Formula Of Immediate Annuity, a financial instrument offering a steady stream of income for life, is a popular choice for retirees and individuals seeking guaranteed payments. This guide explores the intricacies of immediate annuities, delving into their calculation, factors influencing payments, and the diverse options available to suit individual needs.
It’s important to understand the tax implications of variable annuities. You can learn more about variable annuity taxability in 2024 here.
Immediate annuities provide a predictable income stream, transforming a lump sum into a series of regular payments. This can be a valuable tool for retirement planning, ensuring a steady source of income even in the absence of other investments. However, understanding the nuances of annuity calculations, payment options, and tax implications is crucial for making informed decisions.
Contents List
Understanding Immediate Annuities: Formula Of Immediate Annuity
An immediate annuity is a financial product that provides a stream of regular payments to an individual for life or for a specific period. These annuities are purchased with a lump sum payment, and payments begin immediately after the purchase.
Immediate annuities are often used by retirees to provide a guaranteed income stream for their retirement years.
Pioneer Vision 2 is a variable annuity product. If you’re considering this product, check out this website for more information on the Pioneer Vision 2 Variable Annuity in 2024.
Key Features of Immediate Annuities
Immediate annuities are characterized by several key features, including:
- Guaranteed Payments:Immediate annuities provide a guaranteed stream of payments, regardless of market fluctuations or the annuitant’s lifespan. This makes them a popular choice for those seeking financial security.
- Lump Sum Payment:Immediate annuities are purchased with a lump sum payment, which is used to fund the future annuity payments.
- Immediate Payments:Payments from an immediate annuity begin immediately after the purchase, providing an immediate source of income.
- Lifetime or Fixed Term:Immediate annuities can be structured to provide payments for the lifetime of the annuitant or for a specific period.
Types of Immediate Annuities
Immediate annuities come in several different types, each with its own features, benefits, and drawbacks. Here are some common types:
- Fixed Annuities:These annuities provide a fixed payment amount for the duration of the annuity. The payment amount is determined at the time of purchase and does not fluctuate with market conditions.
- Variable Annuities:Variable annuities offer payments that are linked to the performance of a specific investment portfolio. The payment amount can fluctuate based on the performance of the investments.
- Indexed Annuities:Indexed annuities offer payments that are linked to the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. The payment amount can fluctuate based on the performance of the index.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Immediate Annuities
Immediate annuities offer several benefits, including:
- Guaranteed Income Stream:Immediate annuities provide a guaranteed stream of income, which can be a valuable source of financial security.
- Longevity Protection:Immediate annuities can provide income for life, regardless of how long the annuitant lives. This can be particularly beneficial for those concerned about outliving their savings.
- Tax-Deferred Growth:The earnings on some immediate annuities grow tax-deferred, meaning that taxes are not paid until the annuity payments are received.
However, immediate annuities also have some drawbacks, including:
- Limited Flexibility:Once an immediate annuity is purchased, it can be difficult to change the payment amount or the payment schedule. This can limit the flexibility of the annuity.
- Potential for Lower Returns:The returns on immediate annuities may be lower than other investment options, particularly in periods of strong market growth.
- Loss of Principal:In some cases, the annuitant may not receive back the full amount of their initial investment, especially if they die before receiving all of their annuity payments.
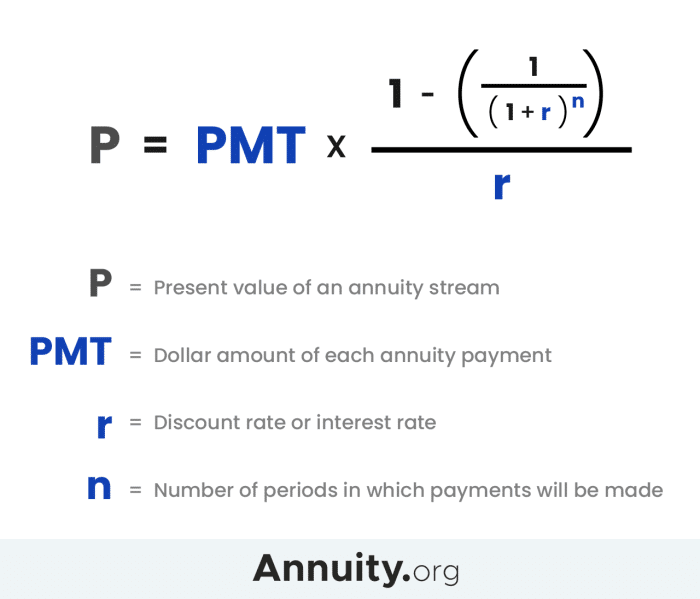
Calculating the Annuity Payment
The payment amount for an immediate annuity is determined by several factors, including the initial investment amount, the annuitant’s age and life expectancy, and the prevailing interest rates. The formula for calculating the immediate annuity payment is as follows:
Annuity Payment = (Initial Investment
- Interest Rate) / (1
- (1 + Interest Rate)^-Number of Payments)
Where:
- Initial Investment:The lump sum payment used to purchase the annuity.
- Interest Rate:The annual interest rate offered by the annuity provider.
- Number of Payments:The total number of payments the annuitant will receive, which is based on their life expectancy or the duration of the annuity contract.
Example Calculation
Suppose an individual invests $100,000 in an immediate annuity that offers an annual interest rate of 4%. If the annuitant is expected to receive payments for 20 years, the annuity payment would be calculated as follows:
Annuity Payment = ($100,000
An immediate annuity is a type of insurance contract that provides a guaranteed stream of income for life. If you’re curious about how it works, you can learn more about immediate annuities on this website.
- 0.04) / (1
- (1 + 0.04)^-20) = $7,358.18
Therefore, the annuitant would receive a monthly payment of $7,358.18 for the next 20 years.
Chapter 9 of many finance textbooks often covers annuities. If you’re interested in learning more about annuities from Chapter 9 in 2024 , this website may be helpful.
Factors Affecting Annuity Payment Amount
Several factors can affect the annuity payment amount, including:
- Interest Rates:Higher interest rates generally result in higher annuity payments, as the annuity provider can earn more on the initial investment.
- Life Expectancy:The annuitant’s life expectancy plays a significant role in determining the annuity payment amount. Individuals with longer life expectancies will receive lower payments to ensure that the annuity provider can afford to make payments for the entire duration of the annuity.
- Inflation:Inflation can erode the purchasing power of annuity payments over time. Some annuities offer inflation protection, which helps to offset the impact of inflation on the payment amount.
- Mortality Rates:The mortality rates of the annuitant’s age group also influence the annuity payment amount. If mortality rates are higher, the annuity provider can expect to make fewer payments, which may result in higher payments for the annuitant.
Factors Affecting Annuity Payments
The amount of an annuity payment is influenced by several key factors, each playing a crucial role in determining the final payout.
For those who prefer to use Excel for their calculations, an annuity calculator template can be helpful. You can find an annuity calculator Excel template in 2024 on this website.
Impact of Interest Rates
Interest rates have a direct impact on annuity payments. Higher interest rates generally lead to higher annuity payments, as the annuity provider can earn more on the initial investment. Conversely, lower interest rates result in lower annuity payments. This relationship is due to the principle of compounding interest, where the initial investment grows over time at a rate determined by the interest rate.
Understanding how growth affects the future value of an annuity is crucial for retirement planning. This website provides a guide to calculating the future value of an annuity with growth in 2024.
Role of Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is another critical factor in determining annuity payments. Individuals with longer life expectancies will generally receive lower annuity payments than those with shorter life expectancies. This is because the annuity provider needs to ensure that they have enough funds to make payments for the entire duration of the annuity, regardless of how long the annuitant lives.
Annuity rates can fluctuate over time. To learn more about annuity rates from 2021 to 2024 , this website provides useful information.
Life expectancy is often calculated based on the annuitant’s age, gender, and health status.
Variable annuities are subject to interest rate fluctuations. Find out more about variable annuity interest rates in 2024 here.
Other Influencing Factors
In addition to interest rates and life expectancy, other factors can also affect annuity payments:
- Inflation:Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. If inflation is high, the annuity payments may not be able to keep up with the rising cost of living. Some annuities offer inflation protection, which helps to offset the impact of inflation on the payment amount.
Transamerica offers a variable annuity called the B Share Variable Annuity. Learn more about the Transamerica B Share Variable Annuity in 2024 on this website.
- Mortality Rates:Mortality rates, which refer to the probability of death within a specific age group, also play a role in determining annuity payments. If mortality rates are higher, the annuity provider can expect to make fewer payments, which may result in higher payments for the annuitant.
A 401k is a retirement savings plan offered by employers. If you’re interested in learning more about annuities within a 401k in 2024 , this website has helpful information.
However, if mortality rates are lower, the annuity provider may need to make payments for a longer period, leading to lower payments for the annuitant.
Comparison of Factor Effects
Here’s a table summarizing the effects of different factors on annuity payments:
| Factor | Effect on Annuity Payment |
|---|---|
| Higher Interest Rates | Higher Payments |
| Lower Interest Rates | Lower Payments |
| Longer Life Expectancy | Lower Payments |
| Shorter Life Expectancy | Higher Payments |
| High Inflation | Lower Purchasing Power of Payments |
| Low Inflation | Higher Purchasing Power of Payments |
| Higher Mortality Rates | Higher Payments |
| Lower Mortality Rates | Lower Payments |
Types of Immediate Annuities
Immediate annuities come in various forms, each with its own unique features, advantages, and disadvantages. Understanding these different types is crucial for choosing the annuity that best aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Fixed Annuities
Fixed annuities offer a guaranteed, fixed payment amount for the duration of the annuity. The payment amount is determined at the time of purchase and does not fluctuate with market conditions. This makes them an attractive option for individuals seeking predictable income and protection from market volatility.
- Advantages:
- Guaranteed, predictable income stream.
- Protection from market downturns.
- Suitable for risk-averse individuals.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited potential for growth.
- Returns may not keep pace with inflation.
- May not be suitable for individuals seeking higher returns.
Variable Annuities
Variable annuities offer payments that are linked to the performance of a specific investment portfolio. The payment amount can fluctuate based on the performance of the investments. This type of annuity provides the potential for higher returns but also carries greater risk.
A handy tool for calculating the future value of an annuity is a dedicated calculator. You can find an FV calculator for annuities in 2024 here.
- Advantages:
- Potential for higher returns.
- Greater investment flexibility.
- Suitable for individuals with higher risk tolerance.
- Disadvantages:
- Payments are not guaranteed and can fluctuate.
- Greater risk of losing principal.
- May not be suitable for individuals seeking predictable income.
Indexed Annuities
Indexed annuities offer payments that are linked to the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. The payment amount can fluctuate based on the performance of the index, but there is typically a minimum guaranteed return.
Immediate annuities can offer a guaranteed stream of income, but they also have drawbacks. You can find a detailed explanation of immediate annuity disadvantages here.
This type of annuity provides a balance between potential growth and downside protection.
An immediate annuity starts payments right away, while an annuity due has a payment period at the beginning of each period. To understand the difference between these two types, check out this article on immediate annuities and annuities due.
- Advantages:
- Potential for growth linked to market performance.
- Downside protection with a minimum guaranteed return.
- Suitable for individuals seeking a balance between growth and security.
- Disadvantages:
- Returns may be limited by the index’s performance.
- May not offer as much growth potential as variable annuities.
- May have complex features and fees.
Annuity Types Comparison
Here’s a table summarizing the different types of immediate annuities:
| Type | Features | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Annuity | Guaranteed, fixed payments | Predictable income, protection from market volatility | Limited growth potential, returns may not keep pace with inflation |
| Variable Annuity | Payments linked to investment portfolio performance | Potential for higher returns, greater investment flexibility | Payments are not guaranteed and can fluctuate, greater risk of losing principal |
| Indexed Annuity | Payments linked to market index performance, with a minimum guaranteed return | Potential for growth linked to market performance, downside protection | Returns may be limited by the index’s performance, may not offer as much growth potential as variable annuities |
Annuity Payment Options
Immediate annuities offer various payment options, allowing you to choose a schedule that best suits your needs and financial goals. Understanding these options is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your annuity and ensuring a steady stream of income.
Payment Frequency Options
Annuity payments can be received at different frequencies, such as:
- Monthly Payments:This is the most common payment frequency, providing a consistent monthly income stream. It’s suitable for individuals who prefer regular, predictable income.
- Quarterly Payments:Payments received every three months offer a balance between frequency and lump sum amounts. This option might be suitable for individuals who need larger, less frequent payments.
- Annual Payments:Receiving payments once a year provides the largest lump sum amount but less frequent income. This option might be suitable for individuals who can manage their finances effectively and have a lower need for frequent income.
Pros and Cons of Payment Options, Formula Of Immediate Annuity
Each payment option has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Monthly Payments:
- Pros:Consistent, predictable income stream.
- Cons:Lower lump sum amount per payment.
- Quarterly Payments:
- Pros:Balance between frequency and lump sum amount.
- Cons:Less frequent income stream.
- Annual Payments:
- Pros:Largest lump sum amount per payment.
- Cons:Least frequent income stream.
Impact of Payment Options on Total Payout
The payment frequency chosen can affect the total annuity payout over time. While the total amount received remains the same, the timing of payments can impact the overall value, considering factors like inflation and investment opportunities. For instance, receiving annual payments might allow for greater investment potential but could be impacted by inflation’s effect on the purchasing power of the lump sum amount.
If you need to access funds from your variable annuity, you may be able to request a hardship withdrawal. For more information on variable annuity hardship withdrawals in 2024 , this resource can help.
Suitability for Different Individuals
The most suitable payment option depends on individual needs and circumstances:
| Payment Option | Features | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Payments | Frequent, consistent income | Individuals needing regular, predictable income |
| Quarterly Payments | Balance between frequency and lump sum amount | Individuals needing larger, less frequent payments |
| Annual Payments | Largest lump sum amount, least frequent income | Individuals who can manage finances effectively and have a lower need for frequent income |
Final Thoughts
Immediate annuities offer a compelling way to secure a reliable income stream, but careful consideration of individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and tax implications is essential. Understanding the various factors influencing annuity payments and exploring different payment options allows individuals to tailor their annuity to their specific needs, maximizing the benefits and ensuring a comfortable financial future.
Annuity drawdown is a popular way to access your retirement savings, allowing you to withdraw money as needed. To see if annuity drawdown is right for you, check out this article on annuity drawdown in 2024.
Clarifying Questions
What are the potential downsides of immediate annuities?
While immediate annuities offer guaranteed income, they also come with some potential downsides. For instance, the initial investment is locked in, limiting access to funds. Additionally, interest rates can affect the return on the annuity, and early withdrawal penalties may apply.
How do I choose the right type of immediate annuity?
The best type of immediate annuity depends on your individual circumstances and risk tolerance. Fixed annuities offer guaranteed payments, while variable annuities provide potential growth but come with market risk. Indexed annuities offer a combination of guaranteed payments and potential growth linked to a specific index.
How do taxes affect immediate annuity payments?
A portion of each annuity payment is generally considered taxable income. The specific tax treatment depends on the type of annuity and whether it was purchased with pre-tax or after-tax dollars. Consulting with a tax professional can help you understand the tax implications of your specific annuity.









