Loan To Value, often abbreviated as LTV, sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a crucial aspect of lending and borrowing. LTV is a simple yet powerful concept that reveals the relationship between the loan amount and the value of the asset being financed.
It plays a pivotal role in determining loan terms, risk assessment, and even the borrower’s financial stability.
Understanding LTV is essential for both borrowers and lenders, as it helps to clarify the dynamics of a loan agreement. This exploration delves into the intricacies of LTV, examining its influence on interest rates, loan eligibility, and the overall cost of borrowing.
For those looking to buy a home, understanding ARM Mortgage Rates is crucial. These rates can fluctuate over time, potentially affecting your monthly payments.
Contents List
- 1 Loan-to-Value (LTV): A Comprehensive Guide
- 1.1 Loan-to-Value (LTV) Definition
- 1.2 LTV Impact on Loan Terms, Loan To Value
- 1.3 LTV and Loan Types
- 1.4 LTV and Risk Assessment
- 1.5 LTV and Borrower Equity
- 1.6 LTV and Loan Repayment
- 1.7 LTV and Real Estate Transactions
- 1.8 LTV and Financial Stability
- 1.9 LTV and Market Trends
- 1.10 LTV and Future Considerations
- 2 Conclusive Thoughts
- 3 Questions and Answers: Loan To Value
Loan-to-Value (LTV): A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of lending and borrowing, understanding the concept of Loan-to-Value (LTV) is crucial for both borrowers and lenders. LTV is a fundamental metric that plays a significant role in determining loan terms, risk assessment, and ultimately, the borrower’s financial stability.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of LTV, providing insights into its definition, impact on loan terms, application across different loan types, and its implications for both borrowers and lenders.
Securing a Home Mortgage is a significant financial decision. Make sure to explore different loan options and compare rates before committing.
Loan-to-Value (LTV) Definition
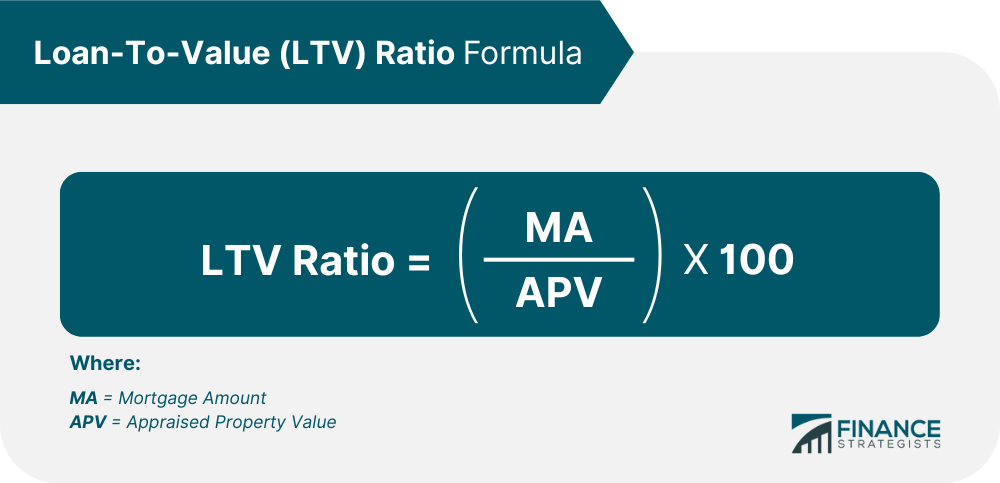
Loan-to-Value (LTV) is a financial ratio that expresses the amount of a loan as a percentage of the value of the asset being purchased or used as collateral. In simpler terms, it indicates the proportion of the asset’s value that is financed by the loan.
A higher LTV ratio implies a larger loan amount relative to the asset’s value, while a lower LTV ratio signifies a smaller loan amount.
For instance, if you are taking out a mortgage loan of $200,000 to purchase a property valued at $250,000, your LTV would be 80% (Loan Amount/Asset Value = $200,000/$250,000 = 0.8 or 80%).
In a pinch? Get A Loan Today offers a quick and convenient way to access funds, but it’s important to compare options and understand the associated costs.
The significance of LTV lies in its ability to reflect the risk associated with a loan. A higher LTV ratio generally translates to a higher risk for lenders, as there is a greater potential for losses in case of default.
Conversely, a lower LTV ratio suggests a lower risk, as the borrower has a larger stake in the asset, reducing the lender’s exposure to potential losses.
LTV Impact on Loan Terms, Loan To Value
LTV exerts a considerable influence on various loan terms, including interest rates, eligibility criteria, and loan-to-value ratios.
Interest Rates
Lenders typically offer lower interest rates on loans with lower LTV ratios. This is because lower LTV loans represent a lower risk for lenders, as the borrower has a larger equity stake in the asset. Conversely, higher LTV loans often come with higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk associated with larger loan amounts.
Bank of America offers a variety of loan products, including personal loans and mortgages. If you’re a Bank of America customer, Bank Of America Loan options might be worth exploring.
Loan Eligibility Criteria
LTV plays a crucial role in determining loan eligibility. Lenders often have specific LTV requirements for different loan types, and borrowers must meet these criteria to qualify for a loan. For instance, a mortgage lender may require an LTV of 80% or less for conventional loans, while non-conventional loans may have higher LTV limits.
Loan-to-Value Ratios
LTV directly impacts the loan-to-value ratio, which is a measure of the loan amount as a percentage of the asset’s value. A higher LTV ratio signifies a larger loan amount relative to the asset’s value, while a lower LTV ratio indicates a smaller loan amount.
If you’re looking for a quick cash solution, Small Payday Loans can provide temporary relief. However, remember these loans often come with high interest rates and should be used with caution.
LTV and Loan Types
LTV ranges vary significantly across different loan types, reflecting the specific risks and characteristics of each loan category.
Mortgages
Mortgages typically have LTV ratios ranging from 80% to 95%, depending on the loan type and lender’s policies. Conventional loans often have LTV limits of 80% or less, while non-conventional loans, such as FHA loans, may allow for higher LTVs, up to 96.5%.
Auto Loans
Auto loans typically have LTV ratios ranging from 100% to 120%, with higher LTVs being more common for used cars. LTV ratios in auto loans reflect the depreciation value of the vehicle over time.
Marcus Loans are known for their competitive rates and transparent terms. If you’re seeking a personal loan with a reputable lender, Marcus Loans might be a good option.
Personal Loans
Personal loans, unlike secured loans, do not have a specific LTV ratio, as they are not secured against an asset. Lenders consider factors such as credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and income stability to assess risk and determine loan terms.
Before applying for a loan, it’s helpful to research different Lending Company options. Look for companies with transparent terms and competitive rates.
LTV and Risk Assessment
Lenders use LTV as a key indicator to assess the risk associated with a loan. A higher LTV ratio generally signals a higher risk for lenders, as there is a greater potential for losses in case of default. Conversely, a lower LTV ratio suggests a lower risk, as the borrower has a larger stake in the asset, reducing the lender’s exposure to potential losses.
When shopping for a new car, don’t forget to compare Auto Loan rates and terms. A good loan can save you money in the long run.
LTV plays a crucial role in determining loan approval and loan terms. Lenders may be more likely to approve loans with lower LTV ratios, as they perceive them as less risky. Additionally, loans with lower LTVs may attract more favorable interest rates and loan terms.
In the lending process, LTV is used to manage risk by ensuring that borrowers have sufficient equity in the asset to mitigate potential losses for lenders. For example, a lender may require a minimum down payment or set a maximum LTV limit to ensure that the borrower has a substantial stake in the asset.
CreditNinja is a reputable online lender that offers personal loans and installment loans. Creditninja is known for its quick approval process and flexible terms.
LTV and Borrower Equity
The relationship between LTV and borrower equity is inversely proportional. A higher LTV ratio implies a lower borrower equity, while a lower LTV ratio signifies a higher borrower equity.
High LTV
A high LTV ratio indicates that the borrower has a smaller equity stake in the asset, meaning they have borrowed a larger proportion of the asset’s value. This can expose the borrower to greater financial risk, as they have less financial cushion in case of a decline in the asset’s value or a default on the loan.
If you’re worried about your credit score, No Credit Check Loans might seem appealing. However, these loans usually come with higher interest rates and can have hidden fees.
Low LTV
A low LTV ratio signifies that the borrower has a larger equity stake in the asset, indicating they have borrowed a smaller proportion of the asset’s value. This generally provides greater financial security for the borrower, as they have more financial protection in case of a decline in the asset’s value or a default on the loan.
LTV and Loan Repayment
LTV can influence loan repayment terms and schedules, affecting the length of the loan repayment period and the overall cost of borrowing.
Need cash fast? Instant Cash Loans can provide quick access to funds, but remember to read the terms carefully before borrowing.
Loan Repayment Terms
Loans with higher LTV ratios may have longer repayment terms, as lenders may be more cautious in extending shorter-term loans with higher risk. Conversely, loans with lower LTV ratios may have shorter repayment terms, as lenders may be more comfortable with shorter-term loans due to the lower risk associated with higher borrower equity.
Loan Repayment Schedules
LTV can affect the loan repayment schedule by influencing the monthly payments. Higher LTV loans may have higher monthly payments, reflecting the higher interest rates and longer repayment terms associated with greater risk. Conversely, lower LTV loans may have lower monthly payments, reflecting the lower interest rates and shorter repayment terms associated with lower risk.
Overall Cost of Borrowing
LTV can influence the overall cost of borrowing by affecting interest rates and loan repayment terms. Higher LTV loans often come with higher interest rates and longer repayment terms, leading to higher overall borrowing costs. Conversely, lower LTV loans generally have lower interest rates and shorter repayment terms, resulting in lower overall borrowing costs.
Cash advances can be a lifesaver in emergencies, but be mindful of the high fees. Cash Advances are best used for short-term needs.
LTV and Real Estate Transactions
LTV plays a crucial role in real estate transactions, particularly in mortgage lending. It determines the amount of down payment required for a property purchase and influences the closing costs associated with the transaction.
When financing a high-value home, you’ll need to understand Jumbo Mortgage Rates. These rates can differ from traditional mortgage rates due to the larger loan amount.
Down Payment
LTV directly affects the down payment required for a property purchase. A higher LTV ratio signifies a larger loan amount, requiring a smaller down payment. Conversely, a lower LTV ratio implies a smaller loan amount, necessitating a larger down payment.
Closing Costs
LTV can influence the closing costs associated with real estate transactions. Higher LTV loans may have higher closing costs due to the larger loan amount and the associated fees and charges. Conversely, lower LTV loans may have lower closing costs due to the smaller loan amount and the associated fees and charges.
LTV and Financial Stability
LTV has a significant impact on borrower financial stability and risk management. A high LTV ratio can expose borrowers to greater financial risk, while a lower LTV ratio generally promotes financial stability.
High LTV Ratio
A high LTV ratio can increase the risk of financial distress for borrowers. If the value of the asset declines or the borrower experiences financial difficulties, they may face a higher risk of defaulting on the loan. This can lead to foreclosure or repossession of the asset, resulting in significant financial losses for the borrower.
Low LTV Ratio
A low LTV ratio can enhance borrower financial stability by providing a greater financial cushion. If the value of the asset declines, the borrower has a larger equity stake, reducing their risk of defaulting on the loan. This financial buffer can also provide greater flexibility in managing financial obligations and weathering economic fluctuations.
LTV and Market Trends
LTV ratios are influenced by prevailing market conditions, including interest rate fluctuations and economic cycles.
Private Mortgage Lenders can offer more flexible terms and faster approvals compared to traditional banks. Private Mortgage Lenders are a good option for those with unique financing needs.
Interest Rate Fluctuations
Interest rate fluctuations can affect LTV ratios. When interest rates rise, lenders may become more cautious, leading to stricter LTV requirements and potentially lower LTV limits. Conversely, when interest rates decline, lenders may become more lenient, allowing for higher LTV ratios.
Economic Cycles
Economic cycles can also impact LTV ratios. During periods of economic expansion, lenders may be more willing to accept higher LTV ratios, as the risk of default is perceived as lower. Conversely, during economic downturns, lenders may become more conservative, reducing LTV limits to mitigate risk.
LTV and Future Considerations
LTV is a dynamic concept that is likely to evolve in the future, influenced by emerging technologies, regulatory changes, and evolving lending practices.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), are transforming the lending landscape. These technologies can enhance risk assessment and automate lending processes, potentially leading to more flexible LTV requirements and customized loan terms.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes, such as new lending regulations and consumer protection laws, can impact LTV ratios. Regulatory bodies may introduce new guidelines or restrictions on LTV limits to protect borrowers and promote financial stability.
Evolving Lending Practices
Evolving lending practices, such as the rise of online lending platforms and alternative financing options, can influence LTV ratios. New lending models may introduce different risk assessment methods and LTV criteria, potentially leading to more flexible and innovative loan products.
Hard Money loans are often used for real estate investments. Hard Money lenders may offer faster approval but typically charge higher rates than traditional lenders.
Conclusive Thoughts
As we’ve journeyed through the landscape of Loan To Value, we’ve discovered its multifaceted nature. LTV is not merely a numerical calculation; it’s a powerful indicator of risk, financial stability, and the terms of a loan agreement. By understanding the nuances of LTV, borrowers can make informed decisions, while lenders can effectively manage their risk exposure.
Ultimately, LTV remains a cornerstone of responsible lending practices, ensuring a balanced and transparent financial landscape for all involved.
Questions and Answers: Loan To Value
What is the maximum LTV for a conventional mortgage?
The maximum LTV for a conventional mortgage typically ranges from 80% to 95%, depending on factors like credit score and loan type.
How does LTV affect my monthly mortgage payment?
A higher LTV generally leads to a larger loan amount, which in turn results in higher monthly payments.
What happens if my LTV exceeds the lender’s limit?
If your LTV exceeds the lender’s limit, you may be required to make a larger down payment or consider a different loan type with a higher LTV allowance.
Can I improve my LTV ratio?
Yes, you can improve your LTV by increasing your equity in the property. This can be achieved through paying down the loan principal or through appreciation in the property’s value.