business travel can change throughout the year. You can find the mileage rate for October 2024 at What is the mileage rate for October 2024?.
Rental Property Expenses
Rental property expenses are the costs associated with owning and maintaining your rental property. These expenses can be deducted from your rental income to reduce your taxable income.
Self-employed individuals have different IRA contribution limits than those who are employed. You can find more information about the IRA contribution limits for self-employed in 2024 at Ira contribution limits for self-employed in 2024.
- Mortgage Interest:The interest you pay on a mortgage for your rental property is deductible.
- Property Taxes:You can deduct the property taxes you pay on your rental property.
- Insurance:Premiums for insurance policies covering your rental property, such as hazard insurance, are deductible.
- Repairs and Maintenance:Expenses for repairs and maintenance, such as fixing a leaky faucet or replacing a broken window, are deductible.
- Depreciation:You can deduct a portion of the cost of your rental property each year to account for its wear and tear. This is known as depreciation.
- Advertising and Marketing:Expenses related to advertising your rental property, such as listing fees and marketing materials, are deductible.
- Utilities:If you pay for utilities, such as water, electricity, and gas, for your rental property, you can deduct these expenses.
- Travel:If you travel to your rental property for management or maintenance purposes, you can deduct your travel expenses.
Tax Implications for Rental Property Owners
Rental property ownership can have various tax implications.
The mileage rate for business travel is set by the IRS. You can find out how the mileage rate is calculated for October 2024 at How is the mileage rate calculated for October 2024?.
Rental income is generally taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can vary depending on your overall income.
The standard deduction amount can help you save on your taxes. You can find out the standard deduction amount for the 2024 tax year at Standard deduction amount for 2024 tax year.
- Capital Gains Tax:If you sell your rental property for a profit, you may have to pay capital gains tax on the profit. This tax rate can vary depending on how long you owned the property and your income level.
- Passive Income Rules:The IRS has specific rules regarding passive income, which includes rental income. If you are considered a “real estate professional” by the IRS, you may be able to deduct certain expenses that are otherwise limited under passive income rules.
Understanding the Tax Calculator
A tax calculator for rental property income is a valuable tool that simplifies the process of calculating your tax obligations. It takes into account various factors, such as rental income, expenses, and deductions, to provide an estimated tax liability.
Purpose of a Tax Calculator
A tax calculator streamlines the process of calculating your tax liability by automating complex calculations. It eliminates the need for manual calculations, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. The calculator analyzes your rental income and expenses, applying relevant tax laws and deductions, to estimate your tax obligations accurately.
Features and Functionalities
A comprehensive tax calculator for rental property income typically includes the following features and functionalities:
- Income Calculation: Calculates total rental income, including base rent, security deposits, and other income sources.
- Expense Tracking: Allows you to track and categorize various expenses related to your rental property, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, repairs, and maintenance.
- Deduction Calculation: Applies relevant tax deductions, including depreciation, interest expense, property taxes, and other allowable deductions.
- Tax Liability Estimation: Calculates your estimated tax liability based on your income, expenses, and deductions.
- Tax Planning Tools: Provides insights and recommendations for tax planning strategies, such as optimizing deductions and minimizing tax obligations.
Benefits of Using a Tax Calculator
Using a tax calculator for rental property income offers several benefits:
- Accuracy: Tax calculators use predefined formulas and algorithms to ensure accurate calculations, reducing the risk of errors.
- Time-Saving: Automating calculations saves you time and effort, allowing you to focus on other aspects of your rental business.
- Transparency: Tax calculators provide a clear breakdown of your income, expenses, deductions, and estimated tax liability, enhancing transparency.
- Tax Planning: The insights and recommendations provided by tax calculators can help you plan your tax strategy effectively and minimize your tax obligations.
Key Factors Affecting Rental Income Tax
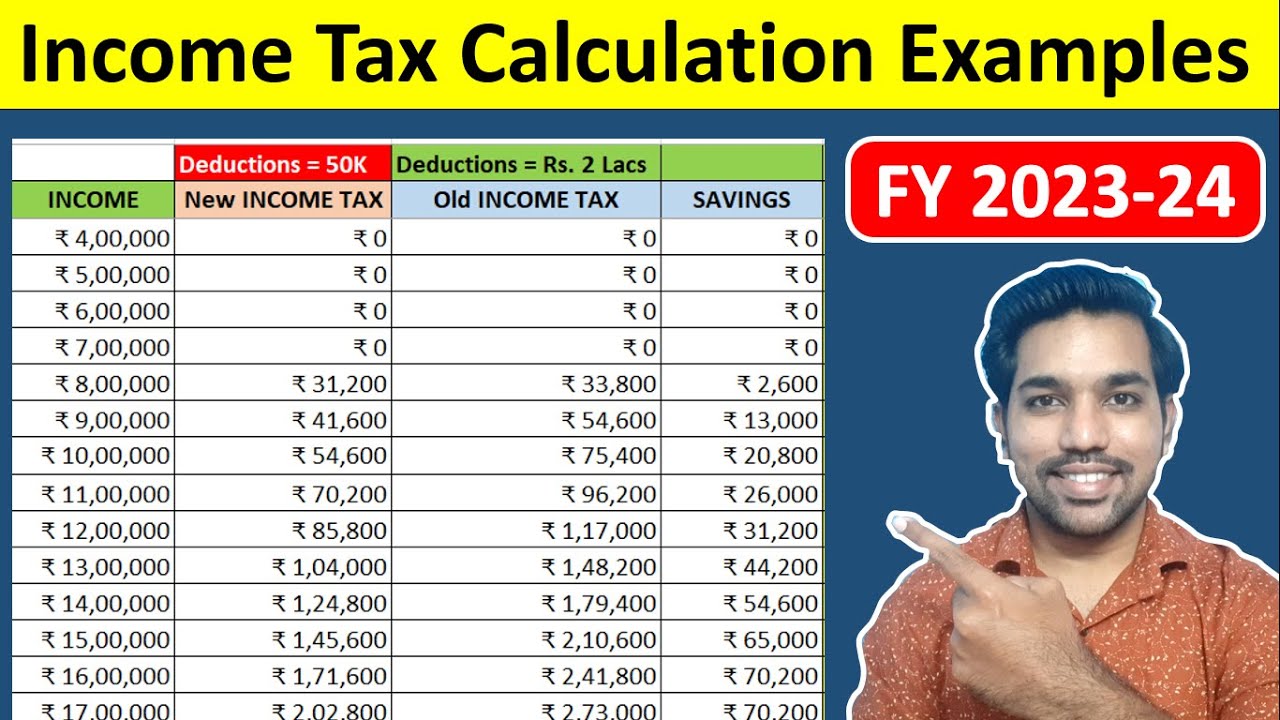
The amount of tax you owe on your rental income depends on several factors, including your expenses, income level, and tax deductions. This section explores some of the key factors that influence your rental income tax liability.
Depreciation
Depreciation is a non-cash expense that allows you to deduct a portion of the cost of your rental property over its useful life. This deduction helps to offset your rental income and reduce your tax liability. The depreciation deduction is calculated based on the property’s cost, its useful life, and the depreciation method you choose.
Depreciation is a non-cash expense that allows you to deduct a portion of the cost of your rental property over its useful life.
If you’re self-employed, you can contribute to a 401k. Check out 401k contribution limits for 2024 for self-employed to see how much you can contribute.
Interest Expenses, Tax calculator for income from rental properties in October 2024
Interest expenses are the costs associated with borrowing money to purchase or improve your rental property. These expenses are deductible on your tax return, which can help to reduce your taxable income.
If you’re over 50, you can contribute more to your IRA than someone younger. Check out IRA contribution limits for 2024 for those over 50 to see how much you can contribute.
Interest expenses are the costs associated with borrowing money to purchase or improve your rental property.
Property Taxes
Property taxes are levied by local governments on the value of your rental property. These taxes are deductible on your tax return, which can help to lower your tax liability.
It’s important to understand your tax obligations, especially if you’re a small business owner. You can find a tax calculator for small businesses in October 2024 at Tax calculator for small businesses in October 2024.
Property taxes are levied by local governments on the value of your rental property.
Rental Income Levels
The amount of rental income you receive directly affects your tax liability. As your rental income increases, your tax liability also increases. However, the specific tax rates and deductions available to you will vary depending on your individual circumstances.
The amount of rental income you receive directly affects your tax liability.
Steps to Use a Tax Calculator
Using a tax calculator for rental property income can simplify the process of calculating your tax liability and help you understand your financial obligations.
Inputting Financial Data
The accuracy of your tax calculations depends on the accuracy of the data you input.
It’s important to know the mileage rate for business travel, especially when you need to track your expenses. You can find the mileage rate for October 2024 at Where can I find the mileage rate for October 2024?.
- Rental Income:Enter the total rental income received during the tax year, including any late fees or other charges.
- Expenses:Provide detailed information about your rental expenses, including:
- Mortgage Interest:Enter the amount of interest paid on your mortgage for the rental property.
- Property Taxes:Include the amount of property taxes paid on the rental property.
- Insurance Premiums:Enter the cost of insurance premiums, such as homeowner’s insurance or liability insurance.
- Repairs and Maintenance:Include the cost of repairs, maintenance, and improvements to the rental property.
- Depreciation:Enter the depreciation expense for the rental property. Depreciation is a non-cash expense that reflects the wear and tear of the property over time.
- Other Expenses:Include any other expenses related to the rental property, such as advertising, utilities, legal fees, and travel expenses.
Deductions
Deductions can significantly reduce your taxable income from rental properties.
- Mortgage Interest:As mentioned previously, you can deduct the interest paid on your mortgage for the rental property.
- Property Taxes:Similar to mortgage interest, you can deduct the property taxes paid on the rental property.
- Insurance Premiums:You can deduct insurance premiums, such as homeowner’s insurance or liability insurance.
- Repairs and Maintenance:Deductible repairs and maintenance expenses include costs for fixing broken appliances, replacing worn-out carpets, and painting the property.
- Depreciation:As discussed earlier, you can deduct depreciation expense for the rental property.
- Other Expenses:You can also deduct other expenses related to the rental property, such as advertising, utilities, legal fees, and travel expenses.
Ensuring Accuracy
- Review Your Data:Carefully review all the data you have entered into the tax calculator to ensure its accuracy.
- Consult with a Tax Professional:If you are unsure about any deductions or tax implications, consult with a tax professional for guidance.
- Keep Detailed Records:Maintain detailed records of all your rental income and expenses, including receipts and invoices.
Tax Planning Strategies for Rental Property Owners
Rental property ownership presents numerous tax advantages, but it’s crucial to employ effective tax planning strategies to maximize benefits and minimize tax liability. By understanding these strategies, rental property owners can optimize their financial outcomes and achieve long-term success.
The amount of taxes you pay depends on your income level and filing status. Check out Tax brackets for single filers in 2024 to see how much you’ll be paying.
Benefits of Incorporating a Rental Property Business
Incorporating your rental property business offers various tax advantages and legal protections.
- Limited Liability:Incorporation shields your personal assets from business liabilities, protecting you from lawsuits or financial losses.
- Tax Advantages:Incorporating allows you to deduct business expenses, such as repairs, maintenance, and insurance, reducing your overall tax liability.
- Retirement Planning:You can contribute to a retirement plan, such as a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k), as a business owner, allowing for tax-advantaged savings.
- Estate Planning:Incorporation simplifies estate planning, making it easier to transfer ownership of the business to heirs.
Strategies for Minimizing Tax Liability
Rental property owners can employ several strategies to reduce their tax liability.
You can contribute a certain amount to your 401k each year. Check out How much can I contribute to my 401k in 2024 to see how much you can contribute.
- Depreciation:Depreciation is a tax deduction that allows you to recover the cost of your rental property over time. You can deduct a portion of the property’s value each year, reducing your taxable income.
- Home Office Deduction:If you use a portion of your rental property as a home office, you can deduct expenses related to that space, such as rent, utilities, and insurance.
- Property Taxes:You can deduct property taxes paid on your rental property.
- Interest Expense:Deductible interest expense includes mortgage interest and any other interest paid on loans related to the property.
- Insurance Premiums:Insurance premiums for your rental property, such as liability insurance and hazard insurance, are deductible expenses.
- Repairs and Maintenance:You can deduct expenses for repairs and maintenance, such as plumbing repairs, electrical work, and landscaping.
- Vacancy Costs:You can deduct expenses related to vacancy periods, such as utilities and property taxes, if the property is vacant for a reasonable period.
- Property Management Fees:If you hire a property manager, you can deduct the management fees as a business expense.
- Travel Expenses:You can deduct travel expenses related to your rental property, such as travel to inspect the property or meet with tenants.
- Advertising Expenses:Expenses incurred for advertising your rental property, such as online listings or print advertisements, are deductible.
- Legal and Accounting Fees:Fees paid to lawyers and accountants for services related to your rental property are deductible expenses.
Tax-Advantaged Investment Strategies
Rental property owners can leverage various tax-advantaged investment strategies to enhance their financial returns.
It’s good to know what the IRA contribution limits are, and they can change from year to year. You can find more information about the IRA contribution limits for 2024 and beyond at Ira contribution limits for 2024 and beyond.
- 1031 Exchange:A 1031 exchange allows you to defer capital gains taxes when selling a rental property by reinvesting the proceeds into a new, like-kind property. This strategy can be particularly beneficial for long-term investors looking to upgrade or diversify their portfolio.
Understanding how tax brackets work can help you make better financial decisions. Understanding tax brackets for 2024 can help you understand how your income is taxed.
- Opportunity Zones:Opportunity Zones are designated areas experiencing economic distress. Investing in qualified Opportunity Zone properties can provide significant tax benefits, including reduced capital gains taxes and potential tax-free gains.
- Retirement Accounts:Rental property owners can utilize retirement accounts, such as a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k), to save for retirement and potentially reduce their taxable income.
Resources and Tools for Rental Property Tax Calculations
Calculating rental property taxes can be complex, involving various deductions and credits. To simplify the process, several online tax calculators and resources are available. These tools can help you estimate your tax liability and make informed decisions regarding your rental property investments.
Online Tax Calculators and Resources
Several online tax calculators and resources can assist you in calculating your rental property taxes. Here’s a table listing some popular options:
| Name | Description | Features | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| TurboTax | A popular online tax preparation software that offers a dedicated section for rental property income and expenses. | Provides comprehensive guidance on rental property tax deductions and credits, generates tax forms, and offers expert support. | https://turbotax.intuit.com/ |
| H&R Block | Another well-known online tax preparation service with features specifically designed for rental property owners. | Offers step-by-step guidance on rental property tax calculations, provides access to tax professionals, and generates tax forms. | https://www.hrblock.com/ |
| TaxAct | A user-friendly online tax preparation platform with tools for rental property income and expense tracking. | Provides detailed instructions on rental property tax deductions and credits, allows for electronic filing, and offers various pricing plans. | https://www.taxact.com/ |
| TaxSlayer | An affordable online tax preparation service with features specifically designed for rental property owners. | Provides comprehensive guidance on rental property tax deductions and credits, generates tax forms, and offers live tax support. | https://www.taxslayer.com/ |
| IRS Free File | A program offered by the IRS that allows taxpayers with certain income levels to file their taxes for free using participating tax preparation software providers. | Provides a user-friendly interface for filing federal income tax returns, including rental property income and expenses. | https://www.irs.gov/filing/free-file-do-your-federal-taxes-for-free |
Government Websites and Tax Information Resources
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides comprehensive information and guidance on rental property taxation. Additionally, various state and local tax agencies offer specific resources for rental property owners.
- IRS Publication 527, Residential Rental Property: This publication provides detailed information on rental property income and expenses, deductions, and credits. It’s a valuable resource for understanding the tax implications of owning and operating rental properties.
- IRS Website: The IRS website offers a wealth of information on rental property taxation, including FAQs, forms, and publications. You can find specific guidance on deductions, credits, and other tax-related matters.
- State and Local Tax Agencies: Each state and local government may have specific rules and regulations regarding rental property taxation. Contact your state and local tax agencies for information on applicable laws and requirements.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Rental property income, like any other form of income, is subject to legal reporting requirements and ethical considerations. Understanding these aspects is crucial for tax compliance and responsible property ownership.
Legal Requirements for Reporting Rental Income
It’s essential to accurately report rental income to avoid penalties and maintain compliance with tax regulations. This involves understanding the legal requirements and ensuring that your reporting is accurate and complete.
The mileage rate for business travel is an important consideration when tracking your expenses. You can find out how much the mileage rate is for October 2024 at How much is the mileage rate for October 2024?.
- IRS Form 1040 Schedule E:Rental income and expenses are reported on this form, which is part of your federal income tax return. You’ll need to provide details about your rental property, income received, and expenses incurred.
- State Tax Reporting:Most states also require reporting of rental income on their respective tax returns. The specific requirements and forms may vary by state, so it’s important to consult your state’s tax guidelines.
- Record Keeping:Maintaining accurate and complete records is crucial for tax compliance. This includes documentation of rental income, expenses, property improvements, and other relevant details. The IRS requires you to keep these records for at least three years after filing your tax return.
The standard deduction amount for qualifying widow(er)s is different than for other filing statuses. You can find the standard deduction amount for qualifying widow(er)s in 2024 at Standard deduction for qualifying widow(er) in 2024.
Ethical Considerations for Tax Compliance
Beyond legal requirements, ethical considerations play a significant role in tax compliance. It’s important to approach tax reporting with honesty and integrity, ensuring that you are paying your fair share of taxes.
- Accurate Reporting:It’s essential to report all rental income, regardless of its source or size. This includes income from short-term rentals, long-term leases, and any other form of rental revenue.
- Transparency:Be transparent with the IRS about your rental activities and expenses. This includes reporting all deductions and credits you claim, ensuring they are legitimate and supported by proper documentation.
- Avoiding Tax Evasion:Deliberately underreporting income or claiming false deductions is considered tax evasion and can lead to severe penalties, including fines and even jail time. It’s crucial to avoid any actions that could be construed as tax evasion.
Maintaining Accurate Records and Documentation
Accurate record keeping is the cornerstone of tax compliance. This involves organizing and documenting all aspects of your rental property activities.
- Rental Agreements:Maintain copies of all lease agreements, including details about rent payments, lease terms, and tenant information. This documentation is essential for verifying rental income and expenses.
- Income Records:Keep a detailed record of all rental income received, including dates, amounts, and payment methods. This can include bank statements, receipts, and online payment records.
- Expense Documentation:Document all expenses related to your rental property, including mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, repairs, maintenance, and utilities. Keep receipts, invoices, and other supporting documentation.
- Property Improvements:Track all property improvements and repairs, including dates, costs, and descriptions. This information is important for calculating depreciation and determining the property’s value for tax purposes.
Conclusion
By understanding the intricacies of rental income taxation and utilizing a tax calculator effectively, you can gain greater control over your financial obligations. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of key factors, tax planning strategies, and valuable resources. Remember, seeking professional advice from a qualified tax advisor is essential for ensuring accurate tax compliance and maximizing your financial benefits.
FAQ Compilation
What are the common deductions for rental property income?
Common deductions include expenses related to property maintenance, repairs, insurance, property taxes, mortgage interest, and depreciation.
How often do I need to file taxes on my rental income?
You typically need to file taxes on your rental income annually, along with your other income, when you file your tax return.
What are the legal implications of not reporting rental income?
Failing to report rental income can result in penalties and interest charges from the tax authorities. It is crucial to comply with all tax regulations.











