Calculating Annuity Cash Flows Excel 2024 – Calculating Annuity Cash Flows in Excel 2024 empowers you to navigate the complex world of annuities with ease. Annuities, a series of equal payments over a set period, are fundamental to financial planning, whether you’re saving for retirement, managing debt, or analyzing investments.
This guide delves into the core concepts of annuities, equipping you with the knowledge and practical skills to confidently perform calculations using Excel’s powerful functions.
Are you considering investing in a fixed annuity within your IRA? This article can provide you with valuable information: Fixed Annuity In Ira 2024.
We’ll start by defining annuities and exploring their key characteristics, including the distinction between ordinary annuities and annuities due. Understanding the concepts of present value and future value is crucial for evaluating the worth of annuities over time. We’ll then delve into the formulas used to calculate these values and demonstrate how to utilize Excel’s PV, FV, and PMT functions for efficient computation.
Practical examples will guide you through the process of applying these concepts to real-world scenarios, such as retirement planning, loan repayments, and investment analysis.
Contents List
Understanding Annuities: Calculating Annuity Cash Flows Excel 2024
Annuities are a powerful financial tool used for various purposes, from retirement planning to loan repayments. They involve a series of regular payments made over a specific period. Understanding the key characteristics of annuities, including their types and present and future values, is crucial for effective financial planning.
Understanding how annuities are calculated is crucial for making informed decisions about your retirement planning. This article provides insights into the calculations involved: How Annuity Is Calculated 2024.
Definition and Characteristics
An annuity is a series of equal payments made at regular intervals over a specific period. Key characteristics of an annuity include:
- Equal payments:Each payment in an annuity is the same amount.
- Regular intervals:Payments are made at fixed intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Specific period:Annuities have a defined start and end date, determining the total number of payments.
Ordinary Annuities vs. Annuities Due
Annuities are categorized into two main types: ordinary annuities and annuities due.
Annuity payments can continue indefinitely, offering a sense of financial security throughout your retirement years. Read more about the concept of a perpetual annuity in this article: Annuity Is Perpetual 2024.
- Ordinary annuities:Payments are made at the end of each period. This is the most common type of annuity.
- Annuities due:Payments are made at the beginning of each period. This type is less common but can be beneficial in certain situations.
Present Value and Future Value
Understanding the present value (PV) and future value (FV) of an annuity is essential for making informed financial decisions.
Curious about how a single premium annuity works? Find out more about how G purchased a $50,000 single premium annuity in 2024 by reading this article: G Purchased A $50 000 Single Premium 2024.
- Present value (PV):The current value of a future stream of payments. It represents the amount of money you would need to invest today to receive the same future cash flows from an annuity.
- Future value (FV):The total value of an annuity at a specific point in the future. It represents the sum of all payments, compounded over time.
Annuity Formulas
Calculating the present and future values of annuities requires specific formulas. These formulas take into account factors such as the interest rate, the number of periods, and the payment amount.
Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity
PV = PMT
- [1
- (1 + r)^-n] / r
Where:
- PV = Present value
- PMT = Payment amount
- r = Interest rate per period
- n = Number of periods
Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity
FV = PMT
- [(1 + r)^n
- 1] / r
Where:
- FV = Future value
- PMT = Payment amount
- r = Interest rate per period
- n = Number of periods
Adjusting Formulas for Annuities Due
To calculate the present or future value of an annuity due, you simply multiply the result obtained from the ordinary annuity formula by (1 + r). This adjustment accounts for the fact that payments are made at the beginning of each period, earning one additional period of interest.
If you’re thinking about an annuity with a starting investment of $70,000, this article might provide helpful information: Annuity 70000 2024.
Excel Functions for Annuity Calculations
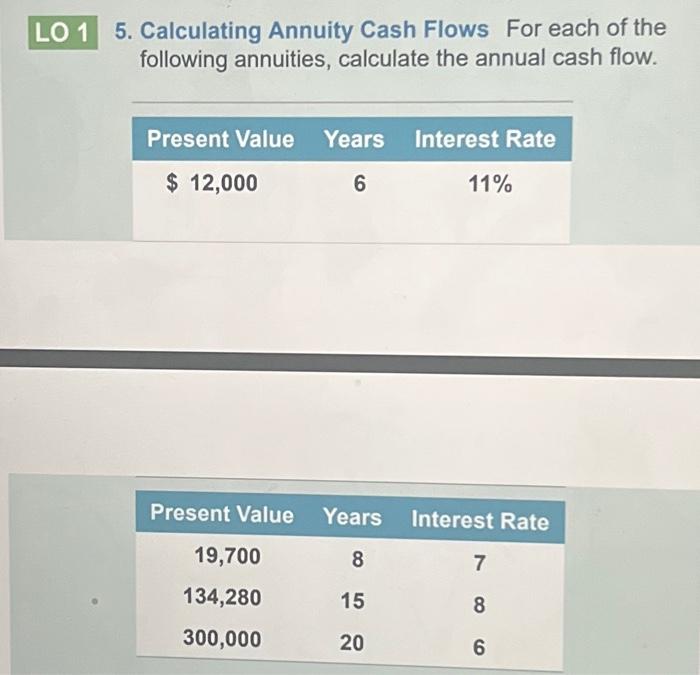
Microsoft Excel provides powerful functions that simplify annuity calculations. These functions automate the calculations, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
Annuity payments can last for an indefinite duration, making them a popular choice for retirement planning. If you’re curious about how long these payments might continue, check out this article on Annuity Is Indefinite Duration 2024.
PV Function
The PV function in Excel calculates the present value of an annuity. The syntax for the PV function is:
=PV(rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type])
Where:
- rate:The interest rate per period.
- nper:The total number of payment periods.
- pmt:The payment amount per period.
- fv:The future value (optional). If omitted, it is assumed to be 0.
- type:Specifies when payments are made (0 for end of period, 1 for beginning of period). If omitted, it is assumed to be 0.
FV Function
The FV function in Excel calculates the future value of an annuity. The syntax for the FV function is:
=FV(rate, nper, pmt, [pv], [type])
Curious about how much annuity income you might receive from an initial investment of $80,000? Find out more by visiting this link: How Much Annuity For 80000 2024.
Where:
- rate:The interest rate per period.
- nper:The total number of payment periods.
- pmt:The payment amount per period.
- pv:The present value (optional). If omitted, it is assumed to be 0.
- type:Specifies when payments are made (0 for end of period, 1 for beginning of period). If omitted, it is assumed to be 0.
PMT Function
The PMT function in Excel calculates the periodic payment amount for an annuity. The syntax for the PMT function is:
=PMT(rate, nper, pv, [fv], [type])
Joint and survivor annuities offer a way to ensure that payments continue even after one spouse passes away. If you’re interested in learning more about this type of annuity, check out this article: Annuity Joint And Survivor 2024.
Where:
- rate:The interest rate per period.
- nper:The total number of payment periods.
- pv:The present value of the annuity.
- fv:The future value (optional). If omitted, it is assumed to be 0.
- type:Specifies when payments are made (0 for end of period, 1 for beginning of period). If omitted, it is assumed to be 0.
Practical Examples
Let’s illustrate the use of Excel functions for annuity calculations with practical examples.
It’s important to understand who is behind the annuity you’re considering. This article delves into the topic of annuity issuers: Annuity Issuer 2024.
Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity
Suppose you want to calculate the present value of an ordinary annuity with the following parameters:
- Payment amount (PMT): $1,000
- Interest rate (rate): 5% per year
- Number of periods (nper): 10 years
In Excel, you would use the following formula:
=PV(0.05, 10, 1000)
Are you a 65-year-old male looking for information about annuities? This article may be of interest to you: Annuity 65 Male 2024.
This formula would return a present value of approximately $7,721.73. This means that you would need to invest $7,721.73 today to receive $1,000 per year for the next 10 years at a 5% annual interest rate.
Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity
Suppose you want to calculate the future value of an ordinary annuity with the following parameters:
- Payment amount (PMT): $1,000
- Interest rate (rate): 5% per year
- Number of periods (nper): 10 years
In Excel, you would use the following formula:
=FV(0.05, 10, 1000)
Need to determine the number of periods for your annuity? This calculator can help: Annuity Number Of Periods Calculator 2024.
This formula would return a future value of approximately $12,577.89. This means that if you invest $1,000 per year for the next 10 years at a 5% annual interest rate, you will have accumulated $12,577.89 at the end of the period.
Periodic Payment Amount for an Annuity
Suppose you want to calculate the periodic payment amount for an annuity with the following parameters:
- Present value (pv): $10,000
- Interest rate (rate): 6% per year
- Number of periods (nper): 5 years
In Excel, you would use the following formula:
=PMT(0.06, 5, 10000)
This formula would return a periodic payment amount of approximately $2,374.04. This means that you would need to make annual payments of $2,374.04 for the next 5 years to fully repay a loan of $10,000 at a 6% annual interest rate.
Still unsure about what an annuity is? This article provides a clear explanation of the concept: Annuity What Is The Meaning 2024.
Annuity Applications
Annuities have numerous real-world applications, playing a crucial role in financial planning, investment analysis, and debt management.
Want to calculate annuity payments using Excel? This article will guide you through the process: Calculating Annuity Payments In Excel 2024.
Retirement Planning
Annuities are widely used in retirement planning. Individuals can use annuities to accumulate savings for retirement or to provide a steady stream of income during their retirement years. Annuities can help ensure financial security and peace of mind during retirement.
Loan Repayments
Annuities are the basis for many loan repayment structures, such as mortgages and car loans. The regular payments made over the loan term constitute an annuity, with the loan amount representing the present value of the annuity.
Investment Analysis, Calculating Annuity Cash Flows Excel 2024
Annuities can be used to analyze the value of investments that generate regular cash flows. By calculating the present value or future value of an investment’s cash flows, investors can make informed decisions about their portfolio allocation.
Annuity rates and terms can vary significantly. This article explores the landscape of annuities in 2021: Annuity 2021 2024.
Practical Tips for Using Excel
Here are some practical tips for using Excel to analyze annuity cash flows:
- Use the appropriate functions:Excel provides a wide range of functions for annuity calculations, including PV, FV, PMT, and others. Select the function that best suits your specific needs.
- Input data carefully:Ensure that the data you enter into the Excel formulas is accurate and consistent. Errors in data input can lead to inaccurate results.
- Format your spreadsheet:Organize your spreadsheet in a clear and logical manner, using headings, formatting, and charts to enhance readability and understanding.
- Perform sensitivity analysis:Vary the input parameters, such as interest rates or payment amounts, to understand how changes in these variables affect the annuity’s value.
Conclusive Thoughts
By mastering the art of calculating annuity cash flows in Excel 2024, you gain a powerful tool for making informed financial decisions. Whether you’re an individual planning for your future or a professional working in the financial industry, understanding annuities is essential.
This guide provides a solid foundation for navigating the intricacies of annuity calculations, empowering you to confidently analyze financial scenarios and make sound decisions.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due?
An ordinary annuity has payments made at the end of each period, while an annuity due has payments made at the beginning of each period. This difference in timing affects the calculation of present and future values.
How can I adjust the annuity formulas for annuities due?
When you receive income from an annuity, it’s important to understand the tax implications. Learn more about whether annuity income is considered capital gains in 2024 by visiting this link: Is Annuity Income Capital Gains 2024.
To adjust the formulas for annuities due, you can multiply the present value of an ordinary annuity by (1 + interest rate) or divide the future value of an ordinary annuity by (1 + interest rate). This accounts for the earlier payment timing in annuities due.
What are some real-world applications of annuities beyond retirement planning?
Annuities have numerous applications, including loan repayments, where the loan amount is divided into equal installments over a specific period. They are also used in investment analysis to evaluate the returns on investments that provide regular income streams.









