Taxes Due October: A time of year when many individuals and businesses find themselves facing a flurry of tax obligations. From estimated income taxes to property taxes, the month of October often presents a deadline-driven landscape for navigating financial responsibilities.
Understanding the various taxes due in October is crucial for maintaining financial stability and avoiding potential penalties.
This guide delves into the intricacies of taxes due in October, providing a comprehensive overview of the different types of taxes, their deadlines, and the potential consequences of missing them. We’ll explore federal, state, and property taxes, as well as taxes specific to businesses.
Furthermore, we’ll offer practical tips for tax planning, minimizing liability, and navigating the complexities of tax payments and audits. By equipping yourself with the knowledge and strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can approach October’s tax deadlines with confidence and peace of mind.
Contents List
Tax Deductions and Credits: Taxes Due October
Tax deductions and credits are valuable tools that can help you reduce your tax liability and save money. Understanding these benefits and how to maximize them is crucial for every taxpayer.
Cigna recently announced layoffs, which might impact some employees. For more information about the Cigna Layoffs October 2023 , you can check out the news articles.
Common Tax Deductions
Tax deductions are expenses you can subtract from your taxable income, ultimately reducing the amount of taxes you owe.
If you’re looking to save money, check out the Best CD Rates October 2024. You might find a great deal that can help you reach your financial goals.
- Standard Deduction:This is a fixed amount you can deduct instead of itemizing. The amount varies based on your filing status.
- Itemized Deductions:These are specific expenses you can deduct, such as medical expenses, mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and state and local taxes. To itemize, you must exceed the standard deduction amount.
- Homeownership Deductions:This includes deductions for mortgage interest, property taxes, and insurance premiums, making homeownership a significant tax advantage.
- Education Expenses:Deductions for student loan interest, tuition and fees, and other education-related expenses can help offset the cost of education.
- Business Expenses:If you are self-employed or own a business, you can deduct various expenses, including rent, utilities, supplies, and travel.
Common Tax Credits
Tax credits are direct reductions to your tax liability, meaning they directly lower the amount of taxes you owe.
Looking for some extra income? The Jepi Dividend October 2023 might be a good option. Check out the latest news for more details.
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC):This credit is available to low- and moderate-income working individuals and families. The amount of the credit depends on your income, filing status, and number of children.
- Child Tax Credit:This credit provides a tax break for families with children under 17. The amount of the credit is $2,000 per child.
- American Opportunity Tax Credit:This credit is available for the first four years of post-secondary education. It can be up to $2,500 per student.
- Premium Tax Credit:This credit helps offset the cost of health insurance premiums purchased through the Marketplace.
Maximizing Tax Savings
- Track Your Expenses:Keep detailed records of all your expenses, especially those related to potential deductions. This will help you identify eligible expenses and ensure you claim all the deductions you deserve.
- Utilize Tax Planning Strategies:Consult with a tax professional to discuss tax planning strategies, such as contributing to retirement accounts, making charitable donations, or adjusting your withholding to maximize your tax savings.
- Take Advantage of All Available Credits:Research and claim all eligible tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit, Child Tax Credit, and American Opportunity Tax Credit.
- Stay Informed:Tax laws and regulations are constantly changing. Stay informed about the latest updates and changes that may affect your tax situation.
Examples of Tax Benefits
- Homeownership:A homeowner with a mortgage and property taxes can deduct both expenses, significantly reducing their tax liability. For example, if you pay $10,000 in mortgage interest and $2,000 in property taxes, your tax deduction could be $12,000, potentially saving you hundreds or even thousands of dollars in taxes.
The Irs October Deadline 2023 is approaching, so make sure you’re prepared. File your taxes on time to avoid any penalties.
- Education Expenses:A student paying $5,000 in student loan interest and $10,000 in tuition can potentially deduct both expenses, reducing their taxable income and saving on taxes.
- Earned Income Tax Credit:A low-income working family with two children could receive a significant tax credit through the EITC, potentially reducing their tax liability to zero or even receiving a refund.
12. Tax Audits and Reviews
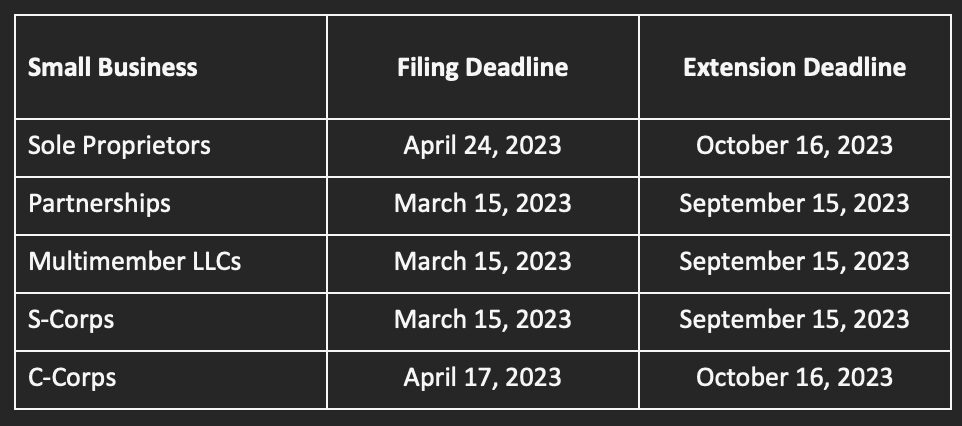
Tax audits are a common part of the tax compliance process, and small businesses are not immune to them. Understanding the audit process, preparing for it, and knowing how to navigate potential consequences are crucial for minimizing disruptions and financial impacts.
It’s important to know When Are Taxes Due In October 2023. Stay organized and make sure you meet all the deadlines.
Understanding the Audit Process
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) conducts tax audits to ensure that taxpayers are accurately reporting their income, expenses, and tax liabilities. There are different types of tax audits, each with its own procedures and level of scrutiny.
- Correspondence Audit: The most common type, involving a simple review of specific items on your tax return. The IRS may request additional information or clarification through mail or email.
- Office Audit: A more in-depth review conducted at an IRS office. You will be required to provide supporting documentation for specific items on your tax return. This may involve meeting with an IRS agent to discuss your tax situation.
- Field Audit: The most comprehensive type, involving an examination of your business records and operations at your place of business. This type of audit typically involves a team of IRS agents and can be quite time-consuming.
The IRS will initiate the audit process by sending a formal notification letter outlining the scope of the audit and the information required. It is crucial to respond promptly and provide all requested documentation. Throughout the audit, the IRS will review your financial records, including income statements, balance sheets, and tax returns.
You will have the opportunity to explain your tax position and provide evidence to support your claims.
Did you file for a tax extension? The Tax Extension Deadline 2023 is approaching, so make sure to get your taxes in order.
Preparing for a tax audit is crucial to minimize stress and potential penalties.
- Gather Relevant Documentation: Organize all relevant financial records, including bank statements, receipts, invoices, contracts, and tax returns for the years under review.
- Organize Financial Records: Create a clear and organized system for accessing your documentation. Use folders, spreadsheets, or accounting software to keep track of your financial records. This will make it easier to find specific information during the audit.
- Maintain a Detailed Record-Keeping System: Implement a comprehensive record-keeping system that tracks all income, expenses, and deductions. This will help you to accurately respond to any audit inquiries.
During the audit, it is essential to communicate effectively with the IRS.
The IRS Tax Deadline October 2023 is fast approaching, so make sure you’re prepared. File your taxes on time to avoid any penalties.
- Be Professional and Courteous: Maintain a professional demeanor and treat IRS agents with respect. This will help to create a positive and productive environment for communication.
- Provide Clear and Concise Explanations: Explain your tax position clearly and concisely, using accurate and relevant documentation to support your claims.
- Ask Questions and Seek Clarification: Do not hesitate to ask questions and seek clarification on any aspect of the audit process. This will ensure that you understand the IRS’s requests and can respond accordingly.
Potential Consequences and Addressing Them
A tax audit can lead to various consequences, including adjustments, penalties, and interest.
Did you file for a tax extension? The October Extension Tax Deadline 2024 is approaching, so make sure to stay organized and get your taxes in order.
- Adjustments: The IRS may adjust your tax return if it finds discrepancies or errors in your reported income, expenses, or deductions. This may result in a higher tax liability or a refund.
- Penalties: Penalties can be imposed for various reasons, including failing to file a tax return, underpayment of taxes, or filing a fraudulent return.
- Interest: Interest may be charged on underpayments or unpaid taxes.
If you disagree with the IRS’s findings, you can appeal the audit decision.
Don’t forget, there are some taxes due in October. Find out more about Taxes Due October to make sure you’re on track.
- Appeal Process: The IRS provides a formal appeals process to challenge audit findings. You can file an appeal within 30 days of receiving the audit notice.
- Negotiation: You can negotiate with the IRS to minimize potential penalties. This may involve providing additional documentation or explaining your tax position in more detail.
13. Tax Fraud and Prevention
Tax fraud is a serious crime that can have significant consequences for individuals and businesses alike. Understanding the different types of tax fraud and implementing preventative measures is crucial to protect yourself from becoming a victim. This section will explore the common types of tax fraud, provide practical tips for safeguarding your financial well-being, and guide you through the process of reporting suspected fraud.
Looking for a new car? The Best Car Lease Deals October 2023 might have the perfect vehicle for you. Start your search today!
Understanding Tax Fraud
Tax fraud encompasses various illegal activities designed to evade or minimize tax obligations. These activities often involve deliberate misrepresentation of financial information, leading to significant financial losses for both individuals and governments.
Planning for next year? Make sure to check out the October 2024 Calendar to keep track of important dates. You don’t want to miss anything!
- Tax Evasion: This involves intentionally underreporting income or overstating deductions to reduce tax liability. Common evasion tactics include:
- Hiding Income: Failing to report all sources of income, such as cash payments or income from side businesses.
- Claiming False Deductions: Inflating expenses or claiming deductions for non-deductible items.
Don’t miss the IRS October Deadline 2024. Make sure you’re prepared to file your taxes on time and avoid any penalties.
- Using Offshore Accounts: Hiding income and assets in offshore accounts to avoid taxation.
- Tax Avoidance: This involves using legal loopholes and strategies to minimize tax obligations. Unlike evasion, which is illegal, tax avoidance is legal and often involves taking advantage of tax breaks and deductions allowed by law.
- Example: A person might choose to invest in a tax-advantaged retirement account, such as a 401(k) or IRA, to reduce their taxable income.
- Identity Theft: This involves using someone else’s personal information to file fraudulent tax returns and claim refunds.
- Example: A thief might steal your Social Security number and use it to file a false tax return, claiming a refund in your name.
- Ghost Employees: This involves creating fictitious employees to claim fraudulent deductions and refunds.
- Example: A business owner might create fake employee records and claim deductions for wages, taxes, and benefits for these nonexistent employees.
- Phantom Expenses: This involves inventing or exaggerating business expenses to reduce taxable income.
- Example: A business might invent fake invoices or inflate the cost of real expenses to claim larger deductions.
Protecting Yourself from Tax Fraud
Protecting yourself from tax fraud requires a proactive approach. By taking preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of becoming a victim.
Planning to lease a new car? The Best Lease Deals October 2024 might have the perfect car for you at a great price. Start your search today!
- Protecting Personal Information:
- Secure Data Storage: Store sensitive documents, such as your Social Security card, birth certificate, and passport, in a safe and secure location.
- Strong Passwords: Use strong and unique passwords for all online accounts, including tax preparation websites and financial institutions.
- Shred Sensitive Documents: Before discarding any documents containing personal information, shred them thoroughly to prevent identity theft.
- Understanding Tax Laws:
- Familiarize Yourself with Basic Tax Rules: Take the time to understand basic tax rules and regulations, such as income tax brackets, deductions, and credits.
- Consult with a Tax Professional: If you are unsure about any aspect of your tax obligations, consult with a qualified tax professional.
- Verifying Tax Professionals:
- Check Credentials: Before engaging a tax preparer or advisor, verify their credentials and ensure they are licensed and registered with the appropriate authorities.
- Read Reviews: Check online reviews and testimonials to get an idea of the tax professional’s reputation and experience.
- Monitoring Tax Accounts:
- Review Tax Documents: Regularly review your tax documents and statements for any discrepancies or errors.
- Monitor Tax Accounts Online: If you have an online tax account, monitor it regularly for any suspicious activity.
- Reporting Suspicious Activity:
- Report to the IRS: If you suspect someone is committing tax fraud, report it to the IRS.
- Contact State Tax Agencies: Report any suspected tax fraud to your state tax agency as well.
Reporting Tax Fraud
Reporting suspected tax fraud is crucial to deterring illegal activities and protecting the integrity of the tax system. Failing to report tax fraud can have serious consequences, including:
- Enabling Criminal Activity: Failure to report suspected fraud allows criminals to continue their illegal activities, potentially harming others.
- Erosion of Public Trust: Unreported tax fraud erodes public trust in the tax system and undermines the fair and equitable distribution of tax burdens.
- Financial Losses: Unreported tax fraud results in financial losses for both individuals and governments, as fraudulent activities deprive legitimate taxpayers of resources.
Looking for the best deals on a new car? Check out the October 2023 Lease Deals for some great options. You might find a car that fits your budget and needs.
There are several channels for reporting tax fraud:
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS): The IRS is the primary agency responsible for investigating and prosecuting tax fraud. You can report suspected fraud online, by phone, or by mail.
- IRS Website: [Insert IRS website link]
- IRS Hotline: [Insert IRS hotline number]
- State Tax Agencies: Each state has its own tax agency responsible for enforcing state tax laws. You should report suspected tax fraud to both the IRS and your state tax agency.
- [Insert State Tax Agency Website Link]
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC): The FTC is responsible for combating identity theft and fraud. You can report identity theft to the FTC online or by phone.
- FTC Website: [Insert FTC website link]
- FTC Hotline: [Insert FTC hotline number]
- Local Law Enforcement: Local law enforcement agencies may also investigate and prosecute tax fraud cases. You can report suspected fraud to your local police department or sheriff’s office.
Tax Changes and Updates
Staying informed about changes in tax laws and regulations is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Understanding recent updates and potential future changes can help you make informed decisions about your financial planning and tax compliance.
Looking for the best CD rates? Check out the PNC Bank Cd Rates October 2023 for some great options.
Recent Tax Law Changes
Recent tax law changes have impacted various aspects of taxation, including individual income taxes, business taxes, and estate taxes.
- Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017:This act significantly altered the tax code, lowering individual and corporate tax rates, expanding the standard deduction, and making changes to the child tax credit. The TCJA also introduced new limitations on deductions, such as the deduction for state and local taxes.
- American Rescue Plan Act of 2021:This act provided economic relief during the COVID-19 pandemic, including enhanced unemployment benefits, stimulus payments, and tax credits for child care and dependent care.
- Inflation Reduction Act of 2022:This act focuses on climate change and healthcare, including provisions related to clean energy, prescription drug pricing, and health insurance subsidies. It also includes some tax changes, such as increased taxes on corporations and high-income earners.
Potential Future Tax Policy Changes
Predicting future tax policy changes can be challenging, but some potential areas of focus include:
- Tax Reform:There is ongoing debate about potential tax reform measures, including simplifying the tax code, addressing income inequality, and increasing revenue for government programs.
- Climate Change Policies:As concerns about climate change grow, there may be increased focus on policies that encourage green energy and sustainable practices, potentially including tax incentives or penalties.
- Digital Economy Taxes:The rapid growth of the digital economy has led to discussions about how to tax companies that operate primarily online, such as tech giants.
Staying Informed about Tax Updates
Staying up-to-date on tax changes is essential for individuals and businesses. Several resources can help you stay informed:
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS):The IRS website (www.irs.gov) provides official tax information, including news releases, publications, and guidance on tax laws and regulations.
- Tax Professionals:Consulting with a qualified tax professional, such as a certified public accountant (CPA) or an enrolled agent (EA), can provide personalized advice and ensure you are compliant with current tax laws.
- Tax News Websites and Publications:Several websites and publications, such as the Tax Foundation, the Tax Policy Center, and Bloomberg Tax, offer in-depth analysis and commentary on tax policy and legislation.
15. Tax Planning for the Future
As you start thinking about your long-term financial goals, it’s crucial to consider how taxes will play a role in achieving them. Proactive tax planning can significantly reduce your overall tax burden and maximize your financial resources, allowing you to reach your goals faster.
Long-Term Tax Planning Strategies
Proactive tax planning involves making strategic financial decisions to minimize your tax liability over time. By understanding the tax implications of different financial choices, you can optimize your financial position and maximize your wealth-building potential.
- Tax-Advantaged Investment Accounts:Utilizing tax-advantaged investment accounts, such as 401(k)s, Roth IRAs, and Traditional IRAs, can offer significant tax benefits.
- Tax-Loss Harvesting:This strategy involves selling losing investments to offset capital gains and reduce your tax liability.
- Asset Diversification:By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can mitigate risk and potentially reduce your tax exposure.
- Charitable Giving:Making charitable donations can provide tax deductions and contribute to a worthy cause.
Tax-Advantaged Investment Accounts
Here’s a table summarizing the key features of popular tax-advantaged investment accounts:
| Account Type | Contributions | Tax Treatment | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 401(k) | Pre-tax contributions | Tax deferred | Employees of participating employers |
| Roth IRA | After-tax contributions | Tax-free withdrawals in retirement | Individuals with lower incomes |
| Traditional IRA | Pre-tax contributions | Tax deductible, taxed in retirement | Individuals with higher incomes |
Tax Considerations in Financial Planning, Taxes Due October
Incorporating tax considerations into your financial planning is essential for maximizing your long-term financial success. Here are some key areas to consider:
- Retirement Planning:Strategic tax planning can help you maximize your retirement savings and minimize your tax liability during retirement.
- Estate Planning:Estate planning strategies can help you minimize estate taxes and ensure your assets are distributed according to your wishes.
- Real Estate Investments:Real estate investments can offer tax advantages, but it’s important to understand the tax implications of owning and selling property.
“Long-term tax planning is not just about saving money on taxes; it’s about maximizing your financial potential and achieving your long-term goals.”
[Financial Expert Name]
Conclusion
Navigating the tax landscape in October can be a daunting task, but with proper planning and preparation, it can be managed effectively. By understanding the different types of taxes due, their deadlines, and the potential consequences of non-compliance, you can minimize your tax liability and maintain financial stability.
Remember, seeking professional advice from a qualified tax advisor can provide personalized guidance and ensure that you’re taking advantage of all available tax benefits. So, take charge of your tax obligations, plan ahead, and approach October’s tax deadlines with confidence.
User Queries
What are the common types of taxes due in October?
Common taxes due in October include estimated income taxes for individuals and corporations, property taxes, excise taxes (like those on alcohol and tobacco), and certain business taxes. The specific types of taxes due may vary depending on your location and circumstances.
What are the consequences of missing a tax deadline in October?
Missing a tax deadline can result in penalties, including late payment fees, interest charges, and potential legal repercussions. The severity of the penalties can vary depending on the type of tax and the amount of time you are late.
It’s crucial to prioritize timely tax compliance to avoid these financial burdens.
How can I avoid late payment penalties?
To avoid late payment penalties, it’s essential to plan ahead and ensure that you have the necessary funds to cover your tax obligations. Make estimated tax payments throughout the year to avoid a large lump sum payment in October.
Consider using tax planning strategies like maximizing deductions and credits to reduce your overall tax liability. And remember, consulting with a tax professional can provide valuable insights and help you create a personalized tax plan.












