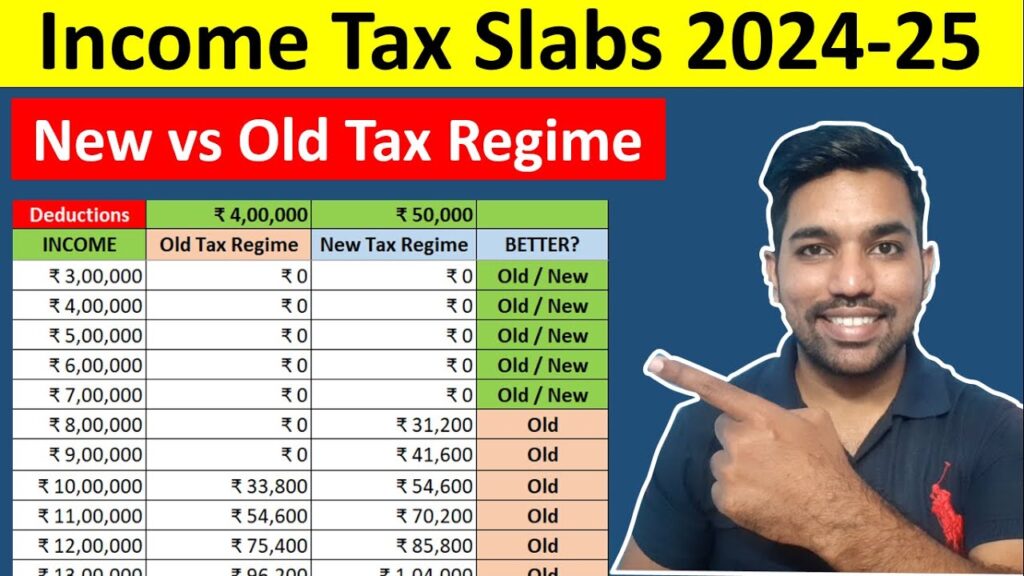
Is Annuity Income Taxable In India 2024? This question arises for many individuals seeking financial security during retirement. Annuities, a popular financial instrument in India, offer a steady stream of income after retirement, but understanding their tax implications is crucial for effective financial planning.
Android app development is a rapidly growing field, and understanding the specific needs of different industries is crucial for success. This article about Android app development for specific industries in 2024 explores the unique challenges and opportunities in various sectors, providing valuable insights for developers.
Annuities in India are financial contracts where an individual pays a lump sum or a series of premiums to an insurance company or financial institution. In return, the insurer promises to provide a regular stream of payments, either for a fixed period or for the lifetime of the annuitant.
Dollify is a popular app for creating cute cartoon avatars, but if you’re looking for alternatives, there are many other options available. You can explore some of the best Dollify alternatives, including their features and pros and cons, in this article about Dollify 2024: The Best Dollify 2024 Alternatives.
These payments can be used to supplement retirement income, provide financial security for dependents, or simply create a steady stream of income for various needs.
Annuity funds are a type of investment that provides a stream of income for a specified period. If you’re interested in learning more about these funds, this article about Annuity Fund Is 2024 provides a comprehensive overview of their workings and potential benefits.
Contents List
- 1 Introduction to Annuities in India
- 2 Taxability of Annuity Income
- 3 Tax Deductions and Exemptions for Annuity Income
- 4 Tax Implications of Different Annuity Types: Is Annuity Income Taxable In India 2024
- 5 Tax Planning Strategies for Annuity Income
- 6 Case Studies and Examples
- 7 Final Wrap-Up
- 8 Question & Answer Hub
Introduction to Annuities in India
Annuity is a financial product that provides a stream of regular payments for a specified period of time. In India, annuities are popular retirement planning tools, offering individuals a guaranteed income stream during their golden years. This article will delve into the intricacies of annuities in India, covering their purpose, types, regulatory framework, and most importantly, their tax implications.
To understand how annuities work in real-world scenarios, it’s helpful to see them in action. This article about Annuity Examples In Real Life 2024 provides practical examples of how annuities can be used to meet different financial goals.
Types of Annuities
Annuities in India come in various forms, each catering to different financial needs and risk appetites. The most common types include:
- Immediate Annuities:Payments start immediately after the purchase of the annuity. These are suitable for individuals seeking an immediate income stream.
- Deferred Annuities:Payments commence at a later date, often after a specified period. These are ideal for individuals who wish to delay their income stream, potentially allowing for greater accumulation of funds.
- Fixed Annuities:Offer guaranteed fixed payments throughout the annuity period. These provide stability and predictability of income.
- Variable Annuities:Payments are linked to the performance of underlying investments, offering potential for higher returns but also carrying greater risk.
Regulatory Framework, Is Annuity Income Taxable In India 2024
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) regulates the annuity market in India. IRDAI sets guidelines for annuity products, including their features, pricing, and distribution.
If you’re encountering issues with your Android apps after updating to WebView 202, you’re not alone. Many users have reported problems, and you can find detailed information and potential solutions on this article about Android WebView 202 compatibility issues.
It’s worth checking out if you’re experiencing any unexpected behavior.
Taxability of Annuity Income
The tax treatment of annuity income in India is governed by the Income Tax Act, 1961. Understanding the tax implications is crucial for individuals planning to invest in annuities.
Taxation of Annuity Income
Annuity income is taxed under the ‘Income from other sources’ category. The taxability of annuity payments depends on the phase of the annuity: the accumulation phase and the payout phase.
- Accumulation Phase:During the accumulation phase, where premiums are paid into the annuity, the premiums are generally not tax-deductible. However, any interest or investment income earned on the accumulated funds is taxable as per the prevailing tax laws.
- Payout Phase:When annuity payments are received, a portion of the payment is considered as a return of capital and is not taxable. The remaining portion, representing the interest or investment income earned, is taxed as income from other sources.
Relevant Sections and Provisions
The following sections of the Income Tax Act, 1961, are relevant to the taxation of annuity income:
- Section 56(2)(x):This section deals with the taxability of capital gains arising from the redemption of annuity contracts.
- Section 57:This section provides for the computation of income from other sources, including annuity income.
- Section 194D:This section requires the payer of annuity income to deduct TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) at the applicable rate.
Tax Deductions and Exemptions for Annuity Income
While annuity income is generally taxable, certain deductions and exemptions can help reduce the tax liability. These provisions aim to encourage retirement planning and provide relief to individuals receiving annuity payments.
Dollify is constantly evolving, with new features and updates being released regularly. If you’re a Dollify user, you can learn about the latest additions, including new customization options and improvements, in this article about Dollify 2024: New Features and Updates.
Deductions and Exemptions
Here are some tax deductions and exemptions available for annuity income:
- Section 80C:This section allows for a deduction of up to ₹1.5 lakhs on investments in various instruments, including certain types of annuity plans. The deduction is available for the premium paid during the accumulation phase.
- Section 80D:This section provides a deduction for health insurance premiums paid. If the annuity plan includes a health insurance component, the premium paid for this component may be eligible for a deduction under this section.
Conditions and Limitations
It is important to note that deductions and exemptions are subject to certain conditions and limitations. These include:
- Eligibility Criteria:Specific eligibility criteria may apply to each deduction or exemption, such as the age of the individual or the type of annuity plan.
- Maximum Limits:The amount of deduction or exemption may be capped at a certain limit. For example, the deduction under Section 80C is limited to ₹1.5 lakhs per financial year.
- Documentation Requirements:Individuals claiming deductions or exemptions need to provide relevant documentation to support their claims.
Tax Implications of Different Annuity Types: Is Annuity Income Taxable In India 2024
The tax implications of annuity income can vary depending on the type of annuity. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Annuities are often referred to by other names, which can be confusing. This article about Annuity Is Also Known As 2024 clarifies the different terms used for annuities and their meanings.
Immediate vs. Deferred Annuities
- Immediate Annuities:Tax treatment is generally similar for immediate and deferred annuities, with the income being taxed as ‘Income from other sources’ during the payout phase. However, the timing of the tax liability differs. For immediate annuities, tax is payable as and when the payments are received.
Annuities are considered a type of life insurance product, but they have unique characteristics. This article about Annuity Is A Life Insurance Product That 2024 explains how annuities differ from traditional life insurance policies and their specific features.
In contrast, for deferred annuities, tax is payable when payments begin, which may be at a later date.
- Deferred Annuities:The tax treatment of deferred annuities depends on the type of investment chosen for the accumulation phase. If the investments are in equity-linked instruments, the capital gains arising from the redemption of these instruments may be subject to long-term capital gains tax at a concessional rate.
Annuity Gator is a popular online platform for comparing and purchasing annuities. If you’re considering using their services, this article about Is Annuity Gator Legit 2024 provides insights into their legitimacy and reputation.
Fixed vs. Variable Annuities
- Fixed Annuities:The tax treatment of fixed annuities is relatively straightforward. The interest component of the annuity payments is taxed as income from other sources. However, the return of capital portion is not taxable.
- Variable Annuities:The tax implications of variable annuities are more complex. The growth in the underlying investments is subject to capital gains tax. If the investments are held for more than a year, the capital gains are taxed at a concessional rate.
However, if the investments are held for less than a year, the capital gains are taxed at a higher rate.
Annuity Payments from Different Sources
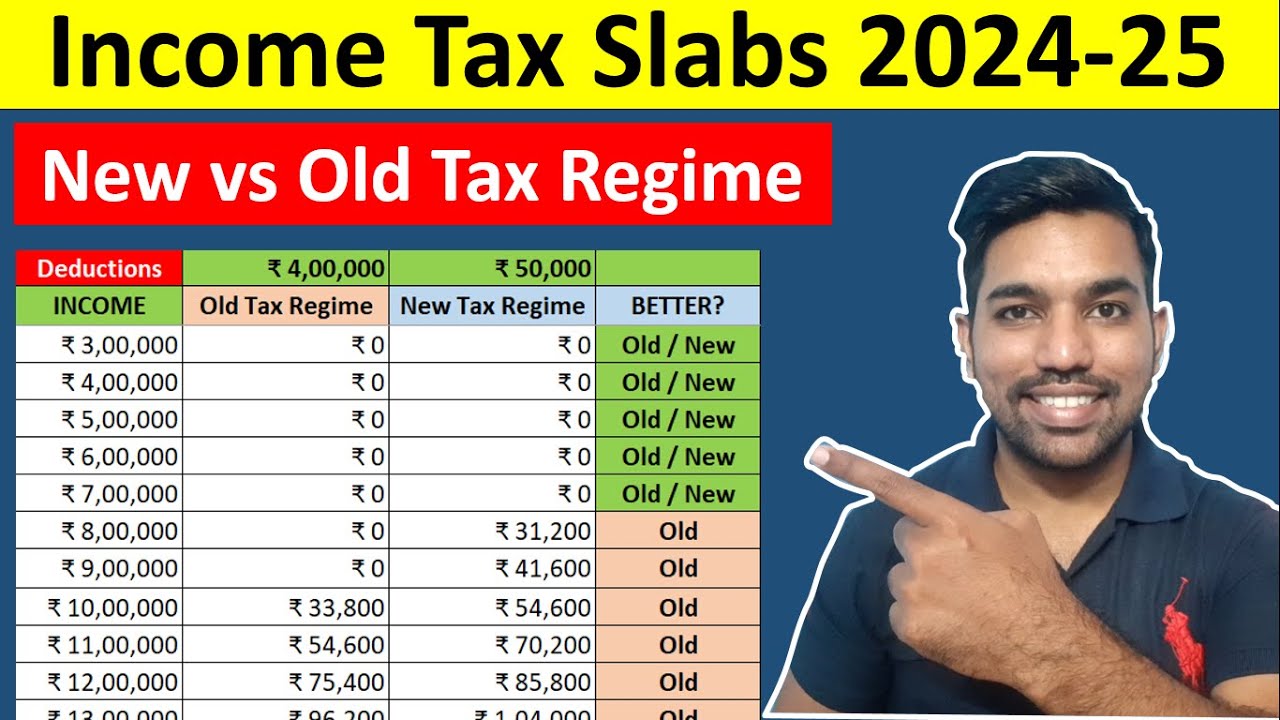
The tax treatment of annuity payments can also vary depending on the source of the payments.
The metaverse is a rapidly developing technology with significant potential for Android app development. This article about Android app development for the metaverse in 2024 explores the opportunities and challenges of building apps for this emerging virtual world.
- Life Insurance Companies:Annuity payments received from life insurance companies are generally taxed as ‘Income from other sources’.
- Banks:Annuity payments received from banks may be subject to TDS at the applicable rate. The TDS is adjusted against the individual’s total tax liability at the end of the financial year.
Annuitization of Pension Funds or Retirement Savings
Annuitizing pension funds or other retirement savings can have tax implications. The tax treatment depends on the specific scheme and the type of annuity chosen.
The annuity exclusion ratio is a key factor in determining the taxable portion of annuity payments. This article about Annuity Exclusion Ratio 2024 explains how to calculate the exclusion ratio and its implications for tax purposes.
- National Pension System (NPS):NPS allows individuals to choose an annuity option at retirement. The annuity payments are generally taxed as ‘Income from other sources’. However, the tax treatment of the lump sum withdrawal from NPS is different and depends on the specific rules applicable to NPS.
- Provident Fund (PF):If an individual chooses to annuitize their PF accumulations, the annuity payments are generally taxed as ‘Income from other sources’.
Tax Planning Strategies for Annuity Income
Effective tax planning can help individuals minimize their tax liability on annuity income. By understanding the tax rules and available strategies, individuals can optimize their retirement income.
Annuity due is a specific type of annuity where payments are made at the beginning of each period. This article about Annuity Due Is 2024 provides a detailed explanation of annuity due, its calculations, and its differences from other annuity types.
Strategies for Minimizing Tax Liability
Here are some tax planning strategies for annuity income:
- Utilize Tax Deductions and Exemptions:Maximize the use of available deductions and exemptions, such as those under Sections 80C and 80D, to reduce taxable income.
- Consider Deferred Annuities:For individuals with a longer time horizon, deferred annuities can be beneficial. The growth of the accumulated funds during the deferral period is typically tax-deferred, allowing for potential tax savings.
- Invest in Tax-Efficient Options:When choosing an annuity plan, consider the tax implications of the underlying investments. Invest in tax-efficient options, such as equity-linked instruments, to potentially minimize capital gains tax liability.
- Spread Out Income:If possible, consider spreading out annuity payments to reduce the tax bracket and minimize the overall tax liability.
- Seek Professional Tax Advice:Consult with a qualified tax advisor to understand the specific tax implications of your annuity plan and to develop personalized tax planning strategies.
Tax-Efficient Investment Options
Here are some tax-efficient investment options for annuity proceeds:
- Equity Mutual Funds:Long-term capital gains from equity mutual funds are taxed at a concessional rate of 10% if held for more than a year.
- Debt Mutual Funds:Interest income from debt mutual funds is taxed at the individual’s applicable tax slab rate.
- Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS):SCSS offers a fixed interest rate and tax benefits for senior citizens. The interest income is taxed at the individual’s applicable tax slab rate.
Case Studies and Examples
To illustrate the tax implications of different annuity scenarios, let’s consider some hypothetical examples.
Annuities can be complex financial products, and it’s important to understand the potential risks and challenges involved. This article about Annuity Issues 2024 explores some of the common issues and concerns associated with annuities.
Hypothetical Scenarios
- Scenario 1:Mr. Sharma, aged 60, purchases an immediate fixed annuity of ₹10 lakhs. The annuity provides a monthly payment of ₹10,000 for a period of 10 years. In this scenario, Mr. Sharma would be required to pay tax on the interest component of the annuity payments as ‘Income from other sources’.
Designing a user-friendly Android app is crucial for its success. This article about How to design a user-friendly Android app in 2024 provides valuable tips and strategies for creating apps that are intuitive, engaging, and easy to navigate.
The return of capital portion would be exempt from tax.
- Scenario 2:Ms. Patel, aged 55, invests in a deferred variable annuity of ₹5 lakhs. The annuity is linked to the performance of a particular equity fund. After 5 years, Ms. Patel receives monthly payments of ₹15,000 for a period of 10 years.
Fixed annuities can be a valuable tool for retirement planning, and there are specific rules and considerations for using them within an IRA. This article about Fixed Annuity In Ira 2024 explores the benefits, drawbacks, and tax implications of this strategy.
In this scenario, Ms. Patel would be required to pay tax on the capital gains earned on the underlying equity fund investments. The tax rate would depend on the holding period of the investments.
Table Showing Different Annuity Types and Tax Treatments
| Annuity Type | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|
| Immediate Fixed Annuity | Interest component taxed as ‘Income from other sources’. Return of capital exempt from tax. |
| Deferred Fixed Annuity | Interest component taxed as ‘Income from other sources’. Return of capital exempt from tax. |
| Immediate Variable Annuity | Capital gains on underlying investments taxed at applicable rate. Interest component taxed as ‘Income from other sources’. Return of capital exempt from tax. |
| Deferred Variable Annuity | Capital gains on underlying investments taxed at applicable rate. Interest component taxed as ‘Income from other sources’. Return of capital exempt from tax. |
Case Study: Tax Liability of an Individual Receiving an Annuity
Let’s consider a case study of Mr. Gupta, aged 62, who receives an immediate fixed annuity of ₹20 lakhs from a life insurance company. The annuity provides a monthly payment of ₹20,000 for a period of 15 years. Assuming Mr.
Gupta’s tax slab rate is 30%, his annual tax liability on the annuity income would be calculated as follows:
- Annual Annuity Income:₹20,000 x 12 = ₹2,40,000
- Taxable Interest Component:Assuming a hypothetical interest rate of 5% per annum, the taxable interest component would be ₹2,40,000 x 5% = ₹12,000.
- Tax Liability:₹12,000 x 30% = ₹3,600.
In this case, Mr. Gupta would be required to pay ₹3,600 in taxes on his annuity income.
Final Wrap-Up
Navigating the taxability of annuity income in India requires careful consideration of the specific type of annuity, the source of the payments, and the individual’s overall financial situation. Consulting a tax professional can provide tailored advice and help you develop effective tax planning strategies to maximize your retirement income and minimize your tax liability.
Remember, staying informed about the latest tax regulations and seeking professional guidance is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Question & Answer Hub
How is annuity income taxed in India?
Annuity income is generally taxed as per the applicable income tax slab rates in India. The taxability depends on whether the annuity is received during the accumulation phase or the payout phase.
Are there any tax deductions or exemptions available for annuity income?
Yes, certain deductions and exemptions are available under the Indian Income Tax Act. These may include deductions for premiums paid during the accumulation phase or exemptions for specific types of annuities. It’s important to consult with a tax professional to understand your specific eligibility.
What are the tax implications of annuitizing a pension fund?
Annuitizing a pension fund can have tax implications depending on the type of pension fund and the terms of annuitization. Consult with a tax professional to determine the specific tax treatment in your situation.