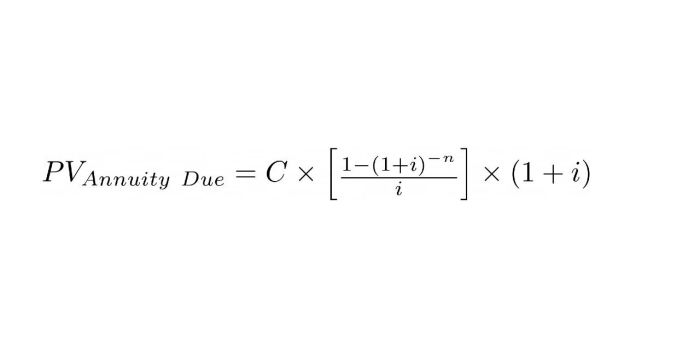Home Loan, a powerful financial tool, unlocks the dream of homeownership for countless individuals. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of securing a home loan, from understanding its basics to navigating the complexities of the buying process and managing your mortgage effectively.
From exploring the diverse loan options available to you, such as fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages, to understanding the key factors lenders consider when evaluating your application, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions throughout your homeownership journey.
Unlocking the equity in your home can provide access to funds for various purposes. Equity Release options allow you to leverage your home’s value, but it’s essential to understand the potential risks and implications.
Contents List
Home Loan Basics
A home loan, also known as a mortgage, is a loan that is secured by real estate. It allows individuals to purchase a home by borrowing money from a lender, typically a bank or mortgage company. The home serves as collateral for the loan, meaning the lender can claim ownership of the property if the borrower defaults on payments.
Looking for a flexible financing option? A Heloc (Home Equity Line of Credit) can offer a revolving line of credit secured by your home’s equity, providing access to funds as needed.
Types of Home Loans
There are various types of home loans available, each with its own features and terms. Some common types include:
- Fixed-Rate Mortgage:This loan offers a fixed interest rate for the entire loan term, ensuring consistent monthly payments. It provides stability and predictability, making it a popular choice for borrowers seeking long-term financial security.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM):An ARM features an interest rate that can change over time, typically tied to an index such as the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR). While initial interest rates may be lower than fixed-rate loans, ARMs can pose risks if interest rates rise significantly.
It is important to understand the potential for fluctuations and the loan’s interest rate adjustment terms before committing.
- Federal Housing Administration (FHA) Loan:Backed by the FHA, these loans are designed to make homeownership more accessible for borrowers with lower credit scores or limited down payments. They offer more lenient eligibility requirements and lower down payment options, typically 3.5%. However, FHA loans come with mortgage insurance premiums, which can increase overall borrowing costs.
Need a new car? Car Finance options can help you secure the financing you need, whether you’re buying new or used. Explore different loan terms and interest rates to find the best fit for your budget.
- Veterans Affairs (VA) Loan:VA loans are available to eligible veterans, active-duty military personnel, and surviving spouses. They offer no down payment requirements and typically have lower interest rates. VA loans are backed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, providing a guarantee to lenders and reducing their risk.
If you’re a veteran, a Va Loan can offer favorable terms for home financing, including no down payment requirements in some cases. Explore the benefits and eligibility criteria to see if this loan option is right for you.
Home Loan Application Process
The home loan application process typically involves the following steps:
- Pre-Approval:Getting pre-approved for a loan before searching for a home is crucial. It provides an estimate of the loan amount you qualify for, demonstrating your financial readiness to sellers and giving you a competitive edge in the market. It also helps you determine your budget and search for homes within your price range.
As a veteran, you may be eligible for a Va Home Loan , which offers favorable terms and benefits, including no down payment requirements in some cases.
- Loan Application:Once you find a home, you’ll need to submit a formal loan application to your chosen lender. This typically involves providing personal and financial information, including income, assets, debts, and credit history.
- Credit and Income Verification:Lenders will verify your credit history and income to assess your creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan. They may request documentation such as pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements.
- Property Appraisal:An appraisal is conducted to determine the fair market value of the property you’re buying. The appraisal helps ensure that the loan amount aligns with the property’s worth.
- Loan Underwriting:Underwriters review your loan application and supporting documentation to make a final decision on whether to approve your loan. They assess your creditworthiness, debt-to-income ratio, and overall financial profile.
- Loan Closing:Once your loan is approved, you’ll attend a closing meeting where you sign the loan documents and finalize the purchase of the property. This involves transferring ownership of the property to you and securing the mortgage.
Factors Considered by Lenders
Lenders consider several factors when evaluating loan applications, including:
- Credit Score:A higher credit score generally indicates a lower risk to lenders. A good credit score can lead to lower interest rates and more favorable loan terms.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI):This ratio measures your monthly debt payments compared to your gross monthly income. Lenders typically prefer a lower DTI, as it suggests you have more financial flexibility to manage loan payments.
- Income and Employment History:Lenders will verify your income and employment history to assess your ability to repay the loan. Stable income and a consistent work history are important factors.
- Down Payment:The amount of down payment you can afford will affect your loan amount and monthly payments. A larger down payment generally results in lower monthly payments and may lead to more favorable loan terms.
- Property Value:The appraised value of the property serves as collateral for the loan. Lenders want to ensure that the loan amount is not exceeding the property’s worth.
Understanding Loan Terms

Interest Rates, Home Loan
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money. Lenders charge interest on home loans to compensate for the risk of lending and to generate profits. Higher interest rates result in higher monthly payments and overall borrowing costs. Factors influencing interest rates include the prevailing market conditions, the lender’s risk assessment, and your creditworthiness.
Simplify your debt payments with a Debt Consolidation Loan. This type of loan combines multiple debts into a single loan with potentially lower interest rates, making it easier to manage your finances.
Loan Fees
In addition to interest, various fees are associated with home loans. These fees can add to the overall cost of borrowing and should be considered when comparing loan options. Common loan fees include:
- Origination Fee:A fee charged by the lender for processing and underwriting your loan application. This fee is typically a percentage of the loan amount.
- Closing Costs:A variety of expenses incurred during the closing process, such as appraisal fees, title insurance, and recording fees. Closing costs can vary depending on the lender, property location, and other factors.
- Mortgage Insurance:Required for borrowers with low down payments, mortgage insurance protects the lender against potential losses in case of default. The premium for mortgage insurance is typically added to your monthly payments.
Loan Terms
Understanding key loan terms is essential for making informed decisions about your home loan. Common terms include:
- Amortization:The process of gradually paying off a loan over time through regular payments. Each payment includes both principal (the original loan amount) and interest.
- Principal:The original amount of money borrowed for the loan. As you make payments, the principal balance decreases over time.
- Interest:The cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the principal. Interest payments are calculated based on the interest rate and the outstanding principal balance.
Mortgage Payments
Mortgage payments are typically made monthly and include both principal and interest. The amount of each payment is determined by the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term.
A Fha Loan can be a great option for first-time homebuyers or those with lower credit scores. These loans often have lower down payment requirements and more flexible eligibility criteria compared to conventional mortgages.
A mortgage payment can be calculated using the following formula:Monthly Payment = (Loan Amount x Interest Rate) / (1
Understanding HELOC interest rates is crucial before taking out a loan. Check out Heloc Rates to compare current offerings and find the best terms for your financial situation.
(1 + Interest Rate)^-Loan Term)
Consolidating your debts can simplify your financial life. Consolidation Loans combine multiple debts into a single loan, potentially lowering your monthly payments and interest rates.
Where:* Loan Amount is the original amount borrowed
Overwhelmed by debt? Debt Relief options can help you explore strategies to manage and potentially reduce your debt burden. It’s essential to carefully evaluate your options and understand the potential risks and costs involved.
- Interest Rate is the annual interest rate, divided by 12 for monthly payments
- Loan Term is the number of months in the loan term
Choosing the Right Loan
Factors to Consider
When selecting a home loan, several factors should be carefully considered to ensure you choose the best option for your needs and financial situation. These factors include:
- Interest Rates:Aim for the lowest interest rate possible, as this will reduce your overall borrowing costs. Compare interest rates from different lenders to find the most favorable terms.
- Loan Terms:Consider the loan term, which is the length of time you have to repay the loan. Longer terms may result in lower monthly payments but lead to higher overall interest costs. Conversely, shorter terms may involve higher monthly payments but result in less interest paid over time.
Need a loan quickly? Loans Near Me can help you find local lenders offering various loan products, including personal loans, auto loans, and more.
- Lender Reputation:Choose a reputable lender with a strong track record and positive customer reviews. Research the lender’s financial stability, customer service, and loan processing efficiency.
- Loan Fees:Carefully review the loan fees associated with each option, including origination fees, closing costs, and mortgage insurance premiums. Compare fees across different lenders to find the most affordable option.
- Loan Type:Determine the best loan type for your situation based on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and long-term plans. Consider factors such as fixed vs. adjustable interest rates, FHA vs. VA loans, and other loan options.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Each loan type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which should be carefully weighed before making a decision.
Looking to simplify your debt management? Best Debt Consolidation Loans can help you consolidate multiple debts into a single, lower-interest loan, potentially saving you money and reducing your monthly payments.
Fixed-Rate Mortgage
- Advantages:Predictable monthly payments, protection against rising interest rates, stability and financial security.
- Disadvantages:Initial interest rates may be higher than ARMs, limited flexibility to refinance or change terms.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM)
- Advantages:Lower initial interest rates, potential for lower monthly payments during the initial period, flexibility to refinance or change terms.
- Disadvantages:Interest rates can fluctuate, potential for higher monthly payments if interest rates rise, uncertainty about future costs.
FHA Loan
- Advantages:Lower down payment requirements, more lenient eligibility requirements, access to homeownership for borrowers with lower credit scores or limited financial resources.
- Disadvantages:Mortgage insurance premiums, higher overall borrowing costs, potential for stricter lending guidelines.
VA Loan
- Advantages:No down payment requirement, typically lower interest rates, no private mortgage insurance, favorable terms for eligible veterans and military personnel.
- Disadvantages:Eligibility restrictions based on military service, potential for funding limits, specific property requirements.
Choosing a Lender
Research and compare different lenders to find the best fit for your needs. Consider factors such as:
- Interest Rates and Loan Fees:Obtain quotes from multiple lenders to compare interest rates, loan fees, and overall borrowing costs.
- Lender Reputation:Check the lender’s financial stability, customer service, and track record through online reviews, industry rankings, and consumer protection agencies.
- Loan Products and Services:Evaluate the lender’s range of loan products, including fixed-rate, adjustable-rate, FHA, VA, and other options. Consider whether the lender offers additional services such as refinancing, home equity loans, or other financial products.
- Customer Service and Communication:Choose a lender that provides clear and transparent communication, responsive customer service, and a user-friendly application process.
Negotiating Loan Terms
Negotiating loan terms can help you secure more favorable rates and conditions. Consider the following tips:
- Shop Around:Obtain quotes from multiple lenders to compare interest rates, loan fees, and overall borrowing costs. This competition can give you leverage during negotiations.
- Improve Your Credit Score:A higher credit score can lead to lower interest rates. Before applying for a loan, take steps to improve your credit score by paying bills on time, reducing debt, and avoiding unnecessary credit inquiries.
- Negotiate Loan Fees:Explore options for lowering or waiving certain fees, such as origination fees or closing costs. Be prepared to discuss your options and make counteroffers if necessary.
- Consider a Pre-Approval:Getting pre-approved for a loan demonstrates your financial readiness and can give you a stronger negotiating position. It can also help you secure a lower interest rate.
Conclusion
Securing a home loan is a significant financial undertaking, but with careful planning and understanding, it can be a rewarding experience. By familiarizing yourself with the different loan types, terms, and processes, you can navigate the path to homeownership with confidence.
Looking for a personal loan? Best Personal Loans can be used for a variety of purposes, from debt consolidation to home improvements. Compare different loan options to find the best rates and terms for your needs.
Remember, seeking guidance from trusted financial professionals and utilizing available resources can make the process smoother and more successful.
FAQ Guide
What is the difference between a fixed-rate and an adjustable-rate mortgage?
High credit card debt? A Credit Card Consolidation Loan can help you consolidate your balances into a single, lower-interest loan, potentially saving you money on interest charges.
A fixed-rate mortgage offers a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments. An adjustable-rate mortgage, on the other hand, has an interest rate that can fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially leading to higher or lower payments over time.
How much of a down payment do I need for a home loan?
The required down payment for a home loan varies depending on the loan type and lender. Conventional loans typically require a 20% down payment, while government-backed loans like FHA loans may offer lower down payment options.
What are closing costs and how much can I expect to pay?
Unlocking your home’s equity can be a smart financial move. A Home Equity Line Of Credit (HELOC) offers a flexible way to access funds, but remember to consider the potential risks and long-term implications.
Closing costs are fees associated with finalizing a home purchase, including loan origination fees, appraisal fees, and title insurance. The total amount of closing costs can vary depending on the loan type, property location, and other factors.