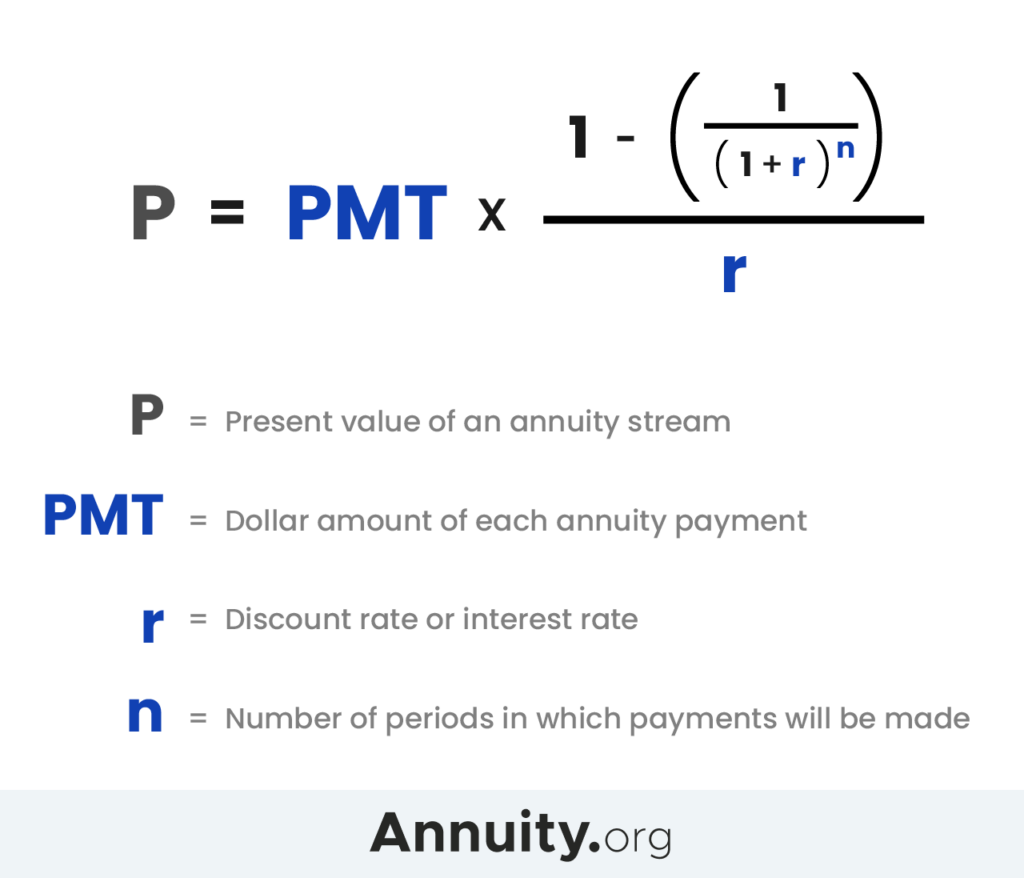
Annuity Exclusion Ratio 2024 is a crucial factor in retirement planning, determining how much of your annuity payments are tax-free. This ratio, calculated based on your age and the annuity’s interest rate, influences your retirement income and tax liability. Understanding the Annuity Exclusion Ratio is essential for maximizing your retirement savings and ensuring a comfortable financial future.
Google Tasks is a great way to stay organized in 2024. This article provides a guide to using it effectively: Google Tasks 2024: How to Use Google Tasks Effectively. It offers tips and tricks to maximize its potential and boost your productivity.
This guide delves into the concept of the Annuity Exclusion Ratio, explaining its purpose, calculation, and key factors influencing its value. We’ll also explore its implications for retirement income planning, analyze any changes for 2024, and provide real-world examples to illustrate its practical application.
Dollify has been making waves in 2024. If you’re curious about its latest updates and changes, check out this article: Dollify 2024: What’s New and Different. It highlights the new features, improvements, and unique aspects of the app.
Contents List
Annuity Exclusion Ratio: A Comprehensive Guide
Annuities are a popular retirement planning tool that provides a steady stream of income for life. However, understanding the tax implications of annuities is crucial to maximizing your retirement income. One important concept to grasp is the Annuity Exclusion Ratio, which determines the portion of your annuity payments that is tax-free.
Security is paramount in 2024, especially for Android WebView. This article focuses on the latest security updates: Android WebView 202 security updates. It highlights the vulnerabilities addressed and the importance of staying up-to-date.
This guide will provide a detailed explanation of the Annuity Exclusion Ratio, its calculation, influencing factors, implications, and how it applies in 2024.
Annuity concepts can be complex. This article tackles the topic through a multiple-choice question format: Annuity Is A Mcq 2024. It’s a great way to test your knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of this financial instrument.
Annuity Exclusion Ratio: Definition and Purpose
The Annuity Exclusion Ratio is a crucial element in retirement planning, as it directly impacts the taxability of your annuity payments. It represents the portion of each annuity payment that is considered a return of your original investment (principal) and therefore not subject to income tax.
Annuity investments have become a popular topic in 2024. If you’re wondering if they’re a good fit for you, this article can provide some insight: Annuity Is It A Good Investment 2024. It explores the advantages and disadvantages of annuities, helping you decide if they’re a smart move for your portfolio.
The remaining portion, which represents the interest earned on your investment, is taxable.
Annuity definitions can be confusing. This article provides a clear explanation in a multiple-choice format: Annuity Is Defined As Mcq 2024. It’s a simple way to learn the basics and get a grasp of the key concepts.
Calculation of the Annuity Exclusion Ratio
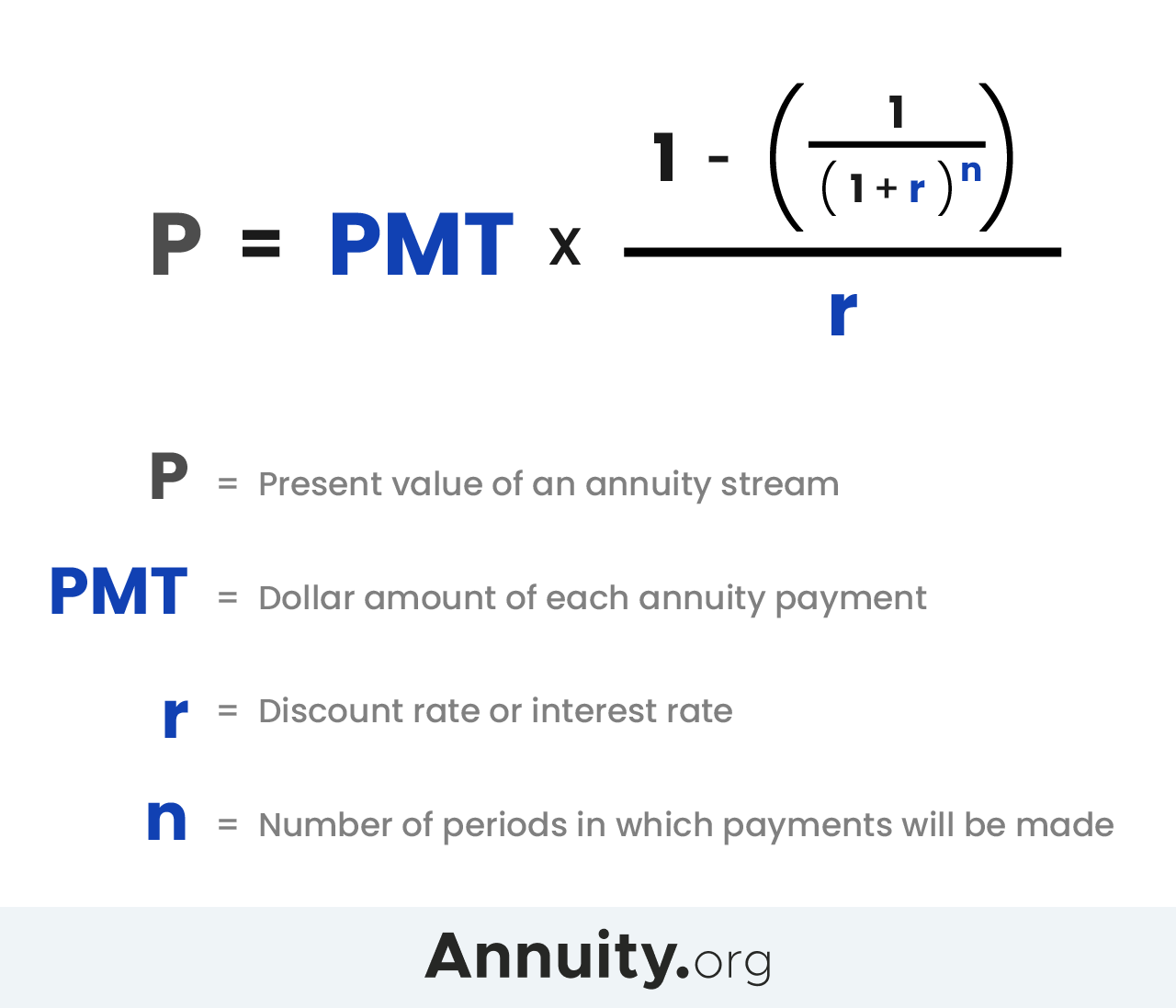
The Annuity Exclusion Ratio is calculated using a simple formula that considers the total amount invested in the annuity (principal) and the expected total annuity payments over the annuity’s lifetime.
Snapdragon is bringing its power to tablets in 2024. Discover how it’s enhancing the tablet experience: Snapdragon 2024 for tablets. It details the benefits of Snapdragon’s technology for tablets, including improved performance, battery life, and features.
Annuity Exclusion Ratio = Principal / Expected Total Annuity Payments
Android WebView is a powerful tool, but it’s essential to follow best practices in 2024. This article provides guidance on how to do just that: Android WebView 202 best practices. It outlines the key considerations and strategies for maximizing security and performance.
For instance, if you invested $100,000 in an annuity and are expected to receive $200,000 in total payments over the annuity’s lifetime, your Annuity Exclusion Ratio would be 0.5 or 50%. This means that 50% of each annuity payment would be considered a return of your original investment and therefore tax-free, while the remaining 50% would be taxable.
Annuity drawdown is a common question in 2024. If you’re considering this option, this article offers some valuable information: Is Annuity Drawdown 2024. It explains how annuity drawdown works and explores its potential benefits and drawbacks.
Factors Affecting the Annuity Exclusion Ratio
- Interest Rates:Higher interest rates generally result in a lower Annuity Exclusion Ratio. This is because a higher interest rate means a larger portion of each payment is considered interest income, which is taxable.
- Inflation:Inflation can also affect the Annuity Exclusion Ratio. If inflation is high, the purchasing power of your annuity payments may decrease over time, leading to a lower Annuity Exclusion Ratio. This is because the total amount you receive from the annuity may not be sufficient to cover the original investment, resulting in a larger portion of each payment being considered interest income.
Snapdragon’s latest chips are packed with AI and machine learning capabilities, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in 2024. Discover more about these advancements: Snapdragon 2024 AI and machine learning capabilities. It delves into the specific features and applications of Snapdragon’s AI technology.
- Annuity Type:The type of annuity you choose can also influence the Annuity Exclusion Ratio. Fixed annuities typically have a lower Annuity Exclusion Ratio than variable annuities, as fixed annuities generally have a lower interest rate.
Implications of the Annuity Exclusion Ratio
The Annuity Exclusion Ratio has significant implications for your retirement income planning. It directly impacts the taxability of your annuity payments, which can affect your overall retirement income and tax liability.
Deciding between an annuity and a 401k can be tough, especially in 2024. To help you make the best choice, check out this article: Is Annuity Better Than 401k 2024. It breaks down the pros and cons of each, giving you a clearer understanding of which option might be better for your individual situation.
- Taxability of Annuity Payments:The Annuity Exclusion Ratio determines the portion of each annuity payment that is subject to income tax. A higher exclusion ratio means a smaller portion of your payments will be taxed, leading to lower tax liability in retirement.
- Retirement Income Planning:Understanding the Annuity Exclusion Ratio is crucial for accurate retirement income planning. By factoring in the tax implications of your annuity payments, you can create a more realistic budget and ensure you have enough income to meet your retirement needs.
- Optimizing Retirement Income Strategies:The Annuity Exclusion Ratio can be used to optimize your retirement income strategies. For example, if you have a high exclusion ratio, you may consider withdrawing more from your annuity in retirement to take advantage of the tax-free portion of your payments.
Conversely, if your exclusion ratio is low, you may want to withdraw less from your annuity to minimize your tax liability.
Annuity Exclusion Ratio in 2024
The Annuity Exclusion Ratio is not subject to annual changes or updates. It remains consistent based on the original investment amount and expected total payments, as determined at the time the annuity is purchased. However, it’s important to consult with a financial advisor to understand the potential tax implications of your specific annuity contract and how it may be affected by changes in interest rates, inflation, or other economic factors.
Examples and Case Studies, Annuity Exclusion Ratio 2024
| Case | Annuity Type | Exclusion Ratio | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| John, age 65, invested $200,000 in a fixed annuity and expects to receive $400,000 in total payments. | Fixed Annuity | 50% | John will receive $200,000 in tax-free payments and $200,000 in taxable payments over the life of the annuity. |
| Mary, age 62, invested $150,000 in a variable annuity and expects to receive $300,000 in total payments. | Variable Annuity | 50% | Mary will receive $150,000 in tax-free payments and $150,000 in taxable payments over the life of the annuity. |
Epilogue
The Annuity Exclusion Ratio is a complex but vital aspect of retirement planning. By understanding its intricacies, you can make informed decisions about your retirement income strategies, optimize your tax benefits, and ensure a financially secure future. As the ratio evolves with changes in interest rates and other economic factors, staying informed is crucial for maximizing your retirement savings.
Clarifying Questions: Annuity Exclusion Ratio 2024
How often is the Annuity Exclusion Ratio updated?
The Annuity Exclusion Ratio is typically updated annually, reflecting changes in interest rates and other economic factors.
Does the Annuity Exclusion Ratio apply to all types of annuities?
Yes, the Annuity Exclusion Ratio applies to all types of annuities, but the specific calculation may vary depending on the annuity’s terms.
Can I change my Annuity Exclusion Ratio after I purchase an annuity?
No, the Annuity Exclusion Ratio is determined at the time of annuity purchase and cannot be changed later.
While annuities can be a valuable investment, some argue that they’re not always the best choice in 2024. Explore this perspective in this article: Annuity Is Bad 2024. It examines the potential drawbacks and risks associated with annuities.
Kathy’s annuity is facing challenges in 2024. Learn more about her experience and the potential causes: Kathy’s Annuity Is Currently Experiencing 2024. It provides a real-world example of the complexities and uncertainties that can arise with annuities.
If you’re looking for a flexible side hustle in 2024, becoming a Glovo app delivery driver could be a good option. This article provides a guide on how to get started: How to become a Glovo app delivery driver.
It outlines the steps and requirements for joining the Glovo platform.
Annuity is a complex financial product. This article provides a concise explanation of what it is: Annuity Is What 2024. It defines annuity and explains its core features and functions.