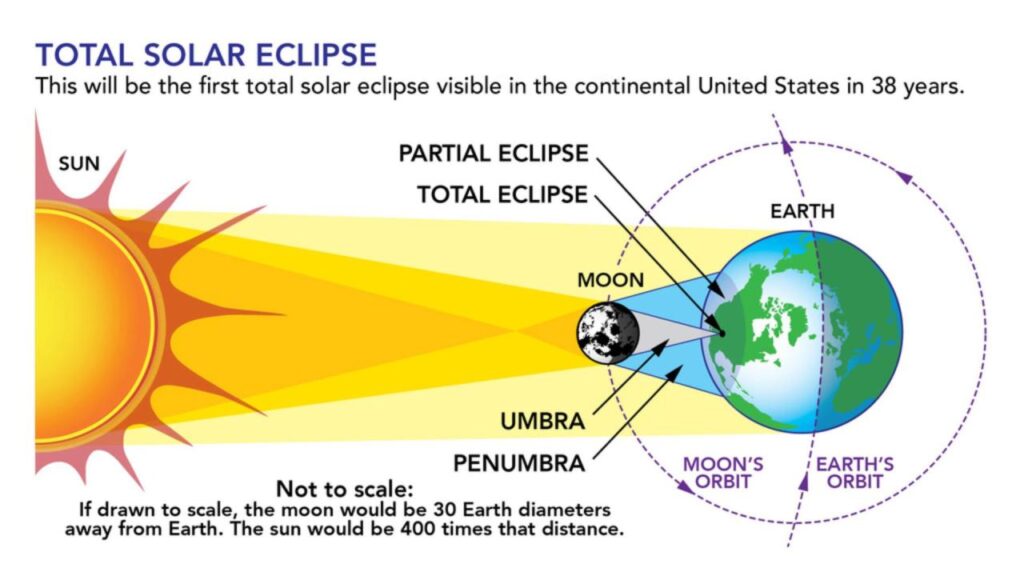
What scientific research can be conducted during a total solar eclipse? This celestial event, where the moon completely blocks the sun’s light, offers a unique window into the mysteries of our solar system. During these fleeting moments of darkness, scientists can observe phenomena that are otherwise obscured by the sun’s overwhelming brightness, providing invaluable insights into the workings of our star and its influence on Earth.
From studying the sun’s corona, the outermost layer of its atmosphere, to testing Einstein’s theory of general relativity, total solar eclipses provide a rare opportunity to push the boundaries of our understanding of the cosmos. By analyzing the data gathered during these events, scientists can unravel the secrets of solar activity, investigate the composition and dynamics of the sun’s atmosphere, and explore the intricate interactions between the sun and Earth.
Contents List
- 1 Observing the Sun’s Corona
- 2 Studying Solar Activity
- 3 Investigating the Sun’s Atmosphere
- 4 Testing General Relativity
- 5 Exploring the Earth’s Atmosphere: What Scientific Research Can Be Conducted During A Total Solar Eclipse?
- 5.1 Earth’s Atmosphere’s Reaction to Solar Radiation Change
- 5.2 Atmospheric Phenomena Observable During a Total Solar Eclipse
- 5.3 Instruments Used to Study the Earth’s Atmosphere During a Total Solar Eclipse, What scientific research can be conducted during a total solar eclipse?
- 5.4 Understanding Atmospheric Dynamics
- 6 Conducting Astronomical Observations
- 7 Last Word
- 8 FAQs
Observing the Sun’s Corona
The corona, the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, is only visible during a total solar eclipse when the Moon completely blocks out the Sun’s bright face. This rare event provides a unique opportunity for scientists to study this enigmatic region of the Sun.
Data privacy is a major concern in the digital age. Android Advertising Data 2024 sheds light on how Android handles user data in the context of advertising.
Significance of Observing the Corona
Observing the corona during a total solar eclipse is crucial for understanding the Sun’s behavior and its influence on Earth. The corona is a dynamic and complex region, where temperatures reach millions of degrees Celsius, much hotter than the Sun’s surface.
Tired of seeing ads on your Android device? Android Stop Advertising 2024 explores various methods to reduce or eliminate unwanted ads on your phone.
Studying the corona helps scientists unravel the mysteries of solar activity, such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which can have significant impacts on Earth’s atmosphere and technology.
Stay informed about the latest Android updates with Android Update January 2024. This article covers all the important changes and new features you can expect.
Unique Features and Structures of the Corona
The corona exhibits a variety of fascinating features and structures that are only visible during a total solar eclipse. These include:
- Coronal streamers:Large, bright plumes of plasma extending outwards from the Sun’s poles.
- Coronal loops:Arcs of plasma that connect different regions of the Sun’s magnetic field.
- Coronal holes:Dark regions in the corona where the magnetic field lines open up into space.
- Prominences:Large, bright clouds of plasma that erupt from the Sun’s surface.
Instruments Used to Study the Corona
Scientists use various instruments to study the corona during a total solar eclipse, including:
- Optical telescopes:To capture images of the corona in visible light.
- Spectrographs:To analyze the light emitted by the corona and determine its composition and temperature.
- Polarimeters:To measure the polarization of light from the corona, providing information about the magnetic field.
- Radio telescopes:To study the corona at radio wavelengths, revealing different aspects of its structure and activity.
Coronal Observations During and Outside a Total Solar Eclipse
While the corona is only visible during a total solar eclipse, scientists can also study it using other techniques. For example, space-based telescopes, such as the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO), can observe the corona continuously. However, the observations made during a total solar eclipse provide unique insights due to the absence of the Sun’s bright light.
Having trouble updating your Android device? My Android Won’t Update 2024 explores the common reasons behind this issue and provides solutions to get your device updated.
These observations allow scientists to study the corona in greater detail and with higher resolution.
Understanding MAC addresses is crucial for BLE advertising. Android Ble Advertising Mac Address 2024 provides a detailed explanation and practical examples to help you understand this important concept.
Studying Solar Activity
Solar activity, the dynamic processes occurring on the Sun’s surface and atmosphere, has a profound impact on Earth and its environment. A total solar eclipse provides a valuable opportunity to study these processes in detail.
Can’t connect your Airtag? Don’t worry, it happens! My Airtag Is Not Connecting 2024 provides a comprehensive troubleshooting guide to help you resolve the issue.
Solar Phenomena Observable During a Total Solar Eclipse
During a total solar eclipse, scientists can observe various solar phenomena, including:
- Sunspots:Darker, cooler regions on the Sun’s surface caused by intense magnetic activity.
- Solar flares:Sudden bursts of energy that release immense amounts of radiation into space.
- Coronal mass ejections (CMEs):Giant clouds of plasma that erupt from the Sun’s corona.
- Prominences:Large, bright clouds of plasma that erupt from the Sun’s surface.
Impact of Solar Activity on Earth
Solar activity can have significant impacts on Earth, including:
- Auroras:When charged particles from solar flares and CMEs interact with Earth’s atmosphere, they create beautiful displays of light in the sky, known as auroras.
- Radio blackouts:Solar flares can disrupt radio communications and navigation systems.
- Satellite malfunctions:CMEs can damage satellites and interfere with their operation.
- Power grid disruptions:Intense geomagnetic storms caused by CMEs can induce currents in power grids, leading to blackouts.
Methods to Measure Solar Activity During a Total Solar Eclipse
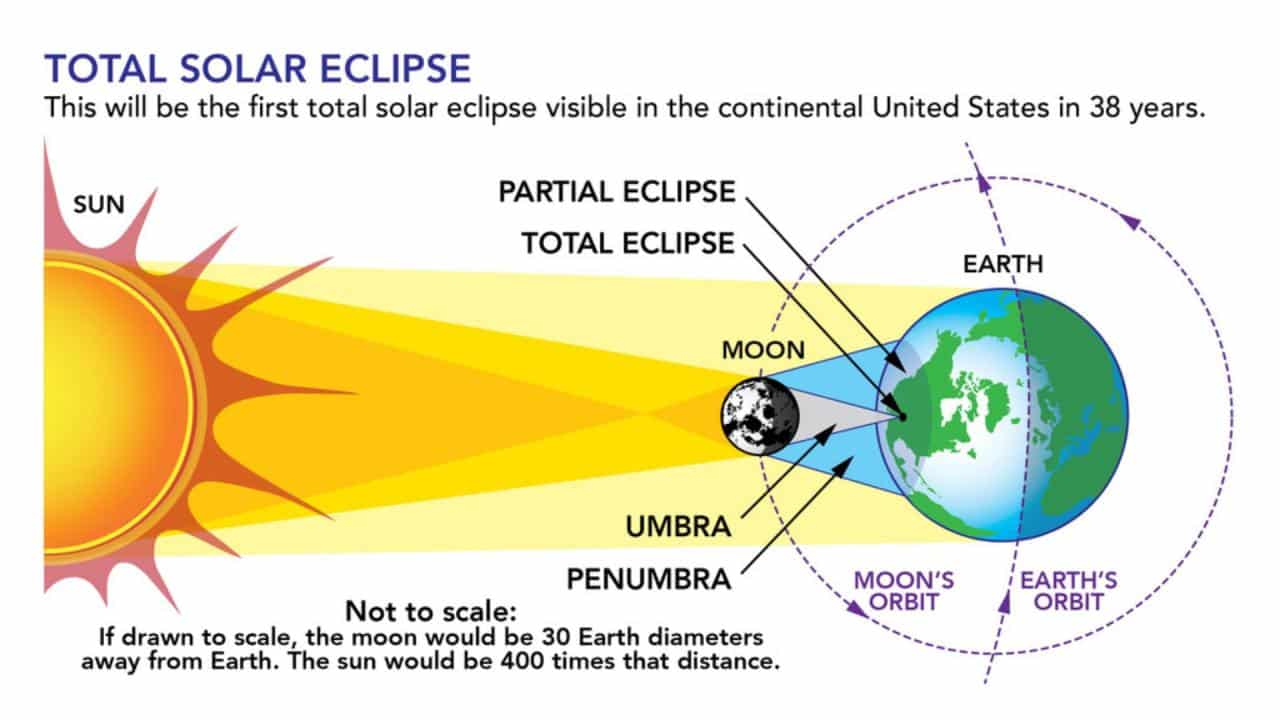
Scientists use various methods to measure solar activity during a total solar eclipse, including:
- Spectroscopy:To analyze the light emitted by the Sun and determine its composition, temperature, and magnetic field.
- Radio interferometry:To study the corona at radio wavelengths and map its structure and activity.
- Coronagraphy:To create artificial eclipses using a device called a coronagraph, allowing scientists to study the corona outside of a total solar eclipse.
Hypothetical Experiment to Investigate Solar Activity and Terrestrial Events
A hypothetical experiment could investigate the relationship between solar activity and specific terrestrial events, such as auroras. Scientists could use ground-based instruments to measure the intensity and location of auroras during a total solar eclipse. They could then compare these measurements with data from space-based instruments, such as SOHO, to determine the specific solar events that triggered the auroras.
R&R Advertising is a well-known company in the industry. R And R Advertising 2024 offers insights into their latest strategies and campaigns.
Investigating the Sun’s Atmosphere
The Sun’s atmosphere is composed of several distinct layers, each with unique characteristics and playing a crucial role in solar activity and energy transport. A total solar eclipse provides a rare opportunity to study these layers in detail.
Halloween is just around the corner, and if you’re looking for costume inspiration, Halloween costume trends for 2024 has got you covered. Get ready for some spooky and creative ideas!
Layers of the Sun’s Atmosphere
| Layer | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Photosphere | The visible surface of the Sun, where light is emitted. |
| Chromosphere | A thin layer above the photosphere, characterized by reddish light. |
| Transition Region | A thin layer between the chromosphere and the corona, where temperature increases rapidly. |
| Corona | The outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, extending millions of kilometers into space. |
Studying the Chromosphere and Photosphere During a Total Solar Eclipse
During a total solar eclipse, the Moon blocks out the Sun’s bright photosphere, allowing scientists to study the fainter chromosphere and transition region. These layers are typically difficult to observe due to the overwhelming brightness of the photosphere. The eclipse provides a unique opportunity to study their structure, temperature, and composition in detail.
Visual Representation of the Sun’s Atmosphere
[A visual representation of the Sun’s atmosphere with labels for each layer. This would include a labeled diagram of the Sun showing the photosphere, chromosphere, transition region, and corona.]
Understanding Solar Physics through Observing the Sun’s Atmosphere
Observing the Sun’s atmosphere during a total solar eclipse provides valuable insights into solar physics, helping scientists understand:
- Energy transport:How energy is generated in the Sun’s core and transported through its atmosphere.
- Magnetic field dynamics:The role of magnetic fields in driving solar activity and heating the corona.
- Plasma behavior:The behavior of ionized gas (plasma) in the Sun’s atmosphere and its interaction with magnetic fields.
Testing General Relativity
Einstein’s theory of general relativity predicts that massive objects, like the Sun, warp the fabric of spacetime, causing light to bend around them. This phenomenon, known as gravitational lensing, can be observed during a total solar eclipse.
What’s next for Android? Next Android Update 2024 provides a glimpse into the future of Android, highlighting the upcoming features and improvements.
Observing the Bending of Light During a Total Solar Eclipse
During a total solar eclipse, stars that are normally behind the Sun become visible. Due to gravitational lensing, their light bends around the Sun, causing them to appear slightly displaced from their true positions. This effect can be measured by comparing the positions of these stars during the eclipse with their positions when the Sun is not in the way.
Are you having trouble connecting your Android device to Android Studio? Android Device Not Showing On Android Studio 2024 offers troubleshooting tips and solutions to get you back on track.
Validating Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity
The observation of gravitational lensing during a total solar eclipse provides strong evidence for Einstein’s theory of general relativity. This theory has been validated by numerous experiments and observations, making it the most accurate description of gravity we have today.
Comparing General Relativity with Other Theories of Gravity
While general relativity is the most widely accepted theory of gravity, other theories have been proposed. However, these theories have failed to explain the observed bending of light during a total solar eclipse as accurately as general relativity. This observation provides compelling evidence for the validity of Einstein’s theory.
Android advertising is constantly evolving. Android Extended Advertising 2024 provides an overview of the latest advancements and how they affect the advertising landscape.
Historical Experiments to Test General Relativity
The first successful test of general relativity using a total solar eclipse was conducted by Sir Arthur Eddington in 1919. He observed the bending of light from stars near the Sun during a total solar eclipse and found that the results matched Einstein’s predictions.
Since then, numerous other experiments have been conducted during total solar eclipses, further validating Einstein’s theory.
If you’re looking for the latest updates on Android, you’re in the right place! My Android Update 2024 provides all the information you need about the new features and improvements coming to your device.
Exploring the Earth’s Atmosphere: What Scientific Research Can Be Conducted During A Total Solar Eclipse?
A total solar eclipse provides a unique opportunity to study the Earth’s atmosphere as it reacts to the sudden change in solar radiation.
Earth’s Atmosphere’s Reaction to Solar Radiation Change
During a total solar eclipse, the Earth’s atmosphere experiences a rapid decrease in solar radiation. This change can cause various atmospheric phenomena, such as a drop in temperature and changes in wind patterns.
Looking for a practical example of Android BLE advertising? Android Ble Advertising Example Github 2024 offers a helpful guide and code snippets to get you started.
Atmospheric Phenomena Observable During a Total Solar Eclipse
Scientists can observe various atmospheric phenomena during a total solar eclipse, including:
- Temperature drop:The sudden decrease in solar radiation causes a noticeable drop in temperature.
- Wind changes:The change in solar heating can alter wind patterns, creating localized breezes.
- Cloud formation:The decrease in temperature can cause condensation and cloud formation.
Instruments Used to Study the Earth’s Atmosphere During a Total Solar Eclipse, What scientific research can be conducted during a total solar eclipse?
Scientists use various instruments to study the Earth’s atmosphere during a total solar eclipse, including:
- Weather balloons:To measure temperature, pressure, and humidity at different altitudes.
- Ground-based weather stations:To monitor temperature, wind speed, and direction.
- Radiosondes:To measure atmospheric conditions using radio signals.
Understanding Atmospheric Dynamics
Observing the Earth’s atmosphere during a total solar eclipse provides valuable insights into atmospheric dynamics, helping scientists understand:
- Radiative transfer:How solar radiation interacts with the atmosphere.
- Convection:The movement of air due to temperature differences.
- Cloud formation processes:The mechanisms that lead to cloud formation.
Conducting Astronomical Observations
A total solar eclipse provides a unique opportunity for astronomers to observe celestial objects that are normally obscured by the Sun’s glare.
Celestial Objects Visible During a Total Solar Eclipse
During a total solar eclipse, astronomers can observe various celestial objects, including:
- Stars:Stars that are normally hidden by the Sun’s light become visible during the eclipse.
- Planets:Planets, such as Venus, Mars, and Jupiter, can be observed during the eclipse.
- Comets:If a comet is visible in the sky during the eclipse, it can be observed in detail.
Unique Opportunities for Observing Celestial Objects
The eclipse provides unique opportunities for observing these objects due to the absence of the Sun’s light. Astronomers can use this time to study these objects in greater detail and with higher resolution than is possible during normal daytime conditions.
Want to advertise your business on Android phones? Advertising On Android Phone 2024 provides valuable insights and strategies to help you reach your target audience.
Types of Astronomical Observations
Astronomers can conduct various types of astronomical observations during a total solar eclipse, including:
- Photometry:Measuring the brightness of stars and planets.
- Spectroscopy:Analyzing the light emitted by celestial objects to determine their composition, temperature, and velocity.
- Astrometry:Measuring the positions of stars and planets.
Table of Astronomical Observations and Objectives
| Type of Observation | Objective |
|---|---|
| Photometry | To measure the brightness of stars and planets, providing information about their physical properties. |
| Spectroscopy | To analyze the light emitted by celestial objects, revealing their composition, temperature, and velocity. |
| Astrometry | To measure the positions of stars and planets, providing information about their motion and distances. |
Last Word
Total solar eclipses are more than just breathtaking spectacles; they are invaluable scientific laboratories. By harnessing the unique conditions created during these celestial events, scientists can unlock a wealth of knowledge about the sun, our planet, and the universe at large.
From studying the sun’s corona to observing the bending of light, each eclipse presents an opportunity to advance our understanding of the cosmos and the forces that govern it.
FAQs
How often do total solar eclipses occur?
Total solar eclipses happen at a particular location on Earth roughly every 375 years. However, somewhere on Earth, a total solar eclipse occurs about every 18 months.
What are the safety precautions for observing a total solar eclipse?
Never look directly at the sun without proper eye protection, as it can cause serious eye damage. Use certified solar eclipse glasses or viewers that meet international safety standards.
Are there any other scientific benefits of studying total solar eclipses?
Yes, eclipses also provide opportunities to study the Earth’s atmosphere, including changes in temperature, wind patterns, and atmospheric composition.
Ever wonder how Android uses advertising to fund its services? Android Enable Advertising 2024 delves into the details, explaining the process and its implications for users.