401k contribution limits 2024 for self-employed are a crucial aspect of retirement planning for those who work for themselves. Understanding these limits and how they differ from traditional 401(k) plans is essential for maximizing savings and tax benefits. This guide will delve into the specifics of these limits, the factors that influence them, and strategies to make the most of your contributions.
Self-employed individuals have unique options for retirement savings, and solo 401(k) plans offer significant advantages. These plans allow both “employee” and “employer” contributions, which can be a powerful tool for building a robust retirement nest egg. This guide will provide a clear overview of the rules and regulations surrounding these contributions, helping you make informed decisions for your financial future.
Contents List
- 1 Understanding 401(k) Contribution Limits for Self-Employed Individuals in 2024
- 2 Contribution Limits for 2024
- 3 Factors Influencing Contribution Limits
- 4 Benefits of Maximizing Contributions
- 5 Strategies for Maximizing Contributions
- 6 Considerations for Self-Employed Individuals
- 7 Final Review: 401k Contribution Limits 2024 For Self-employed
- 8 FAQ Compilation
Understanding 401(k) Contribution Limits for Self-Employed Individuals in 2024
For self-employed individuals, understanding 401(k) contribution limits is crucial for maximizing retirement savings. This guide will break down the key aspects of 401(k) contributions for the self-employed in 2024, covering both traditional and solo 401(k) plans.
Retirement planning is crucial, and understanding your tax obligations is a key part of the process. You can find a helpful tax calculator for retirees in October 2024 online, helping you estimate your tax liability in retirement.
Contribution Limits for Self-Employed Individuals
The 401(k) contribution limit for 2024 applies to both traditional and solo 401(k) plans. The total amount you can contribute in 2024 is $22,500, or $30,000 if you are 50 or older. This limit encompasses both employee and employer contributions.
As a sole proprietor, staying on top of your tax forms is crucial. The W9 form is a vital document for reporting your tax information. You can find out everything you need to know about the W9 form for sole proprietorships in October 2024 online, ensuring you’re prepared for tax season.
Traditional 401(k) vs. Solo 401(k) Plans
The primary difference between traditional 401(k) plans and solo 401(k) plans lies in the eligibility criteria. Traditional 401(k) plans are offered by employers to their employees, while solo 401(k) plans are designed specifically for self-employed individuals and small business owners.
Types of Contributions for Solo 401(k) Plans
Solo 401(k) plans allow for two distinct types of contributions:
- Employee Contributions: These contributions are made by you as an employee of your own business. The limit for employee contributions in 2024 is $22,500, or $30,000 if you are 50 or older.
- Employer Contributions: These contributions are made by you as the employer of your own business. The limit for employer contributions is 25% of your net adjusted self-employed income (which is your net earnings from self-employment minus one-half of your self-employment tax).
Retirement savings limits can vary based on your age. You can find out the specific 401(k) contribution limits for 2024 by age online, helping you make informed decisions about your retirement planning.
Contribution Limits for 2024
The contribution limits for solo 401(k) plans in 2024 are designed to help you save for retirement while maximizing your tax advantages. Understanding these limits is crucial for making informed decisions about your retirement savings.
If you’re using your vehicle for business purposes, knowing the current IRS mileage rate is essential. You can quickly find out what the IRS mileage rate is for October 2024 online, making it easy to calculate your deductions.
Contribution Limits for 2024
The contribution limits for solo 401(k) plans in 2024 are divided into two categories: employee contributions and employer contributions.
Corporations need to stay on top of their tax forms, including the W9 form. You can find out everything you need to know about the W9 form for corporations in October 2024 online, ensuring you’re prepared for tax season.
Employee Contributions
The maximum amount you can contribute as an employee to a solo 401(k) plan in 2024 is $22,500. This limit applies to individuals aged 50 and under.
Employer Contributions
The maximum amount you can contribute as an employer to a solo 401(k) plan in 2024 is 25% of your net adjusted self-employed income. This limit is calculated after deducting half of your self-employment taxes.
You might be wondering if you can contribute to an IRA even if you have a 401(k). The good news is, in most cases, you can! Check out this helpful resource to find out if you can contribute to an IRA if you have a 401(k) and how much you can contribute.
Combined Contribution Limits
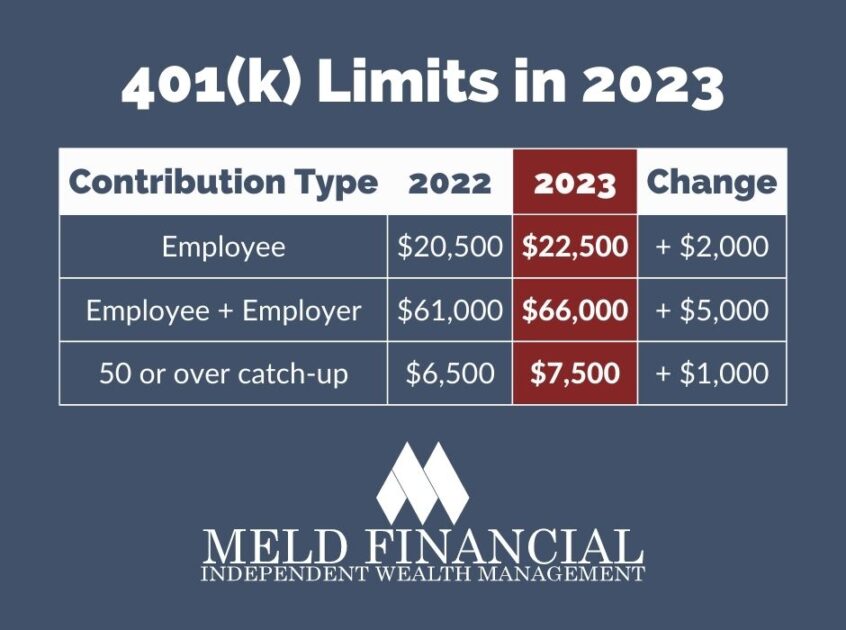
The combined contribution limit for both employee and employer contributions in 2024 is $66,000. This means that the total amount you can contribute to your solo 401(k) plan, including both employee and employer contributions, cannot exceed $66,000.
Comparison to Previous Years
The contribution limits for solo 401(k) plans have been adjusted for inflation in recent years. Here’s a comparison of the contribution limits for the past few years:
| Year | Employee Contribution Limit | Employer Contribution Limit | Combined Contribution Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $22,500 | 25% of net adjusted self-employed income | $66,000 |
| 2022 | $22,500 | 25% of net adjusted self-employed income | $66,000 |
| 2021 | $20,500 | 25% of net adjusted self-employed income | $61,000 |
As you can see, the contribution limits for solo 401(k) plans have remained consistent for the past few years.
Saving for retirement is crucial, and knowing your contribution limits is key to maximizing your savings. If you’re wondering about your 401(k) contribution limits, you can find out exactly how much you can contribute to your 401(k) in 2024 with a quick online search.
Implications of Exceeding Contribution Limits
Exceeding the contribution limits for solo 401(k) plans can result in penalties. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) may impose a 10% penalty on any excess contributions, plus any applicable interest.
As we approach the 2024 tax year, it’s essential to understand the standard deduction amount to properly plan your finances. You can find out the exact standard deduction amount for the 2024 tax year online, helping you determine your tax liability.
Important Note:It’s essential to consult with a qualified tax advisor to ensure you understand the contribution limits and avoid any potential penalties.
If you’re over 50, you may be eligible for catch-up contributions to your 401(k). You can find out exactly how much you can contribute to your 401(k) in 2024 with catch-up contributions online, helping you maximize your retirement savings.
Factors Influencing Contribution Limits
While the contribution limits for self-employed individuals are generally fixed, certain factors can influence how much you can contribute to your 401(k) plan. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing your retirement savings.
If you’re self-employed, you have a different tax deadline than those who work for an employer. You can find out the specific October 2024 tax deadline for self-employed individuals online, helping you avoid any late penalties.
Contribution Limits for Solo 401(k) Plans
Solo 401(k) plans offer a unique structure that allows self-employed individuals to contribute as both an employee and an employer. This structure allows for higher contribution limits compared to traditional 401(k) plans. The contribution limit for the employee portion of a solo 401(k) is the same as the traditional 401(k) limit, which is $22,500 for 2024.
Moving can be a big expense, and knowing the current mileage rate for moving expenses can help you maximize your deductions. You can find out the October 2024 mileage rate for moving expenses online, making it easier to track your expenses and save money.
However, you can also contribute as an employer. The employer contribution limit for 2024 is 25% of your net adjusted self-employed income. This means that you can contribute up to $66,000 in total for 2024, combining both the employee and employer contributions.
Understanding your tax bracket is essential for effective financial planning. You can find a detailed breakdown of the tax brackets for qualifying widow(er)s in 2024 online, helping you make informed decisions about your finances.
For example, if your net adjusted self-employed income is $100,000 for 2024, your maximum employer contribution would be $25,000 (25% of $100,000). Combined with the employee contribution limit of $22,500, your total contribution limit for 2024 would be $47,500.
Age and Income Levels
The contribution limits for self-employed individuals are not directly influenced by age. However, your income level does play a role in determining the maximum employer contribution limit, as it’s calculated as a percentage of your net adjusted self-employed income.Here’s a table illustrating the different contribution limits based on income levels:
| Income Level | Employee Contribution Limit (2024) | Maximum Employer Contribution Limit (2024) | Total Contribution Limit (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $50,000 | $22,500 | $12,500 (25% of $50,000) | $35,000 |
| $100,000 | $22,500 | $25,000 (25% of $100,000) | $47,500 |
| $200,000 | $22,500 | $50,000 (25% of $200,000) | $72,500 |
Benefits of Maximizing Contributions
Maximizing your 401(k) contributions as a self-employed individual in 2024 can yield significant benefits, particularly in terms of retirement savings and tax advantages. By fully leveraging the contribution limits, you can set yourself up for a more secure financial future while potentially reducing your current tax liability.
Potential Tax Advantages
The tax advantages associated with 401(k) contributions for self-employed individuals can be substantial. These benefits stem from the tax-deferred nature of these contributions, allowing you to potentially save on taxes now while your investments grow tax-free.
- Reduced Tax Liability:Contributions to a 401(k) are made with pre-tax dollars, which means you’ll pay less in taxes in the current year. This can result in a lower tax bill and potentially more disposable income. For example, if you contribute $22,500 to your 401(k) in 2024, and you’re in the 22% tax bracket, you’ll save $4,950 in taxes that year.
- Tax-Deferred Growth:The earnings on your 401(k) investments grow tax-deferred, meaning you won’t pay taxes on those gains until you withdraw them in retirement. This can lead to significant tax savings over the long term, as your investments have more time to compound without being eroded by taxes.
Figuring out your tax obligations as a head of household can be a bit confusing, especially with the ever-changing tax laws. Thankfully, you can find a detailed breakdown of the standard deduction for head of household in 2024 online, so you can get a clear picture of what to expect.
- Potential for Lower Taxes in Retirement:If you maximize your 401(k) contributions, you may be able to lower your taxable income in retirement. This could result in a lower tax bracket and potentially less tax owed on your retirement withdrawals.
Strategies for Maximizing Contributions
Maximizing your 401(k) contributions as a self-employed individual can significantly boost your retirement savings. Here are some practical strategies to help you achieve your financial goals.
It’s important to be aware of the potential penalties for exceeding IRA contribution limits. Don’t worry, you can easily find out what the penalties are for exceeding IRA contribution limits online, helping you stay within the guidelines.
Setting Realistic Financial Goals and Budgeting for Contributions
Setting clear financial goals is crucial for maximizing your contributions. Determine how much you need to save for retirement, considering your desired lifestyle and expected expenses. Once you have a goal in mind, create a budget that allocates funds for your 401(k) contributions.
Knowing your tax obligations is essential, especially if you have a disability. You can find out about the standard deduction for people with disabilities in 2024 online, helping you understand how your disability may affect your taxes.
This will help you prioritize your savings and ensure you contribute consistently.
Adjusting Contribution Amounts Throughout the Year
Your income and expenses may fluctuate throughout the year. Adjusting your 401(k) contributions accordingly can help you optimize your savings. For example, if you have a particularly profitable quarter, consider increasing your contributions to take advantage of the higher income.
Conversely, if you anticipate a period of lower income, you may need to reduce your contributions temporarily. However, it’s essential to ensure you meet the minimum required contributions to avoid penalties.
Considerations for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals have unique considerations when determining their 401(k) contribution strategy, as they are responsible for both employer and employee contributions. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing retirement savings.
Impact of Business Income Fluctuations, 401k contribution limits 2024 for self-employed
Fluctuations in business income can significantly impact the amount you can contribute to your 401(k). When income is high, you may be able to contribute more, but during slow periods, you may need to adjust your contribution levels. This can make it challenging to maintain a consistent savings plan.
Checklist of Essential Factors
Before making 401(k) contributions, consider these essential factors:
- Current Income:Evaluate your current income and determine a contribution amount that is sustainable and does not strain your cash flow.
- Future Income Projections:Consider your future income projections and estimate how much you can contribute over the long term.
- Retirement Goals:Define your retirement goals and estimate the amount of savings you’ll need to achieve them.
- Investment Strategy:Choose an investment strategy that aligns with your risk tolerance and long-term goals.
- Tax Implications:Understand the tax implications of contributing to a 401(k) and the potential tax benefits you can receive.
- Contribution Limits:Stay informed about the annual contribution limits for self-employed individuals, as they can change yearly.
- Fees and Expenses:Review the fees and expenses associated with your 401(k) plan and compare them to other options.
Final Review: 401k Contribution Limits 2024 For Self-employed
Navigating the world of self-employed retirement savings can seem complex, but understanding the 401k contribution limits for 2024 is a critical step. By taking advantage of the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can make informed decisions to maximize your contributions, build a strong retirement foundation, and enjoy the benefits of tax advantages.
Remember, planning for the future is an ongoing process, and staying informed about changes in regulations is essential.
FAQ Compilation
What are the specific contribution limits for solo 401(k) plans in 2024?
For 2024, the total contribution limit for both employee and employer contributions is $66,000. This limit includes both the employee contribution (up to $22,500) and the employer contribution (up to 25% of your net adjusted self-employed income).
Can I make both employee and employer contributions to a solo 401(k) plan?
Yes, you can make both employee and employer contributions to a solo 401(k) plan. However, the total contribution limit for both types of contributions cannot exceed $66,000 in 2024.
What happens if I exceed the contribution limit for my solo 401(k)?
Exceeding the contribution limit for your solo 401(k) can result in penalties, including a 10% tax on the excess contribution. It’s essential to stay within the limits to avoid these penalties.
Are there any income limitations for contributing to a solo 401(k)?
There are no income limitations for contributing to a solo 401(k). However, your employer contribution limit is based on your net adjusted self-employed income, which is your income after business expenses.











