Calculating Simple Annuity 2024 delves into the world of annuities, providing a comprehensive understanding of these financial instruments. Annuities, a series of equal payments made over a set period, are powerful tools for managing finances, whether for retirement planning, loan repayment, or savings and investment goals.
In simple terms, an annuity can be defined as a financial product that provides regular payments over a set period. You can learn more about An Annuity Is Best Defined As 2024 to understand its core concept.
This guide explores the fundamentals of annuities, covering concepts like present and future value calculations, the impact of interest rates and payment frequencies, and real-world applications. We’ll also examine various tools and resources available for calculating annuities, empowering you to make informed financial decisions.
Contents List
- 1 Understanding Simple Annuities
- 2 Calculating Present Value of an Annuity
- 3 Calculating Future Value of an Annuity
- 4 Annuity Applications in Real-World Scenarios: Calculating Simple Annuity 2024
- 5 Factors Affecting Annuity Calculations
- 6 Tools and Resources for Annuity Calculations
- 7 Closure
- 8 FAQ Compilation
Understanding Simple Annuities
An annuity is a series of equal payments made over a specified period of time. Simple annuities are a type of annuity where the payments are made at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually. Understanding annuities is crucial for financial planning, as they play a vital role in retirement planning, loan repayment, and savings and investment strategies.
Defining Simple Annuities
A simple annuity is a stream of equal payments made at regular intervals. Key characteristics of a simple annuity include:
- Equal Payments:Each payment in an annuity is the same amount.
- Regular Intervals:Payments are made at consistent time intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Fixed Period:The annuity has a predetermined duration, after which payments cease.
Ordinary Annuities vs. Annuities Due
There are two main types of simple annuities: ordinary annuities and annuities due. The difference lies in the timing of the payments:
- Ordinary Annuity:Payments are made at the end of each period. For example, in a monthly ordinary annuity, payments are made on the last day of each month.
- Annuity Due:Payments are made at the beginning of each period. In a monthly annuity due, payments are made on the first day of each month.
Time Value of Money and Annuities
The time value of money is a fundamental concept in finance that states that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. This is due to the potential for earning interest or returns on the money over time.
For those unfamiliar with the term, it’s helpful to understand what an annuity means in Hindi. You can find the explanation for Annuity Ka Hindi Meaning 2024 to gain clarity.
Annuities are closely tied to the time value of money because they involve payments made over a period, and the value of each payment is affected by the interest rate and the time until it is received.
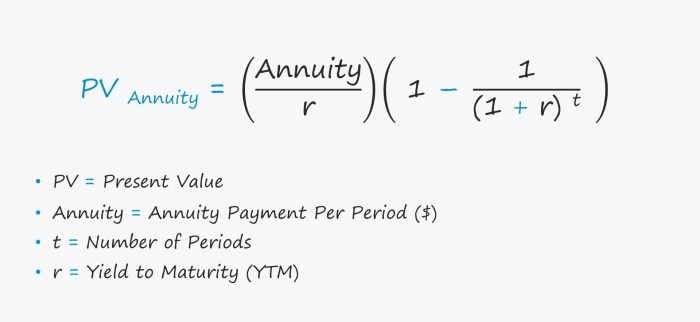
Calculating Present Value of an Annuity
The present value of an annuity is the current value of a stream of future payments, discounted back to the present using an appropriate interest rate. Understanding the present value of an annuity is essential for making informed financial decisions, such as evaluating investment opportunities or determining the affordability of a loan.
Formula for Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity, Calculating Simple Annuity 2024
PV = PMT- [1 – (1 + r)^-n] / r
Annuity payments can be guaranteed for a specific period, but it’s important to know if this guarantee extends indefinitely. You can find out more about Is Annuity Certain 2024 to understand the terms.
Where:
- PV = Present Value
- PMT = Payment Amount
- r = Interest Rate per Period
- n = Number of Periods
Components of the Present Value Formula
The present value formula takes into account the following factors:
- Payment Amount (PMT):This is the amount of each payment in the annuity.
- Interest Rate (r):This is the rate of return used to discount future payments to their present value. The interest rate reflects the opportunity cost of money, meaning the potential return that could be earned by investing the money elsewhere.
- Number of Periods (n):This represents the total number of payments in the annuity.
Calculating Present Value: Numerical Example
Let’s say you are considering an investment that promises to pay you $1,000 per year for the next 5 years. The annual interest rate is 5%. To calculate the present value of this annuity, we can use the formula:
PV = $1,000- [1 – (1 + 0.05)^-5] / 0.05 = $4,329.48
When it comes to taxes, you might be curious about the tax implications of annuities from LIC. Find out if Is Annuity From Lic Taxable 2024 to understand the potential tax liabilities.
Therefore, the present value of this annuity is $4,329.48. This means that the future stream of payments is worth $4,329.48 today, given the specified interest rate and time period.
Calculating Future Value of an Annuity
The future value of an annuity is the total value of the stream of payments at the end of the annuity period, taking into account the interest earned on each payment. Calculating the future value of an annuity is crucial for financial planning, such as determining the future value of a savings plan or estimating the future amount of a loan.
To get a comprehensive understanding of annuity rates, it’s helpful to compare them over time. You can explore Annuity Rates 2021 2024 to see how they have changed.
Formula for Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity
FV = PMT- [(1 + r)^n – 1] / r
Are you interested in exploring the possibility of a large annuity payout? You might want to research Annuity 3 Million 2024 to see if it’s a suitable option for your needs.
Where:
- FV = Future Value
- PMT = Payment Amount
- r = Interest Rate per Period
- n = Number of Periods
Components of the Future Value Formula
The future value formula considers the following components:
- Payment Amount (PMT):This is the amount of each payment in the annuity.
- Interest Rate (r):This is the rate of return earned on each payment over the annuity period. It reflects the growth potential of the money over time.
- Number of Periods (n):This represents the total number of payments in the annuity.
Calculating Future Value: Numerical Example
Let’s assume you invest $500 per month for 10 years at an annual interest rate of 6%. To calculate the future value of this annuity, we first need to convert the annual interest rate to a monthly rate: 6% / 12 = 0.5% per month.
We also need to convert the number of years to months: 10 years – 12 months/year = 120 months. Now, we can apply the formula:
FV = $500- [(1 + 0.005)^120 – 1] / 0.005 = $82,353.88
Therefore, the future value of this annuity is $82,353.88. This means that the total amount accumulated at the end of 10 years, including the interest earned on each payment, will be $82,353.88.
Annuity Applications in Real-World Scenarios: Calculating Simple Annuity 2024
Annuities have a wide range of applications in real-world financial scenarios, impacting various aspects of personal and business finance. Here are some key examples:
Retirement Planning
Annuities are often used in retirement planning to provide a steady stream of income during retirement years. Individuals can purchase annuities with a lump sum of money, and the annuity provider will then make regular payments to them for a specified period.
This provides a reliable source of income to supplement other retirement savings.
Loan Repayment
Many loans, such as mortgages, car loans, and student loans, are structured as annuities. The borrower makes regular payments over a predetermined period to repay the principal and interest on the loan. Annuities ensure that the loan is repaid systematically and that the lender receives a consistent return on their investment.
When considering an annuity, a common question is whether it provides lifetime income. You can find out more about Is Annuity Lifetime 2024 to make an informed decision.
Savings and Investment
Annuities can be used for savings and investment purposes. For example, individuals can contribute to an annuity account on a regular basis, allowing their savings to grow over time with the benefit of compounding interest. Annuities can be a suitable investment option for individuals seeking long-term growth and a steady stream of income.
If you’re considering an annuity, understanding the potential payouts is crucial. You can find information about Annuity 300 000 2024 to gain insights into the potential returns.
Factors Affecting Annuity Calculations
Several factors can influence the present and future values of annuities, impacting the overall financial outcomes. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed financial decisions and maximizing the benefits of annuity investments.
A popular strategy for retirement planning is the “59.5 rule,” which can impact your access to funds. Understanding the Annuity 59.5 Rule 2024 can help you plan accordingly.
Interest Rate Changes
Interest rates play a significant role in annuity calculations. Higher interest rates generally result in higher future values and lower present values. This is because higher interest rates mean that each payment earns more interest over time, increasing the future value.
Understanding the timing of annuity payments is essential. You can find out more about the Annuity Date Is 2024 to know when to expect your payments.
Conversely, higher interest rates discount future payments more heavily, leading to lower present values.
Payment Frequencies
The frequency of payments can also impact annuity values. More frequent payments generally lead to higher future values and lower present values. This is because more frequent payments mean that interest is earned on the payments more often, leading to faster growth.
If you’re looking to calculate the payments for an annuity loan, you can utilize a formula. Learn more about the Annuity Loan Formula 2024 to understand how it works.
However, more frequent payments also require a higher present value to fund the same future value, as the payments are being made more often.
Hargreaves Lansdown offers a handy tool for calculating annuity payments. You can use the Annuity Calculator Hargreaves Lansdown 2024 to estimate your potential income.
Number of Periods
The number of periods in an annuity significantly affects its value. A longer annuity period generally results in higher future values and lower present values. This is because payments have more time to accumulate interest over a longer period, leading to greater growth.
Before committing to an annuity, it’s crucial to evaluate if it aligns with your financial goals. You can explore the pros and cons of Is Getting An Annuity Worth It 2024 to make a well-informed decision.
However, a longer annuity period also requires a higher present value to fund the same future value, as the payments are being made over a longer time.
Some individuals may have concerns about annuities. If you’re wondering if Annuity Is Bad 2024 , it’s important to carefully weigh the pros and cons.
Tools and Resources for Annuity Calculations
Various tools and resources are available to assist in annuity calculations, simplifying the process and ensuring accuracy. These tools can be particularly helpful for individuals unfamiliar with the intricacies of annuity formulas or those seeking to compare different annuity options.
Online Calculators and Software
| Tool | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calculator.net | A comprehensive online calculator that offers various annuity calculations, including present value, future value, and payment amount. | User-friendly interface, customizable options, multiple calculation types. | Limited customization for specific annuity types. |
| Financial Calculators by Bankrate | A collection of financial calculators, including annuity calculators, offered by Bankrate. | Wide range of calculators, clear explanations, integration with other financial tools. | May require registration for full access to all calculators. |
| Excel Spreadsheet | Microsoft Excel provides built-in functions for annuity calculations, allowing for flexible and customized calculations. | Highly customizable, allows for complex calculations, integrates with other spreadsheet tools. | Requires knowledge of Excel formulas, may not be suitable for beginners. |
Using a Calculator for Annuity Calculations
To use an online annuity calculator, typically you will need to input the following information:
- Payment Amount
- Interest Rate
- Number of Periods
- Type of Annuity (Ordinary or Due)
Once you enter the required information, the calculator will automatically compute the present value, future value, or payment amount, depending on the type of calculation you are performing.
Closure
Understanding annuities is crucial for individuals seeking to plan for their financial future. By grasping the principles of annuity calculations, you can make informed decisions regarding investments, retirement planning, and debt management. This guide provides a solid foundation for navigating the world of annuities, equipping you with the knowledge to leverage these financial tools effectively.
FAQ Compilation
What is the difference between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due?
An ordinary annuity’s payments are made at the end of each period, while an annuity due’s payments are made at the beginning of each period. This difference impacts the present and future value calculations.
How do interest rate changes affect annuity values?
Higher interest rates generally lead to higher future values of annuities and lower present values. Conversely, lower interest rates result in lower future values and higher present values.
Wondering how much you could receive from an annuity? You might be interested in exploring the potential of an Annuity 2 Million 2024. This could be a good starting point to understand the potential payouts.
What are some real-world examples of annuity applications?
Annuities are commonly used in retirement planning, providing a steady stream of income after retirement. They can also be used for loan repayment, particularly for mortgages, and for savings and investment purposes, such as funding college education or building a nest egg.









