Formula For Calculating The Annuity 2024, delves into the world of annuities, providing a comprehensive understanding of how these financial instruments work. Annuities, often described as a stream of regular payments, can be a valuable tool for retirement planning, income generation, and even estate planning.
Annuities can be complex, and understanding the basics is key. You can find general information about annuities here. If you’re considering an annuity with BMO, their calculator can provide helpful insights. Sometimes, an annuity is deferred , which means you’ll receive payments later on.
It’s important to understand if annuity payments are considered earned income for tax purposes.
This guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the intricacies of annuity calculations, empowering you to make informed financial decisions.
We’ll explore the different types of annuities, including fixed, variable, immediate, and deferred, highlighting their unique characteristics and applications. You’ll discover the key variables that influence annuity calculations, such as interest rates, investment returns, and payment periods. The formula for calculating annuity payments will be presented step-by-step, along with illustrative examples to solidify your understanding.
Furthermore, we’ll examine factors that can affect annuity payments, including inflation, longevity, and market volatility.
Contents List
Understanding Annuities
An annuity is a financial product that provides a stream of regular payments over a set period of time. Think of it like a retirement plan, where you make payments over time and then receive a steady income stream in retirement.
Annuities can be a valuable tool for securing your financial future, but it’s crucial to understand the different types and how they work before making a decision.
Types of Annuities
Annuities come in various forms, each with unique characteristics and benefits. Here are some common types:
- Fixed Annuities:These annuities offer a guaranteed rate of return on your investment, providing predictable payments. They are ideal for those seeking stability and protection against market fluctuations.
- Variable Annuities:These annuities offer the potential for higher returns, but they also carry more risk. The payments are tied to the performance of underlying investments, such as stocks or mutual funds.
- Immediate Annuities:These annuities begin paying out immediately after you purchase them. They are perfect for individuals who need an immediate source of income, such as retirees.
- Deferred Annuities:These annuities start paying out at a future date, typically after a certain period of time or upon reaching a specific age. They are suitable for long-term financial planning and can be a good option for saving for retirement.
Real-World Examples of Annuities
- Retirement Income:Annuities can provide a steady stream of income during retirement, ensuring financial security in your later years.
- Supplemental Income:Annuities can serve as a supplemental income source, providing additional funds for living expenses or discretionary spending.
- Long-Term Care:Annuities can be used to cover the costs of long-term care, such as nursing homes or assisted living facilities.
- Estate Planning:Annuities can be incorporated into estate planning strategies, providing a steady income stream for beneficiaries after your passing.
Key Variables in Annuity Calculations
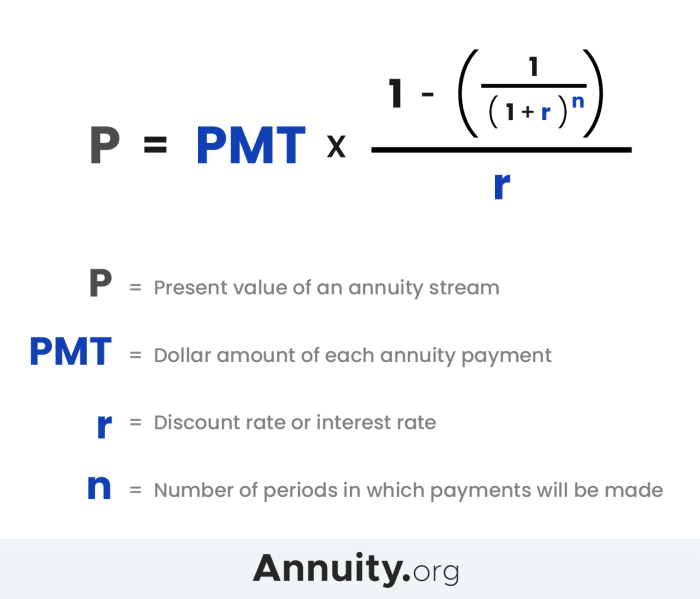
Calculating annuity payments involves several key variables that determine the amount of each payment. These variables interact to create a personalized payment structure for each individual.
Variables Affecting Annuity Payments
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Principal Amount | The initial amount invested in the annuity. |
| Interest Rate | The annual rate of return on the annuity. |
| Payment Frequency | How often payments are made (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually). |
| Term of Annuity | The total duration of the annuity, or the number of payments. |
Understanding these variables is crucial, as they directly influence the size of your annuity payments. For instance, a higher principal amount or interest rate will generally result in larger payments. Similarly, a longer term or more frequent payments can also impact the overall payment amount.
Formula for Calculating Annuity Payments
The formula for calculating annuity payments is a straightforward mathematical equation that considers all the key variables discussed above. Understanding the formula is essential for accurately calculating and comprehending the payment structure of an annuity.
Annuity Payment Formula
Annuity Payment = (PV- r) / (1 – (1 + r)^-n)
Where:
- PV = Present Value (principal amount)
- r = Interest Rate per Payment Period (annual interest rate divided by the number of payments per year)
- n = Total Number of Payments
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Annuity Payments, Formula For Calculating The Annuity 2024
- Determine the Present Value (PV):This is the initial amount you invest in the annuity.
- Calculate the Interest Rate per Payment Period (r):Divide the annual interest rate by the number of payments per year. For example, if the annual interest rate is 5% and payments are made monthly, then r = 0.05 / 12 = 0.0041667.
- Calculate the Total Number of Payments (n):Multiply the number of payments per year by the term of the annuity. For example, if payments are made monthly and the annuity term is 10 years, then n = 12
10 = 120.
- Plug the values into the formula:Substitute the values of PV, r, and n into the annuity payment formula and solve for the annuity payment.
Annuity Payment Examples
Let’s illustrate the annuity payment calculation with three distinct examples, each showcasing different scenarios. These examples will provide a practical understanding of how the formula works and the factors that can influence annuity payments.
Annuity Payment Examples
| Scenario | Principal Amount (PV) | Interest Rate (r) | Payment Frequency | Term (n) | Annuity Payment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1: High Principal, Low Interest | $100,000 | 3% (annual) | Monthly | 10 years | $966.64 |
| Example 2: Low Principal, High Interest | $50,000 | 5% (annual) | Quarterly | 5 years | $3,033.26 |
| Example 3: Medium Principal, Medium Interest | $75,000 | 4% (annual) | Annually | 20 years | $6,049.78 |
As you can see from the examples, the annuity payment can vary significantly depending on the principal amount, interest rate, payment frequency, and term. In Example 1, a high principal amount with a low interest rate results in a lower annuity payment.
Conversely, Example 2 demonstrates that a low principal amount with a high interest rate leads to a larger payment. Example 3 showcases a medium principal amount and interest rate, resulting in a moderate annuity payment. These examples highlight the importance of considering all variables when calculating annuity payments.
The owner of an annuity is the person who receives the payments, but the life expectancy used to calculate the payout is often based on the annuitant. While annuities can be a good option for retirement income, they aren’t right for everyone.
Some people might find that annuities are bad for their specific situation. It’s important to accurately calculate your potential annuity payout to make an informed decision.
Factors Affecting Annuity Payments
Several factors can influence the size of annuity payments, impacting the overall financial outcome of your investment. It’s crucial to understand these factors and their potential impact on your annuity payments.
Factors Affecting Annuity Payments
| Factor | Impact on Payment |
|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Higher interest rates generally lead to larger annuity payments. |
| Inflation | Inflation can erode the purchasing power of your annuity payments over time. |
| Investment Performance (Variable Annuities) | The performance of the underlying investments in a variable annuity directly impacts the size of your payments. |
| Fees and Expenses | Annuity contracts often include fees and expenses that can reduce your overall payments. |
| Withdrawal Options | The terms and conditions of your annuity contract can affect the amount you can withdraw and when. |
For instance, rising interest rates can boost your annuity payments, but inflation can diminish their real value. Investment performance in variable annuities can significantly impact the size of your payments, while fees and expenses can reduce your overall returns. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed decisions about your annuity investment.
When calculating an annuity, it’s important to consider the compounding frequency. You can use an annuity calculator that allows for monthly compounding. Hargreaves Lansdown also offers an annuity calculator that can be helpful. If you’re using a financial calculator, you can calculate annuities using the HP10bii.
Annuity Calculators and Resources
Numerous online annuity calculators are available to help you estimate potential annuity payments and compare different annuity options. These calculators can be a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of annuities and making informed financial decisions.
Figuring out your retirement income can be tricky, but an Annuity Calculator Nz 2024 can help you estimate how much you might receive. It’s important to understand if the death benefit is taxable, as well as how to calculate it using a financial calculator like the BA II Plus.
There are also specific rules surrounding annuities, like the 5-year rule , that you should be aware of.
Reputable Online Annuity Calculators
- Bankrate:Bankrate offers a comprehensive annuity calculator that allows you to explore various annuity types and scenarios.
- Investopedia:Investopedia provides a user-friendly annuity calculator that helps you estimate payments and understand different annuity features.
- NerdWallet:NerdWallet offers a simple and intuitive annuity calculator that can assist you in comparing annuity options and understanding their potential returns.
While these calculators can provide valuable insights, it’s important to remember that they are only estimations. Consulting with a financial advisor is crucial to receive personalized advice and make informed decisions based on your specific financial circumstances.
Additional Resources for Learning About Annuities
- The American Council of Life Insurers (ACLI):ACLI provides educational resources and information about annuities, including consumer guides and FAQs.
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC):The SEC offers investor education materials and resources on annuities, including information on how to protect yourself from scams.
- The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC):NAIC provides consumer resources and information on annuities, including state-specific regulations and consumer protection tips.
Closing Notes
By understanding the formula for calculating annuities and the factors that influence their payments, you can make informed decisions about incorporating them into your financial strategies. Whether you’re planning for retirement, seeking guaranteed income, or looking to protect your loved ones, annuities offer a versatile and potentially valuable financial tool.
Remember to consult with a qualified financial advisor to determine if annuities are the right fit for your individual needs and circumstances.
FAQ Insights: Formula For Calculating The Annuity 2024
What are the tax implications of annuities?
The tax implications of annuities vary depending on the type of annuity and how it is structured. It’s crucial to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific tax treatment of your annuity.
How do I choose the right annuity for my needs?
The best annuity for you depends on your individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Consulting with a financial advisor can help you determine the most suitable type of annuity.
Are annuities safe investments?
Annuities can offer a level of security, particularly fixed annuities, but they are not risk-free. The value of variable annuities can fluctuate based on market performance. It’s important to understand the risks and potential downsides before investing in an annuity.









