Calculating Annuity Present Value In Excel 2024 is a powerful tool for financial planning and investment decisions. Understanding how to calculate the present value of an annuity allows you to compare different investment options, make informed decisions about retirement savings, and even assess the affordability of loans.
Planning to invest a substantial amount in an annuity? This article explores the implications of investing $400,000 in an annuity.
This guide will walk you through the process of calculating annuity present value in Excel 2024, starting with the fundamental concepts and then diving into the practical application of Excel functions and spreadsheet design. We’ll explore the key input parameters, their impact on the final result, and how to interpret the calculated present value for financial decision-making.
Winning the lottery can be life-changing, and annuities are often used to manage lottery winnings. This article discusses how annuities work in lottery situations.
Contents List
- 1 Understanding Annuity Present Value
- 2 Excel Functions for Annuity Present Value Calculation
- 3 Setting Up the Excel Spreadsheet for Calculation
- 4 Input Parameters and Their Significance: Calculating Annuity Present Value In Excel 2024
- 5 Interpreting and Analyzing the Results
- 6 Additional Considerations and Scenarios
- 7 Conclusive Thoughts
- 8 Query Resolution
Understanding Annuity Present Value
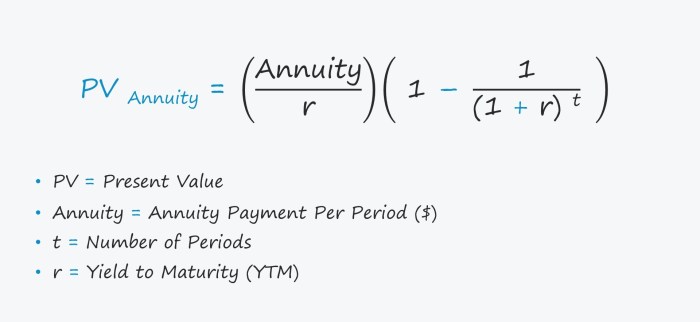
Annuity present value (PV) is the current worth of a series of future payments, discounted to reflect the time value of money. In simpler terms, it tells you how much a stream of future payments is worth today. This concept is crucial in various financial applications, including loan calculations, retirement planning, and investment analysis.
The IRR (Internal Rate of Return) is an important factor in evaluating annuities. This IRR calculator can help you determine the profitability of an annuity investment.
Factors Influencing Annuity Present Value
Several factors influence the present value of an annuity. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed financial decisions.
Annuity insurance is a popular option for retirement planning, but is it right for you? This article explores the pros and cons of annuity insurance in 2024.
- Interest Rate:A higher interest rate results in a lower present value. This is because the future payments are discounted at a higher rate, making them worth less today.
- Number of Payments:The more payments in an annuity, the higher the present value. This is because you receive more payments over time, increasing the overall value.
- Payment Amount:A larger payment amount naturally leads to a higher present value. The more you receive per payment, the more valuable the annuity becomes.
- Timing of Payments:The timing of payments also impacts the present value. Receiving payments sooner rather than later increases the present value because you have more time to earn interest on the funds.
Real-World Examples of Annuity Present Value Applications
Annuity present value has practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
- Loan Calculations:Banks use annuity present value to determine the loan amount based on the monthly payments you can afford. They calculate the present value of all future payments to arrive at the loan principal.
- Retirement Planning:Individuals use annuity present value to estimate the current value of their future retirement income. This helps them plan for their retirement needs and make informed investment decisions.
- Investment Analysis:Investors use annuity present value to evaluate the profitability of investments that generate regular cash flows. By comparing the present value of future cash flows to the initial investment cost, they can determine the investment’s attractiveness.
Excel Functions for Annuity Present Value Calculation
Microsoft Excel provides a convenient function, PV, to calculate the present value of an annuity. This function simplifies the complex calculations involved, making it easy to determine the present value of future payments.
Need a tool to calculate annuities for HL (Health and Life) insurance? This calculator can help you with your calculations.
Using the PV Function in Excel
The PV function in Excel takes several input parameters:
- Rate:The interest rate per period. This is usually the annual interest rate divided by the number of compounding periods per year.
- Nper:The total number of payment periods. This is the total number of payments in the annuity.
- Pmt:The payment amount per period. This is the constant amount paid each period.
- Fv:The future value, if any. This is the value of the annuity at the end of the payment period. In most cases, this is zero.
- Type:This argument indicates when payments are made. 0 indicates payments at the end of the period (ordinary annuity), and 1 indicates payments at the beginning of the period (annuity due).
The formula for the PV function is:
=PV(rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type])
Determining the right annuity amount for a specific timeframe is crucial. This article helps you calculate the annuity needed over a 12-year period.
Examples of Using the PV Function, Calculating Annuity Present Value In Excel 2024
Let’s consider some examples of using the PV function in Excel:
- Example 1:You are considering a loan with an annual interest rate of 5% for 5 years. The monthly payment is $ 500. To calculate the present value of the loan, you can use the following formula: =PV(0.05/12, 5*12, 500, 0, 0) This will return a present value of approximately $27,182.52.
Fixed annuities offer predictable income streams. This article explores the features and benefits of fixed annuities in 2024.
- Example 2:You are planning to invest in an annuity that pays $1,000 per year for 10 years. The annual interest rate is 4%. To calculate the present value of the annuity, you can use the following formula: =PV(0.04, 10, 1000, 0, 0) This will return a present value of approximately $7,360.09.
Looking for a monthly income of $1,000? This article explores how to achieve a $1,000 monthly annuity payment.
Adjusting the PV Function for Compounding Frequencies
The PV function assumes that interest is compounded annually by default. However, interest can be compounded more frequently, such as monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually. To adjust the PV function for different compounding frequencies, you need to modify the interest rate and the number of periods accordingly.
- Monthly Compounding:Divide the annual interest rate by 12 and multiply the number of periods by 12.
- Quarterly Compounding:Divide the annual interest rate by 4 and multiply the number of periods by 4.
- Semi-Annual Compounding:Divide the annual interest rate by 2 and multiply the number of periods by 2.
Setting Up the Excel Spreadsheet for Calculation
To calculate annuity present value in Excel, you can set up a simple spreadsheet with appropriate columns for input parameters. This organized approach helps ensure accuracy and ease of use.
Curious how much annuity you could get with a lump sum of $40,000? This article provides insights into annuity payouts for that amount.
Sample Excel Spreadsheet
Here’s a sample Excel spreadsheet structure for calculating annuity present value:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Interest Rate | [Enter Interest Rate] |
| Number of Periods | [Enter Number of Periods] |
| Payment Amount | [Enter Payment Amount] |
| Future Value | [Enter Future Value (if any)] |
| Payment Type | [Enter Payment Type (0 for end of period, 1 for beginning of period)] |
| Present Value | =PV(Interest Rate/Number of Compounding Periods per Year, Number of Periods
Annuities can play a role in retirement planning for 401(k) holders. This article explains how annuities can be incorporated into your 401(k) strategy.
|
This table provides a clear structure for entering input parameters and calculating the present value. You can easily adjust the values in the “Value” column to explore different scenarios and analyze the impact of changes on the present value.
Input Parameters and Their Significance: Calculating Annuity Present Value In Excel 2024
The input parameters used in the PV function are crucial for determining the annuity present value. Understanding the significance of each parameter helps you make informed financial decisions.
Key Input Parameters
- Interest Rate:This represents the rate at which future payments are discounted. A higher interest rate implies a higher discount rate, resulting in a lower present value.
- Number of Periods:This indicates the total number of payment periods in the annuity. A longer period generally leads to a higher present value, as more payments are received over time.
- Payment Amount:This represents the constant amount paid each period. A larger payment amount results in a higher present value.
- Future Value:This is the value of the annuity at the end of the payment period. In most cases, it is zero, but it can be non-zero if there is a lump sum payment at the end.
- Payment Type:This indicates whether payments are made at the beginning or end of the period. An annuity due (payments at the beginning) has a higher present value than an ordinary annuity (payments at the end).
Impact of Input Parameters on Present Value
Each input parameter has a direct impact on the calculated present value. For instance:
- Increasing the interest ratewill decrease the present value. This is because future payments are discounted at a higher rate, making them worth less today.
- Increasing the number of periodswill generally increase the present value, as more payments are received over time.
- Increasing the payment amountwill directly increase the present value.
- Adding a future valuewill increase the present value, as it represents an additional lump sum payment at the end of the annuity.
- Changing the payment typefrom an ordinary annuity to an annuity due will increase the present value, as payments are received earlier and have more time to earn interest.
Interpreting and Analyzing the Results
Once you have calculated the annuity present value in Excel, it’s essential to understand its meaning and implications for financial decision-making.
Downloadable Excel templates can make calculating annuities easier. This article offers links to useful Excel templates.
Interpreting the Present Value
The calculated present value represents the current worth of all future payments in the annuity, discounted to reflect the time value of money. It essentially tells you how much you would need to invest today to receive the same stream of future payments.
Want to understand the basics of annuity numbers? This article provides a clear explanation of annuity numbers.
Meaning of the Present Value Result
The present value result can be used in various financial contexts:
- Loan Calculations:The present value represents the loan principal, the amount you borrow from the lender.
- Retirement Planning:The present value estimates the current value of your future retirement income, helping you plan for your financial needs.
- Investment Analysis:The present value helps evaluate the profitability of investments that generate regular cash flows.
Using the Calculated Present Value for Decision-Making
The calculated present value provides valuable insights for making informed financial decisions:
- Loan Decisions:Comparing the present value of a loan to the amount you can afford to borrow helps you determine if the loan is financially viable.
- Investment Decisions:Comparing the present value of an investment’s future cash flows to the initial investment cost helps you assess the investment’s profitability.
- Retirement Planning:Understanding the present value of your future retirement income helps you plan for your financial needs and make necessary adjustments to your savings strategy.
Additional Considerations and Scenarios
Annuity present value calculations can be further explored with additional considerations and scenarios.
Implications of Different Interest Rates and Payment Periods
The present value is highly sensitive to changes in interest rates and payment periods.
Need to calculate your annuity payments? Calculator.Net’s annuity tool is a handy resource for making those calculations.
- Higher interest rateslead to lower present values, as future payments are discounted at a higher rate.
- Longer payment periodsgenerally result in higher present values, as more payments are received over time.
Annuity Present Value in Financial Planning and Investment Decisions
Annuity present value is a fundamental concept in financial planning and investment decisions.
Wondering how the annuity method works in 2024? This article breaks down the process and explains its significance in financial planning.
- Retirement Planning:Annuity present value helps determine the current value of your future retirement income, allowing you to plan for your financial needs and make necessary adjustments to your savings strategy.
- Investment Analysis:Annuity present value is used to evaluate the profitability of investments that generate regular cash flows, helping you make informed investment decisions.
Calculating Present Value for Annuities with Varying Payment Patterns
Annuity present value can be calculated for annuities with different payment patterns, such as:
- Growing Annuities:Annuities where payments increase at a constant rate over time. The present value of a growing annuity reflects the increasing value of future payments.
- Deferred Annuities:Annuities where payments begin after a certain period. The present value of a deferred annuity accounts for the delay in receiving payments.
Conclusive Thoughts
By mastering the calculation of annuity present value in Excel 2024, you gain valuable insights into the time value of money and its implications for financial planning. Whether you’re managing your personal finances, evaluating investment opportunities, or making critical business decisions, understanding this concept empowers you to make informed choices and maximize your financial outcomes.
Excel is a powerful tool for managing finances, including calculating annuities. This guide shows you how to calculate annuities on Excel.
Query Resolution
What is the difference between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due?
An ordinary annuity has payments made at the end of each period, while an annuity due has payments made at the beginning of each period. This difference affects the calculation of present value.
How do I account for inflation when calculating annuity present value?
You can adjust the discount rate used in the PV function to account for inflation. This requires estimating the future inflation rate and incorporating it into the discount rate.
Can I use the PV function for uneven cash flows?
The PV function is primarily designed for regular cash flows. For uneven cash flows, you can use the NPV function, which calculates the net present value of a series of cash flows.









