How To Find Annuity Formula 2024 is a comprehensive guide that delves into the intricacies of annuities, demystifying their workings and empowering you to confidently navigate this essential financial tool. Annuities, essentially a series of regular payments over a specified period, are a powerful instrument for securing your financial future, whether you’re planning for retirement, saving for a major purchase, or simply seeking a steady stream of income.
In some cases, an annuity is reversionary 2024 , meaning it pays out to a beneficiary after the original annuitant passes away. This can be a helpful tool for estate planning, ensuring your loved ones are taken care of after you’re gone.
This guide will walk you through the fundamentals of annuities, exploring their different types, the key variables that influence their calculations, and the various formulas used to determine their present and future values. We’ll also discuss the practical applications of annuities in real-world scenarios, providing insights into how they can be leveraged to achieve your financial goals.
Contents List
Understanding Annuities: How To Find Annuity Formula 2024
An annuity is a financial product that provides a series of regular payments over a set period of time. Annuities can be used for a variety of purposes, such as retirement planning, income generation, and estate planning. There are many different types of annuities, each with its own unique features and benefits.
There are many different types of annuities available, each with its own unique features. Understanding the 4 annuity 2024 can help you make an informed decision about which type is right for you.
Understanding the different types of annuities and their characteristics can help you make informed decisions about your financial future.
Types of Annuities
Annuities can be categorized based on various factors, such as the payment structure, the investment options, and the timing of payments. Here are some common types of annuities:
- Fixed Annuities:These annuities guarantee a fixed rate of return, providing predictable income payments. The payments are typically based on a predetermined interest rate, which remains constant throughout the annuity period. Fixed annuities offer stability and security, but they may not provide the potential for high returns.
- Variable Annuities:Variable annuities offer the potential for higher returns, but they also come with greater risk. The payments are linked to the performance of a specific investment portfolio, such as a mutual fund or stock index. The value of the annuity can fluctuate with market conditions, and there is no guarantee of returns.
- Immediate Annuities:Immediate annuities begin making payments immediately after the purchase. These annuities are ideal for those who need immediate income, such as retirees or individuals who have recently received a lump sum payment.
- Deferred Annuities:Deferred annuities start making payments at a future date, such as at retirement. These annuities allow individuals to accumulate funds over time and then receive income payments later in life. Deferred annuities are a popular choice for long-term retirement planning.
Purpose and Benefits of Annuities
Annuities can serve various financial goals, offering several benefits:
- Guaranteed Income:Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed stream of income, ensuring a steady flow of payments for a specified period. This can be particularly valuable for retirees who need a reliable source of income.
- Tax Advantages:Annuity payments are typically taxed as ordinary income, but the growth of the annuity’s value is tax-deferred. This means that you won’t have to pay taxes on the earnings until you start receiving payments.
- Longevity Protection:Annuities can provide longevity protection, ensuring that you have income for as long as you live. Some annuities offer lifetime income guarantees, which can be beneficial if you live longer than expected.
- Estate Planning:Annuities can be used as part of an estate plan to provide income for beneficiaries after your death. Some annuities offer death benefits that can be paid to your heirs.
Risks Associated with Annuities
While annuities offer potential benefits, it’s important to understand the risks involved:
- Market Risk:Variable annuities are subject to market risk, meaning that the value of your annuity can fluctuate with market conditions. You could lose money if the investments in your annuity portfolio perform poorly.
- Interest Rate Risk:Fixed annuities are subject to interest rate risk. If interest rates rise after you purchase a fixed annuity, your annuity may become less attractive compared to other investment options.
- Fees and Expenses:Annuities can come with a variety of fees and expenses, such as surrender charges, administrative fees, and mortality and expense charges. These fees can erode your returns over time.
- Lack of Liquidity:Annuities are generally illiquid, meaning that you may not be able to access your money easily if you need it. Some annuities have surrender charges that apply if you withdraw funds before a certain period.
Key Annuity Variables
The calculation of annuity payments and values involves several key variables that influence the outcome. Understanding these variables is crucial for making informed decisions about annuities.
Primary Variables in Annuity Calculations
- Principal Amount (PV):This is the initial amount of money invested in the annuity. The principal amount serves as the foundation for future annuity payments and calculations.
- Interest Rate (r):The interest rate represents the annual rate of return earned on the annuity investment. A higher interest rate generally leads to larger annuity payments or a higher future value.
- Payment Period (n):This refers to the number of periods over which annuity payments are made. The payment period can be monthly, quarterly, annually, or based on other time intervals.
- Time Horizon (t):The time horizon represents the total duration of the annuity contract, indicating the length of time over which annuity payments are made. A longer time horizon generally results in larger accumulated values.
Impact of Variables on Annuity Formula
Each variable plays a significant role in determining the outcome of annuity calculations. For example, a higher principal amount will result in larger annuity payments or a higher future value. Similarly, a higher interest rate will also lead to larger payments or a higher future value.
The number of payment periods and the time horizon also directly impact the calculations.
Winning the lottery can be a life-changing event, but it’s important to consider the long-term implications. An annuity lottery 2024 can provide a structured and reliable income stream for years to come, allowing you to manage your winnings wisely and avoid financial pitfalls.
Annuity Formula Variations
The basic annuity formula can be modified to account for different scenarios and variations in payment structures. Here are some common variations of the annuity formula:
Simple Annuity Formula
The basic annuity formula calculates the present value (PV) of an annuity, given the periodic payment amount (PMT), the interest rate (r), and the number of periods (n). The formula is as follows:
PV = PMT
Not all annuities are created equal. Understanding whether an annuity is qualified 2024 can help you maximize tax advantages and make the most of your retirement savings. Qualified annuities offer specific tax benefits, so it’s crucial to understand these distinctions when making your financial decisions.
- [(1
- (1 + r)^-n) / r]
This formula assumes that payments are made at the end of each period. For example, if you want to calculate the present value of an annuity that pays $1,000 per year for 10 years, with an interest rate of 5%, the formula would be:
PV = $1,000
If you’re looking for a way to guarantee a steady stream of income in retirement, an annuity 400k 2024 might be a good option for you. These annuities provide a fixed amount of income for a specific period of time, offering peace of mind knowing you’ll have financial stability in your later years.
- [(1
- (1 + 0.05)^-10) / 0.05] = $7,721.73
This means that the present value of the annuity is $7,721.73. This is the amount you would need to invest today at a 5% interest rate to receive $1,000 per year for 10 years.
Tax implications are an important factor when considering any financial product. In India, you might wonder, “Is annuity income taxable in India 2024 ?” Understanding the tax treatment of annuities in your specific location is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Compound Annuity Formula
The compound annuity formula calculates the future value (FV) of an annuity, given the periodic payment amount (PMT), the interest rate (r), and the number of periods (n). The formula is as follows:
FV = PMT
Annuity income can be a valuable source of financial security in retirement. But it’s important to understand how it’s treated for tax purposes. If you’re unsure about “Is annuity income 2024 ?” it’s best to seek professional advice to ensure you’re making informed financial decisions.
- [((1 + r)^n
- 1) / r]
For example, if you want to calculate the future value of an annuity that pays $1,000 per year for 10 years, with an interest rate of 5%, the formula would be:
FV = $1,000
Whether you’re in India or another country, understanding the tax implications of annuities is essential. If you’re wondering, “Is annuity income taxable 2024 ?” it’s best to consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to determine the specific tax treatment in your jurisdiction.
For those who follow Islamic principles, it’s important to ensure financial products align with their beliefs. If you’re considering an annuity, you might wonder, “Is annuity halal 2024 ?” Researching the specific terms and conditions of an annuity is crucial to determine its compliance with Islamic law.
- [((1 + 0.05)^10
- 1) / 0.05] = $12,577.89
This means that the future value of the annuity is $12,577.89. This is the amount you would have at the end of 10 years if you invested $1,000 per year at a 5% interest rate.
Annuity Due Formula
The annuity due formula calculates the present value (PV) of an annuity where payments are made at the beginning of each period. The formula is as follows:
PV = PMT
- [(1
- (1 + r)^-n) / r]
- (1 + r)
For example, if you want to calculate the present value of an annuity due that pays $1,000 per year for 10 years, with an interest rate of 5%, the formula would be:
PV = $1,000
- [(1
- (1 + 0.05)^-10) / 0.05]
- (1 + 0.05) = $8,116.81
This means that the present value of the annuity due is $8,116.81. This is the amount you would need to invest today at a 5% interest rate to receive $1,000 per year for 10 years, with payments made at the beginning of each year.
The annuity 2000 mortality table 2024 is a key factor in determining annuity rates. It provides data on life expectancy, which helps insurance companies calculate the cost of providing annuity payments. Understanding this table can give you insight into how annuity rates are determined.
Perpetuity Formula
A perpetuity is an annuity that continues forever. The formula for calculating the present value of a perpetuity is as follows:
PV = PMT / r
Annuities come in a variety of forms, each designed to meet different needs and financial goals. To make the best decision for your situation, it’s important to understand the various annuity kinds 2024 available. Whether you prefer a fixed income stream or a more flexible option, there’s an annuity out there for you.
For example, if you want to calculate the present value of a perpetuity that pays $1,000 per year, with an interest rate of 5%, the formula would be:
PV = $1,000 / 0.05 = $20,000
This means that the present value of the perpetuity is $20,000. This is the amount you would need to invest today at a 5% interest rate to receive $1,000 per year forever.
The world of annuities can be complex, with various types and features to consider. Exploring the 9 annuity 2024 can help you understand the different options available and choose the best fit for your needs.
Calculating Annuity Payments
The annuity formula can be rearranged to solve for the periodic payment amount (PMT), given the present value (PV), the interest rate (r), and the number of periods (n). This calculation is useful for determining the amount of income you can expect from an annuity or the amount you need to contribute to reach a specific financial goal.
Calculating Periodic Payment Amount
To calculate the periodic payment amount, we can use the following formula:
PMT = PV
If you’re in Canada and considering an annuity, it’s helpful to use a tool that can calculate your potential income stream. An annuity calculator Canada 2024 can provide you with a personalized estimate of your future income, allowing you to plan for retirement with greater confidence.
- [r / (1
- (1 + r)^-n)]
For example, if you want to calculate the periodic payment amount for an annuity with a present value of $100,000, an interest rate of 4%, and a time horizon of 20 years, the formula would be:
PMT = $100,000
- [0.04 / (1
- (1 + 0.04)^-20)] = $7,358.18
This means that the periodic payment amount for this annuity would be $7,358.18. This is the amount you would receive each year for 20 years if you invested $100,000 today at a 4% interest rate.
The primary purpose of an annuity is primarily used to provide 2024 a consistent income stream during retirement. They can also serve as a valuable tool for estate planning, ensuring your loved ones are financially secure after you’re gone.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify the known variables:Determine the present value (PV), the interest rate (r), and the number of periods (n).
- Plug the variables into the formula:Substitute the known values into the formula for calculating the periodic payment amount.
- Solve for PMT:Perform the calculations to determine the periodic payment amount.
Calculating Future Value of an Annuity
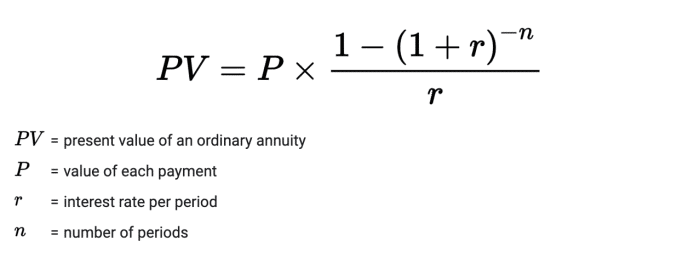
The future value of an annuity represents the total amount of money you will have at the end of the annuity period, including both the principal amount and the accumulated interest. Calculating the future value is essential for financial planning, as it allows you to estimate the amount of money you will have available for retirement, investment, or other purposes.
Calculating Future Value
The formula for calculating the future value (FV) of an annuity is as follows:
FV = PMT
- [((1 + r)^n
- 1) / r]
For example, if you want to calculate the future value of an annuity that pays $1,000 per year for 10 years, with an interest rate of 5%, the formula would be:
FV = $1,000
- [((1 + 0.05)^10
- 1) / 0.05] = $12,577.89
This means that the future value of the annuity is $12,577.89. This is the amount you would have at the end of 10 years if you invested $1,000 per year at a 5% interest rate.
Financial Planning Applications, How To Find Annuity Formula 2024
The future value of an annuity can be used for various financial planning purposes:
- Retirement Planning:By calculating the future value of your retirement savings, you can estimate the amount of income you will have available in retirement.
- Investment Strategies:The future value of an annuity can help you evaluate different investment options and make informed decisions about your investment portfolio.
- College Savings:You can use the future value formula to calculate the amount of money you need to save to pay for your child’s college education.
Calculating Present Value of an Annuity
The present value of an annuity represents the current value of a stream of future payments, discounted back to the present using a specific interest rate. Calculating the present value is essential for financial decision-making, as it allows you to compare different investment options and make informed choices based on their present worth.
Annuity rates can fluctuate over time, influenced by various factors. If you’re interested in understanding the trends in annuity rates, researching the annuity rates 2021 2024 can provide valuable insights. This information can help you make informed decisions about when to purchase an annuity and how to maximize your returns.
Calculating Present Value
The formula for calculating the present value (PV) of an annuity is as follows:
PV = PMT
- [(1
- (1 + r)^-n) / r]
For example, if you want to calculate the present value of an annuity that pays $1,000 per year for 10 years, with an interest rate of 5%, the formula would be:
PV = $1,000
- [(1
- (1 + 0.05)^-10) / 0.05] = $7,721.73
This means that the present value of the annuity is $7,721.73. This is the amount you would need to invest today at a 5% interest rate to receive $1,000 per year for 10 years.
Financial Decision-Making Applications
The present value of an annuity can be used for various financial decision-making purposes:
- Investment Comparisons:By calculating the present value of different investment options, you can compare their current worth and make informed decisions about where to allocate your funds.
- Loan Repayments:The present value formula can be used to calculate the present value of a loan, which can help you determine the total cost of borrowing.
- Business Valuations:In business, the present value of an annuity can be used to value assets that generate a stream of future income, such as rental properties or patents.
Annuity Calculators and Tools
Several online annuity calculators and tools are available to assist individuals in calculating annuity payments, future values, and present values. These calculators can save time and effort, providing quick and accurate results.
Availability and Use of Annuity Calculators
Annuity calculators are readily accessible online, often provided by financial institutions, insurance companies, and independent financial websites. These calculators typically require you to input the key variables, such as the principal amount, interest rate, payment period, and time horizon. Once you enter the information, the calculator will generate the desired output, such as the periodic payment amount, future value, or present value.
Popular Resources and Features
Some popular online annuity calculators include:
- Bankrate:This website offers a comprehensive annuity calculator that allows you to calculate various annuity types, including fixed, variable, and immediate annuities. The calculator provides detailed results, including the future value, present value, and periodic payment amount.
- Investopedia:Investopedia provides an annuity calculator that allows you to compare different annuity options based on their interest rates, fees, and guarantees. The calculator also provides information about the tax implications of annuities.
- Financial Calculators:Many financial institutions and insurance companies offer their own annuity calculators on their websites. These calculators may be specific to their own annuity products, providing detailed information about their features and benefits.
Last Point
By understanding the principles behind annuity calculations, you can confidently make informed decisions about incorporating annuities into your financial strategy. Whether you’re seeking to maximize your retirement savings, protect your assets from market fluctuations, or simply gain a deeper understanding of this financial instrument, the knowledge gained from this guide will equip you to make sound financial choices.
FAQ Explained
What are the main types of annuities?
There are several types of annuities, including fixed, variable, immediate, and deferred. Each type has its own unique features and risks.
How do I choose the right annuity for my needs?
The best annuity for you depends on your individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. It’s important to consult with a financial advisor to determine the most suitable option.
What are the tax implications of annuities?
Tax implications vary depending on the type of annuity and how it’s structured. It’s essential to understand the tax treatment of your specific annuity before making any decisions.
Are there any risks associated with annuities?
Yes, annuities do carry certain risks, such as the potential for low returns, the risk of losing principal, and the possibility of outliving your annuity payments. It’s crucial to carefully consider these risks before investing in an annuity.









