Tax calculator for capital gains in October 2024 provides a crucial tool for individuals and investors navigating the complexities of capital gains taxation. Understanding how capital gains are taxed is essential for making informed financial decisions, and this calculator simplifies the process by providing a clear and concise overview of the relevant tax rules and regulations.
This calculator is designed to help you estimate your potential tax liability on capital gains, taking into account various factors such as the type of asset, holding period, and applicable tax rates. By inputting relevant details, you can obtain a personalized estimate of your capital gains tax obligation, allowing you to plan accordingly and potentially explore strategies for tax optimization.
Contents List
Introduction to Capital Gains Tax
Capital gains tax is a tax levied on the profit realized from the sale or exchange of capital assets. Capital assets are generally defined as any property held for investment or personal use that is not considered inventory or property held for sale in the ordinary course of business.
This tax applies to the difference between the selling price and the original purchase price, minus any associated expenses.
Types of Capital Assets Subject to Capital Gains Tax
Capital gains tax applies to various types of capital assets. The most common examples include:
- Real Estate:This includes properties such as homes, apartments, land, and commercial buildings.
- Stocks and Bonds:Profits from the sale of stocks, bonds, and other securities are subject to capital gains tax.
- Precious Metals:Gold, silver, and platinum are examples of precious metals that are subject to capital gains tax.
- Collectibles:This includes items such as stamps, coins, art, antiques, and other valuable items that are held for investment purposes.
- Cryptocurrencies:The IRS considers cryptocurrencies as property, and profits from their sale are subject to capital gains tax.
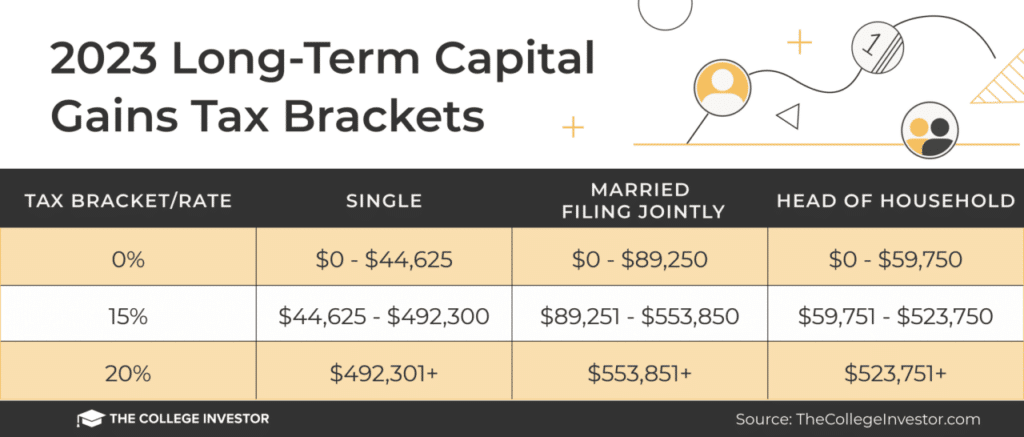
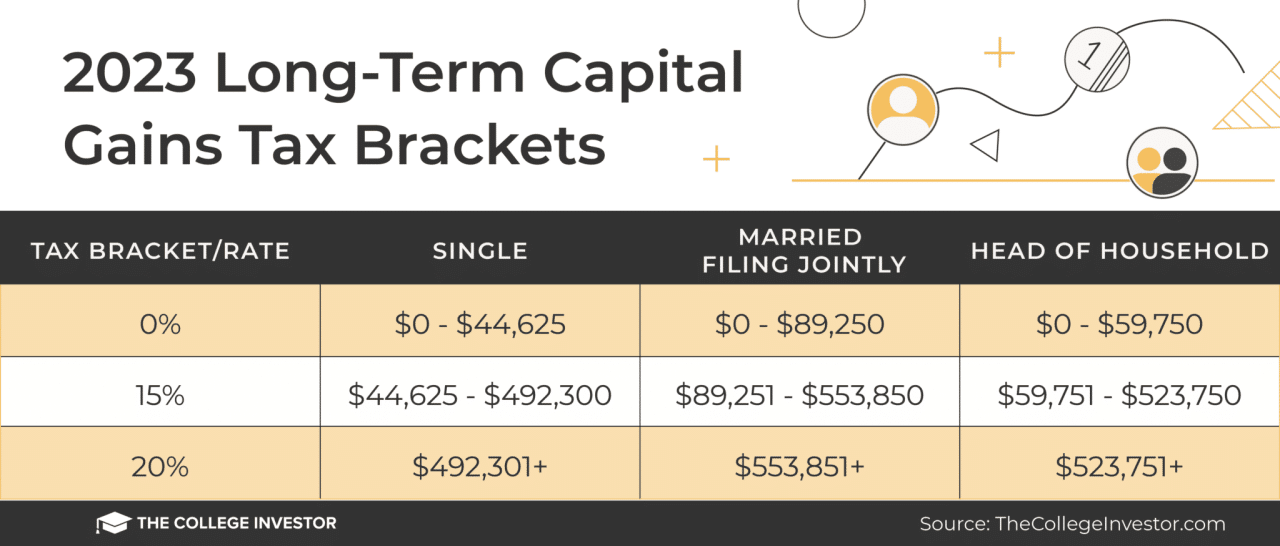
Capital Gains Tax Rates in October 2024
The capital gains tax rates in October 2024 will depend on the holding period of the asset and the taxpayer’s income level. Capital gains are classified into two categories: short-term and long-term.
Understanding tax brackets is crucial for anyone planning their finances. The tax brackets for 2024 in the United States are designed to ensure fairness and progressivity in the tax system. It’s also important to note that these brackets can change depending on your filing status, like if you’re married filing separately.
You can find the tax brackets for married filing separately in 2024 in a separate article. And don’t forget to check the IRA contribution limits for 2024 and 2025 to maximize your retirement savings.
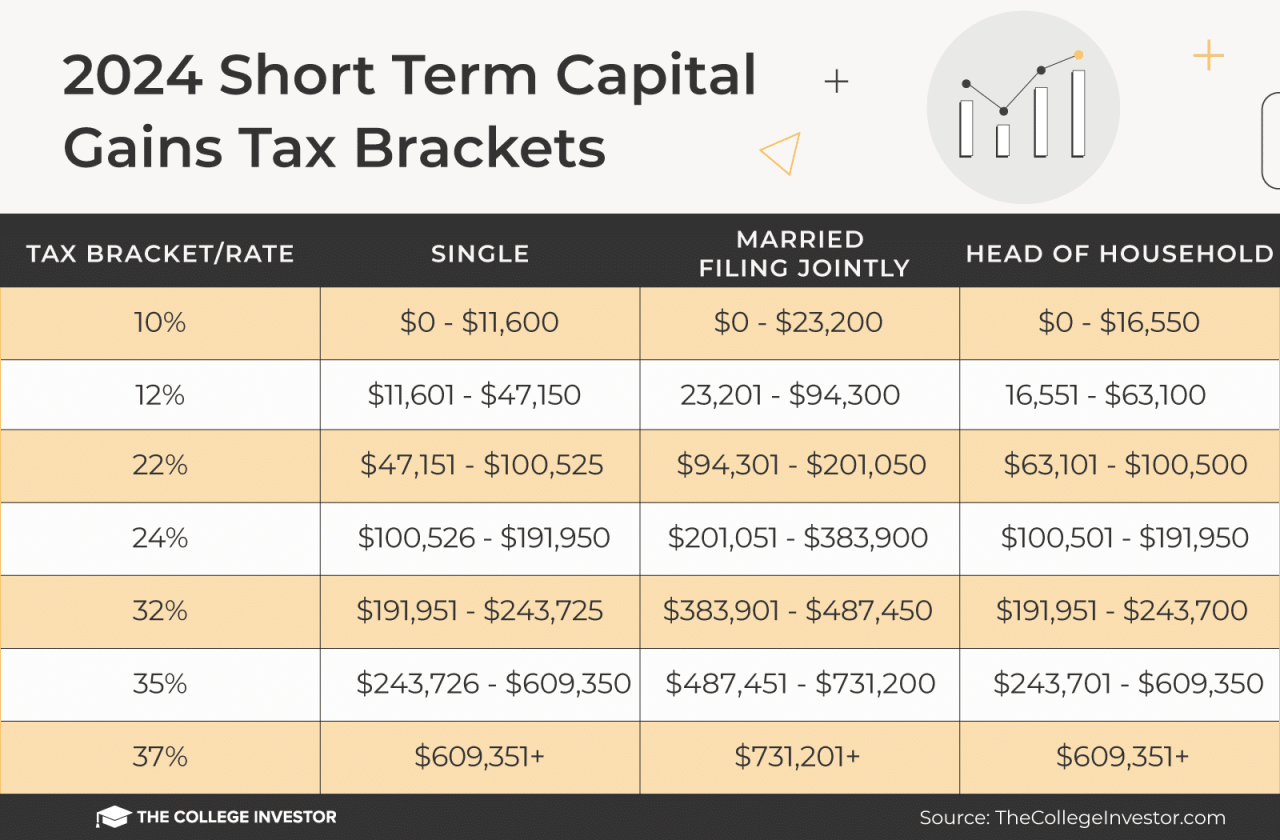
- Short-term Capital Gains:These are gains realized from assets held for less than a year. Short-term capital gains are taxed at the taxpayer’s ordinary income tax rate, which can range from 10% to 37% depending on their income bracket.
- Long-term Capital Gains:These are gains realized from assets held for more than a year. Long-term capital gains are generally taxed at lower rates than short-term gains. In October 2024, the long-term capital gains tax rates are expected to be:
- 0%for taxpayers in the 10% and 12% income tax brackets.
- 15%for taxpayers in the 22%, 24%, 32%, and 35% income tax brackets.
- 20%for taxpayers in the highest income tax bracket (37%).
Tax Calculator Functionality
A user-friendly capital gains tax calculator can simplify the process of determining your tax liability. The calculator would gather necessary information from the user, such as the details of the asset sold and the holding period, and then automatically calculate the taxable capital gain and potential tax owed.
Calculator Interface Design
The calculator interface would be designed with user-friendliness in mind, featuring clear input fields and straightforward instructions. Here’s a hypothetical example of the key input fields:
- Asset Type: Dropdown menu allowing selection of asset type (e.g., stocks, bonds, real estate, cryptocurrency).
- Purchase Date: Date field for entering the date the asset was acquired.
- Purchase Price: Numeric field for entering the original purchase price of the asset.
- Sale Date: Date field for entering the date the asset was sold.
- Sale Price: Numeric field for entering the price at which the asset was sold.
- Capital Gains Tax Rate: This field would automatically populate based on the user’s income tax bracket and the holding period of the asset.
Calculating Taxable Capital Gain
The calculator would determine the taxable capital gain using the following formula:
Taxable Capital Gain = Sale Price
- Purchase Price
- Expenses
Where:* Sale Price: The price at which the asset was sold.
Purchase Price
The original price paid for the asset.
Expenses
Any expenses directly related to the sale of the asset, such as brokerage fees or legal fees.
Scenarios and Calculations
Here are different scenarios and calculations involved in determining capital gains tax liability:
- Short-Term Capital Gains: If the asset is held for less than one year, the capital gain is considered short-term and taxed at the ordinary income tax rate, which can be as high as 37% in 2024.
- Long-Term Capital Gains: If the asset is held for more than one year, the capital gain is considered long-term and taxed at preferential rates, ranging from 0% to 20% in 2024, depending on your income level.
- Losses: If the sale price is lower than the purchase price, resulting in a capital loss, the loss can be used to offset capital gains.
When filing your taxes, you have the option to claim the standard deduction or itemize your deductions. If you choose the standard deduction, make sure you understand the process. You can find helpful information about how to claim the standard deduction on your 2024 taxes in a dedicated article.
Remember, the standard deduction can vary based on your filing status and other factors, like whether you have a disability. Check out the article on the standard deduction for people with disabilities in 2024 to see if you qualify for an increased deduction.
If the loss exceeds the gains, a portion of the loss can be deducted from ordinary income, subject to certain limitations.
Example Calculation
Let’s assume an individual purchased 100 shares of XYZ stock for $50 per share on January 1, 2023. The individual sold the shares for $75 per share on January 1, 2024. The brokerage fees for the sale were $100.* Purchase Price: 100 shares$50/share = $5,000
-
Sale Price
100 shares
- $75/share = $7,500
- $5,000
- $100 = $2,400
Expenses
$100
Taxable Capital Gain
$7,500
Since the holding period is less than one year, the capital gain is considered short-term. The individual would need to report the $2,400 capital gain on their tax return and pay taxes at their ordinary income tax rate.
Tax Deductions and Exemptions
When calculating capital gains tax, you might be eligible for certain deductions and exemptions that can reduce your tax liability. These deductions and exemptions are designed to provide relief in specific circumstances, such as investments held for a long period or those made in specific sectors.
Trusts, like individuals, need to file W9 forms for tax purposes. The W9 Form October 2024 for trusts is a crucial document that provides the necessary information for tax reporting. It’s important to be compliant with these requirements, as failing to do so can lead to penalties.
Check out the article on W9 Form October 2024 penalties for non-compliance to learn more about the consequences of non-compliance.
Deductions for Capital Gains
Deductions can directly reduce your taxable capital gains, potentially lowering your overall tax bill.
- Capital Gains Tax Exemption for Small Business Shares:This exemption allows you to avoid paying capital gains tax on the first $10,000 of capital gains from the sale of small business shares. This exemption applies to shares held for at least 12 months and is available for individuals and trusts.
- Capital Gains Tax Discount for Long-Term Investments:If you hold an asset for more than 12 months, you may qualify for a 50% discount on your capital gains tax liability. This means you only pay tax on half of the capital gain.
Exemptions for Capital Gains, Tax calculator for capital gains in October 2024
Exemptions allow you to exclude certain capital gains from your taxable income altogether, effectively eliminating the tax liability on those gains.
- Main Residence Exemption:You can generally claim a full exemption from capital gains tax on the sale of your main residence, regardless of how long you have owned it. This exemption applies to the first $2.5 million of capital gains.
- Exemption for Certain Investments:Certain investments, such as those in government bonds or infrastructure projects, may be eligible for exemption from capital gains tax. These exemptions are typically designed to encourage investment in specific sectors deemed beneficial to the economy.
Conditions for Claiming Deductions and Exemptions
To claim deductions and exemptions, you must meet specific eligibility criteria. These criteria may vary depending on the specific deduction or exemption.
The Seahawks’ comeback fell short in Week 5, as detailed in the article titled Rapid Reactions: Seahawks Comeback Falls Short In Week 5 Loss. But while football fans may be disappointed, it’s a good time to consider your tax situation, especially if you’re looking to contribute to an IRA.
Check out the IRA contribution limits for married couples in 2024 and see if you can maximize your savings.
- Holding Period:Many deductions and exemptions require that you hold the asset for a certain period. For example, the long-term capital gains discount requires you to hold the asset for more than 12 months.
- Asset Type:Some deductions and exemptions apply only to specific types of assets. For example, the main residence exemption applies only to your primary place of residence.
- Income Limits:Certain deductions and exemptions may be subject to income limits. This means that you may not be eligible for the full deduction or exemption if your income exceeds a certain threshold.
- Other Requirements:There may be other requirements that you need to meet to claim a deduction or exemption. For example, you may need to provide documentation to support your claim.
Common Deductions and Eligibility Criteria
| Deduction | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|
| Capital Gains Tax Discount for Long-Term Investments | Asset held for more than 12 months. |
| Capital Gains Tax Exemption for Small Business Shares | Shares held for at least 12 months, first $10,000 of capital gains. |
Reporting and Filing Requirements
You’ll need to report your capital gains on your tax return. This ensures that you pay the correct amount of tax on your profits from selling investments. The process of reporting capital gains can vary depending on the type of investment and your specific circumstances.
Reporting Capital Gains on Your Tax Return
When you file your tax return, you’ll need to include information about any capital gains or losses you realized during the year. This information is typically reported on Schedule D of Form 1040. You’ll need to provide the following information:
- The description of the asset sold (e.g., stock, bond, real estate)
- The date of the sale
- The selling price
- The cost basis of the asset (the original purchase price plus any expenses incurred to acquire it)
- The amount of any capital gains or losses realized
Filing Taxes Related to Capital Gains
The process of filing your taxes related to capital gains involves several steps:
- Gather all your relevant documentation:This includes your brokerage statements, trade confirmations, and any other records that show your capital gains and losses.
- Calculate your capital gains and losses:This involves subtracting your cost basis from your selling price for each asset.
- Determine your capital gains tax liability:This depends on your tax bracket and the holding period of your investments. Short-term capital gains (held for less than a year) are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, while long-term capital gains (held for a year or more) are taxed at preferential rates.
- Complete and file your tax return:Use the appropriate forms and schedules to report your capital gains and losses. You can file your taxes electronically or by mail.
Deadlines and Penalties
The deadline for filing your tax return is typically April 15th of each year. If you fail to file your return by this deadline, you may be subject to penalties. The penalties for late filing can be substantial, so it’s important to file your return on time.
The penalty for late filing is generally 0.5% of the unpaid tax liability for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25% of the unpaid tax liability.
In addition to penalties for late filing, you may also be subject to penalties for underpayment of tax. This occurs if you fail to pay the correct amount of tax by the due date.
The penalty for underpayment is generally 0.5% of the underpayment for each month or part of a month that the underpayment remains unpaid, up to a maximum of 25% of the underpayment.
If you’re a freelancer, make sure you’re aware of the October 2024 tax deadline for freelancers. It’s important to file your taxes on time to avoid any penalties. Remember, the deadline is for everyone, including self-employed individuals, as stated in the article about the October 2024 tax deadline for self-employed individuals.
Don’t forget to check the tax bracket thresholds for 2024 to see where you fall, especially if you’re filing as a married couple.
It’s crucial to file your taxes accurately and on time to avoid penalties. If you’re unsure about any aspect of the process, it’s always best to consult with a qualified tax professional.
Impact of Holding Period
The length of time you hold an asset before selling it significantly impacts your capital gains tax liability. Understanding the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains is crucial for tax planning.
Tax Rates for Short-Term and Long-Term Capital Gains
The holding period determines whether your capital gains are considered short-term or long-term.
- Short-term capital gains: These occur when you sell an asset within one year of purchasing it. Short-term capital gains are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be significantly higher than the long-term rate.
- Long-term capital gains: These arise when you sell an asset after holding it for more than one year. Long-term capital gains are taxed at preferential rates, which are generally lower than your ordinary income tax rate. The specific long-term capital gains tax rates vary depending on your income level.
Examples of Holding Period Impact
Let’s illustrate how the holding period affects your tax liability:
Assume you have a taxable income of $100,000 and have a capital gain of $20,000.
- Short-term capital gain:If the gain was realized within one year, it would be taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Assuming your ordinary income tax bracket is 24%, your tax liability on the $20,000 gain would be $4,800 (24% x $20,000).
- Long-term capital gain:If the gain was realized after holding the asset for more than a year, it would be taxed at the long-term capital gains rate. Assuming the long-term capital gains rate for your income bracket is 15%, your tax liability on the $20,000 gain would be $3,000 (15% x $20,000).
Tax Planning Strategies
Minimizing your capital gains tax liability is a key aspect of successful investment planning. By strategically managing your investments, you can potentially reduce your tax burden and maximize your after-tax returns. This section explores several tax planning strategies that can help you achieve this goal.
If you’re participating in a SIMPLE IRA, you need to be aware of the contribution limits. The IRA contribution limits for SIMPLE IRA in 2024 are designed to help you save for retirement. Understanding these limits can help you plan your finances and maximize your retirement savings.
Make sure to consult with a financial advisor to determine the best course of action for your individual situation.
Harvesting Losses
Capital losses can offset capital gains, potentially reducing your overall tax liability. This strategy involves selling assets that have decreased in value to realize a loss. The realized loss can then be used to offset capital gains from other investments, reducing your taxable income.
- Advantages:
- Reduces overall tax liability.
- Provides a tax advantage for investors who have experienced losses.
- Disadvantages:
- May involve selling assets that you wish to hold for the long term.
- Could lead to a short-term capital loss if the asset was held for less than a year.
- Real-world example:An investor holds shares of Company A that have declined in value. They sell these shares to realize a capital loss, which they then use to offset capital gains from the sale of shares of Company B, which have appreciated in value.
This reduces their overall capital gains tax liability.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting is a specific strategy that involves selling losing investments to offset capital gains. This can be done throughout the year, but it is often done towards the end of the year to maximize tax benefits.
- Advantages:
- Reduces your tax liability.
- Can help you rebalance your portfolio by selling underperforming assets and reinvesting in better performing ones.
- Disadvantages:
- May trigger a wash sale if you repurchase the same or substantially similar asset within 30 days.
- Could involve selling assets that you wish to hold for the long term.
- Real-world example:An investor sells shares of Company C, which have lost value, to offset capital gains from the sale of shares of Company D. They then repurchase shares of Company C after 31 days to avoid a wash sale.
Long-Term Capital Gains
Holding assets for longer than a year can result in a lower capital gains tax rate. This strategy involves holding investments for the long term, typically more than 12 months, to benefit from the lower tax rate on long-term capital gains.
Foreign nationals living in the United States also have tax obligations. The October 2024 tax deadline for foreign nationals is the same as for US citizens. Remember, it’s important to understand the tax implications of your financial situation.
For example, if you’re a single filer, you might want to look into the IRA contribution limits for 2024 for single filers to make sure you’re taking advantage of all available tax benefits.
- Advantages:
- Lower tax rate compared to short-term capital gains.
- Encourages long-term investment, which can lead to higher returns.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires patience and a long-term investment horizon.
- Market volatility can impact the value of investments over the long term.
- Real-world example:An investor purchases shares of Company E in January 2024 and sells them in February 2025. They will be subject to the lower long-term capital gains tax rate because they held the shares for more than 12 months.
Deferred Capital Gains
In some cases, you can defer capital gains tax liability until a later date. This can be achieved through strategies such as reinvesting proceeds from asset sales into other investments, utilizing tax-advantaged accounts, or employing other tax-deferred strategies.
- Advantages:
- Postpones tax liability, allowing you to potentially grow your investments further.
- Can be beneficial for investors who are in a higher tax bracket currently but expect to be in a lower tax bracket in the future.
- Disadvantages:
- You will eventually have to pay capital gains tax on the deferred gains.
- May not be suitable for all investors, especially those who need the capital gains proceeds immediately.
- Real-world example:An investor sells shares of Company F, realizing a capital gain. They reinvest the proceeds into a Roth IRA, which allows for tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
Tax-Loss Carryforward
If you have more capital losses than capital gains in a given year, you can carry forward the excess losses to offset future capital gains. This strategy allows you to use unused capital losses to reduce your tax liability in subsequent years.
- Advantages:
- Allows you to offset future capital gains with past losses.
- Can be particularly beneficial for investors who experience significant losses in a single year.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires careful planning and tracking of losses.
- The carryforward losses may not be used if you do not realize any capital gains in future years.
- Real-world example:An investor experiences significant capital losses in 2024. They can carry forward these losses to offset future capital gains in 2025 and subsequent years.
Tax Laws and Regulations
This section provides an overview of the relevant tax laws and regulations governing capital gains in October 2024. We will explore the current landscape, highlight recent changes, and discuss their potential impact on taxpayers.
Capital Gains Tax Rates
The capital gains tax rates in October 2024 are likely to remain similar to those in effect in 2023, although some adjustments are possible based on economic conditions and government policy. The rates are generally tiered, with lower rates applying to long-term capital gains (held for more than one year) and higher rates for short-term gains (held for one year or less).
- Long-Term Capital Gains:These gains are typically taxed at a lower rate than ordinary income. For example, in 2023, the long-term capital gains rate for individuals in the lowest income bracket was 0%, while the rate for those in the highest bracket was 20%.
- Short-Term Capital Gains:Short-term capital gains are taxed at the same rate as ordinary income, which can be significantly higher than the long-term capital gains rate.
Holding Period
The holding period is a crucial factor in determining the tax rate on capital gains. It refers to the length of time an asset is held before it is sold.
- Long-Term Holding Period:In 2023, assets held for more than one year qualified for long-term capital gains treatment.
- Short-Term Holding Period:Assets held for one year or less were subject to short-term capital gains tax rates.
Recent Changes and Updates
The tax laws governing capital gains are subject to change, and it’s essential to stay informed about any recent updates. For example, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 introduced several changes to capital gains taxation, including a reduction in the top capital gains rate.
In 2024, there may be further adjustments based on economic conditions, government policy, and political considerations.
- Potential Changes:For example, the government may consider raising the capital gains tax rate for high-income earners or increasing the holding period for long-term capital gains treatment.
Impact of Changes on Taxpayers
Any changes to the capital gains tax laws could have a significant impact on taxpayers. For instance, a higher capital gains tax rate would reduce the after-tax return on investments, potentially discouraging investment activity. Conversely, a lower rate could encourage investment and stimulate economic growth.
- Investment Decisions:Changes in tax rates can influence investment decisions. Investors may adjust their investment strategies to minimize their tax liability.
- Retirement Planning:Tax changes can also impact retirement planning. For example, individuals may consider shifting investments to tax-advantaged accounts or delaying retirement to avoid higher capital gains taxes.
Conclusion: Tax Calculator For Capital Gains In October 2024
Navigating the world of capital gains taxation can be daunting, but this calculator provides a valuable resource for gaining a better understanding of your tax obligations. By understanding the nuances of capital gains tax and utilizing this calculator effectively, you can make more informed financial decisions and potentially minimize your tax liability.
Remember to consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice tailored to your specific circumstances.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains?
Short-term capital gains are realized from assets held for less than a year, while long-term capital gains are realized from assets held for a year or more. The tax rates differ for each category.
Are there any deductions or exemptions available for capital gains?
Yes, certain deductions and exemptions may apply depending on the type of asset and your individual circumstances. Consult the relevant tax regulations or a tax professional for details.
How do I report capital gains on my tax return?
Capital gains are reported on your tax return using specific forms and schedules. The exact process may vary depending on your jurisdiction. Consult the instructions provided by your tax authority.