Immediate Annuity And Annuity Due are crucial financial tools that provide a steady stream of income during retirement. These annuities, unlike traditional investments, offer guaranteed payments for life, eliminating the uncertainty of market fluctuations. Understanding the nuances of immediate annuities and annuities due empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their retirement income strategy.
Immediate annuities offer immediate payments upon purchase, while annuities due provide payments at the beginning of each period. The choice between the two hinges on individual needs and financial goals. Factors such as age, life expectancy, and risk tolerance influence the decision-making process.
By carefully considering these factors, individuals can select the annuity that best aligns with their retirement objectives.
Surrendering a variable annuity can have tax implications. Learn about the process of surrendering a variable annuity and the potential tax consequences: Variable Annuity Out Of Surrender 2024.
Contents List
Introduction to Annuities
An annuity is a financial product that provides a stream of regular payments over a specified period of time. It is a popular tool for retirement planning, as it can provide a steady income stream during retirement years. Annuities are particularly attractive to individuals seeking to protect their savings from market volatility and ensure a consistent income source.
Annuity King is a leading provider of annuity solutions in Sarasota, Florida. Learn about their services and how they can help you secure your financial future: Annuity King Sarasota 2024.
This article delves into the different types of annuities, with a focus on immediate annuities and annuities due, exploring their features, advantages, and considerations.
Considering an annuity for your retirement savings? It’s natural to be concerned about safety. Explore the factors that contribute to annuity safety and learn about the different types of annuities available: Is Annuity Safe 2024.
Types of Annuities
Annuities can be broadly classified into two main categories: fixed annuities and variable annuities.
When you inherit an annuity, it’s essential to know how it’s taxed. The tax implications can vary depending on the type of annuity and your personal circumstances. Get detailed information on how inherited annuities are taxed: How Is Inherited Annuity Taxed 2024.
- Fixed Annuities: These annuities offer guaranteed payments based on a fixed interest rate. The payments are predictable and do not fluctuate with market performance. Fixed annuities provide stability and security but may offer lower returns compared to variable annuities.
- Variable Annuities: These annuities offer payments that are linked to the performance of a specific investment portfolio. The returns are not guaranteed and can fluctuate with market conditions. Variable annuities offer potential for higher returns but also carry greater risk.
Within these categories, annuities can be further classified based on the timing of payments, including:
- Immediate Annuities: These annuities begin paying out immediately after the initial lump sum payment is made.
- Deferred Annuities: These annuities begin paying out at a later date, often after a specific period of time or upon reaching a certain age.
- Annuities Due: These annuities are similar to immediate annuities but have a crucial distinction: payments are made at the beginning of each period instead of at the end.
Real-World Examples of Annuity Use
Annuities are used in various real-world situations, such as:
- Retirement Income: Annuities provide a consistent income stream during retirement, supplementing other sources like pensions and savings.
- Estate Planning: Annuities can be used to create a legacy by providing income for beneficiaries after the annuitant’s death.
- Long-Term Care: Annuities can help cover the costs of long-term care expenses, such as nursing home care or assisted living.
- Income Protection: Annuities can provide a guaranteed income stream even if an individual becomes disabled or experiences a job loss.
Immediate Annuities
Immediate annuities, also known as single premium immediate annuities (SPIAs), are a type of annuity that begins paying out immediately after the initial lump sum payment is made. This makes them an attractive option for individuals who need a steady income stream right away, such as retirees or those who have received a large sum of money.
NSDL is a leading depository in India. Find out if they offer an annuity calculator and explore the tools available for managing your annuity investments: Annuity Calculator Nsdl 2024.
How Immediate Annuities Work, Immediate Annuity And Annuity Due
The process of purchasing an immediate annuity involves:
- Lump Sum Payment: The individual makes a one-time lump sum payment to the insurance company.
- Annuity Contract: The individual and the insurance company sign an annuity contract outlining the terms of the agreement, including the payment amount, frequency, and duration.
- Regular Payments: The insurance company begins making regular payments to the individual according to the agreed-upon schedule.
Advantages of Immediate Annuities
- Guaranteed Income: Immediate annuities provide a guaranteed income stream, regardless of market fluctuations.
- Longevity Protection: Payments continue for the life of the annuitant, ensuring income even if they live longer than expected.
- Tax Advantages: Annuity payments are typically taxed as ordinary income, but the tax burden can be managed strategically.
Disadvantages of Immediate Annuities
- Irreversible Decision: Once the lump sum is paid, the annuity contract is typically irreversible, meaning the individual cannot access the principal amount.
- Limited Flexibility: The payment amount and frequency are fixed at the time of purchase, limiting flexibility in future years.
- Interest Rate Risk: If interest rates rise after the annuity is purchased, the individual may receive a lower return than they could have obtained by investing elsewhere.
Comparison with Other Retirement Income Options
| Feature | Immediate Annuity | 401(k) or IRA | Pension | Social Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guaranteed Income | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Longevity Protection | Yes | No | May vary | Yes |
| Flexibility | Limited | High | Limited | Limited |
| Tax Advantages | Yes | Yes | May vary | Yes |
| Risk | Low | High | Low | Low |
Annuity Due
An annuity due is a type of annuity where payments are made at the beginning of each period, rather than at the end, as is the case with an immediate annuity. This distinction has important implications for the timing and value of payments.
Annuity payments can grow over time, providing a steady stream of income during retirement. Understanding how to calculate a growing annuity is crucial for financial planning. Learn about the key factors involved and the formulas used in this informative guide: Calculating Growing Annuity 2024.
Key Characteristics of an Annuity Due
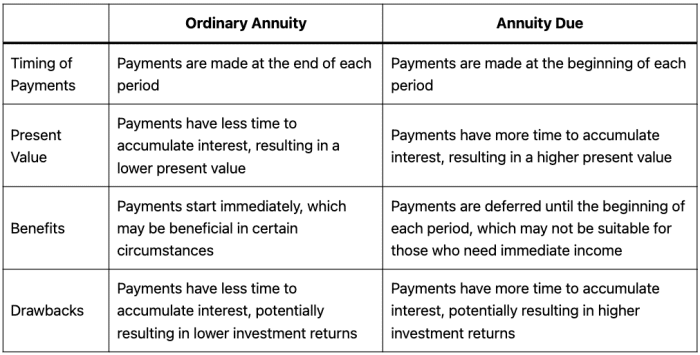
- First Payment at the Beginning: The first payment is made immediately upon the purchase of the annuity, before the first period even begins.
- Payments at the Start of Each Period: Subsequent payments are made at the beginning of each subsequent period, ensuring that the individual receives the payment before any interest is accrued.
Difference Between an Immediate Annuity and an Annuity Due
The main difference between an immediate annuity and an annuity due lies in the timing of payments. An immediate annuity makes its first payment at the end of the first period, while an annuity due makes its first payment at the beginning of the first period.
Variable annuities offer the potential for growth, but they also carry some risk. Understand the basics of variable annuities, including their features, benefits, and drawbacks: Variable Annuity Basics 2024.
This difference can have a significant impact on the overall value of the annuity, as the payments in an annuity due are effectively “compounded” for one extra period.
Variable annuities can provide a range of benefits, including the potential for higher returns. Explore the advantages of variable annuities and how they can fit into your retirement planning: Variable Annuity Advantages 2024.
Payment Schedules
The payment schedules for immediate annuities and annuities due are different. Here is a simple illustration:
- Immediate Annuity: Payment at the end of each period (e.g., end of month, end of year).
- Annuity Due: Payment at the beginning of each period (e.g., beginning of month, beginning of year).
Factors Influencing Choice Between Immediate Annuity and Annuity Due
The choice between an immediate annuity and an annuity due depends on several factors, including:
- Investment Goals: If the individual seeks to maximize the overall value of their annuity, an annuity due may be a better option due to the compounding effect.
- Cash Flow Needs: If the individual requires a payment immediately, an annuity due may be more suitable as it provides an upfront payment.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates tend to favor annuities due, as the compounding effect becomes more pronounced.
Calculating Annuity Payments
Calculating annuity payments requires understanding the specific characteristics of the annuity, including the present value (PV), the interest rate (r), and the number of periods (n).
Variable annuities come in various plans, each with its own features and benefits. Explore the different types of variable annuity plans and choose the one that best suits your needs: Variable Annuity Plans 2024.
Formulas for Calculating Annuity Payments
- Immediate Annuity:
Payment = PV- r / (1 – (1 + r)^-n)
Annuity and IRA are both retirement savings vehicles, but they have distinct features. Find out if an annuity is the same as an IRA and explore the differences between these two popular retirement savings options: Is Annuity Same As Ira 2024.
- Annuity Due:
Payment = PV- r – (1 + r) / (1 – (1 + r)^-n)
Annuity income can provide a steady stream of cash flow during retirement. Discover eight valuable secrets to maximizing your annuity income and achieving your financial goals: 8 Annuity Income Secret 2024.
Real-World Examples
Let’s consider a scenario where an individual has $100,000 to invest in an annuity. The interest rate is 5%, and the annuity will pay out for 20 years. Here’s how to calculate the annuity payments:
- Immediate Annuity:
Payment = $100,000- 0.05 / (1 – (1 + 0.05)^-20) = $7,950.37 per year
Annuity income can be a valuable source of retirement income, but it’s important to understand how it’s taxed. Find out if your annuity income is exempt from taxes and explore the implications for your financial planning: Is Annuity Exempt From Tax 2024.
- Annuity Due:
Payment = $100,000- 0.05 – (1 + 0.05) / (1 – (1 + 0.05)^-20) = $8,347.88 per year
Annuity Payment Scenarios
| Scenario | PV | r | n | Immediate Annuity Payment | Annuity Due Payment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | $50,000 | 4% | 15 | $4,163.47 | $4,331.73 |
| Scenario 2 | $150,000 | 6% | 10 | $21,243.39 | $22,506.13 |
| Scenario 3 | $200,000 | 3% | 25 | $11,571.25 | $11,908.79 |
Factors Affecting Annuity Payments: Immediate Annuity And Annuity Due
Several factors influence the amount of annuity payments an individual receives. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their annuity choices.
Factors and Their Impact
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates generally lead to higher annuity payments. When interest rates are high, insurance companies can afford to pay out more to annuitants.
- Age: Younger annuitants typically receive lower payments than older annuitants. This is because younger individuals have a longer life expectancy, meaning the insurance company has to pay out for a longer period.
- Life Expectancy: Individuals with a longer life expectancy generally receive lower annuity payments. This is because the insurance company needs to spread the payments over a longer period.
- Gender: Women generally receive lower annuity payments than men. This is because women typically have a longer life expectancy.
- Health: Individuals with good health generally receive higher annuity payments. This is because they are expected to live longer, meaning the insurance company has to pay out for a longer period.
- Annuity Type: Different types of annuities, such as fixed annuities and variable annuities, offer different payment structures and potential returns.
Relationship Between Factors and Annuity Payments
The flowchart below illustrates the relationship between various factors and annuity payments.
[Flowchart depicting the relationship between factors such as interest rates, age, life expectancy, and annuity payments. The flowchart should show how these factors influence the overall value of an annuity.]
Tax Implications of Annuities
The tax treatment of annuity payments can vary depending on the type of annuity and the specific terms of the contract. It’s essential to understand the tax implications before purchasing an annuity.
Want to calculate the future value of a growing annuity? You can easily do so using the BA II Plus calculator. Learn how to calculate growing annuities on your BA II Plus calculator in this comprehensive guide: Calculate Growing Annuity Ba Ii Plus 2024.
Tax Treatment of Annuity Payments
- Taxable Portion: A portion of each annuity payment is considered taxable income. This portion represents the return of the annuitant’s principal investment, plus any accumulated interest or earnings.
- Tax-Deferred Growth: In general, the growth of the annuity is tax-deferred, meaning that taxes are not paid on the earnings until they are withdrawn as payments.
- Taxable at Ordinary Income Rates: Annuity payments are typically taxed at ordinary income rates, similar to wages or salary.
Difference in Tax Implications Between Immediate Annuities and Annuities Due
There is no significant difference in the tax implications between immediate annuities and annuities due. Both types of annuities are subject to the same general tax rules, with a portion of each payment being considered taxable income.
Annuity is a financial product that provides a guaranteed stream of income for a specific period. Learn about the meaning of annuity and how it works in this simple explanation: Annuity Meaning In English 2024.
Examples of How Taxes Affect Annuity Payments Over Time
Consider an individual who purchases a $100,000 immediate annuity with a 5% interest rate. Over time, the annuity payments will consist of both principal and interest. The interest portion of the payments will be taxed as ordinary income.
A 1035 exchange allows you to transfer your variable annuity to another type of annuity without incurring tax penalties. Learn about the process and potential benefits of a 1035 exchange: Variable Annuity 1035 Exchange 2024.
- Year 1: The annuity payment may be $8,000, with $5,000 representing the return of principal and $3,000 representing interest. The $3,000 in interest would be taxed as ordinary income.
- Year 10: The annuity payment may be $8,500, with a larger portion representing interest due to the compounding effect. The interest portion of the payment would be taxed as ordinary income.
Risks and Considerations
While annuities can provide a steady income stream, it’s important to understand the potential risks and considerations associated with these financial products.
Potential Risks
- Interest Rate Risk: If interest rates rise after the annuity is purchased, the individual may receive a lower return than they could have obtained by investing elsewhere.
- Longevity Risk: If the individual lives longer than expected, the annuity payments may run out before their death. This can leave them with limited income in their later years.
- Inflation Risk: The purchasing power of annuity payments can erode over time due to inflation. This can lead to a decrease in the standard of living for the annuitant.
- Insurer Risk: The financial stability of the insurance company issuing the annuity is important. If the insurer becomes insolvent, the annuitant may lose their payments.
Important Considerations
- Insurer’s Financial Stability: Before purchasing an annuity, it’s crucial to research the financial stability of the issuing insurance company. Look for companies with strong ratings and a history of financial solvency.
- Annuity Terms and Conditions: Carefully review the terms and conditions of the annuity contract, including the payment amount, frequency, duration, and any fees or penalties.
- Alternative Investment Options: Consider alternative investment options, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, to diversify your portfolio and potentially achieve higher returns.
Questions to Ask Potential Annuity Providers
- What is the insurer’s financial rating?
- What are the fees associated with the annuity?
- What are the terms and conditions of the annuity contract?
- What are the payment options available?
- What are the tax implications of the annuity?
- What are the risks associated with the annuity?
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, immediate annuities and annuities due offer valuable options for retirement income planning. By understanding the key characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of each type, individuals can make informed decisions that meet their specific needs. Consulting with a financial advisor can provide personalized guidance and ensure that the chosen annuity aligns with overall retirement goals.
FAQ Insights
What are the main differences between immediate annuities and annuities due?
Immediate annuities provide payments immediately upon purchase, while annuities due provide payments at the beginning of each period. This difference in payment timing affects the overall value of the annuity.
What are the tax implications of annuity payments?
Annuity payments are typically taxed as ordinary income. However, the tax treatment can vary depending on the type of annuity and the specific terms of the contract. It’s essential to consult with a tax advisor to understand the tax implications of your chosen annuity.
Are there any risks associated with annuities?
Annuities carry certain risks, such as interest rate risk and longevity risk. Interest rate risk arises from potential changes in interest rates that can impact the value of the annuity. Longevity risk refers to the possibility of living longer than expected, which could lead to outliving the annuity’s payments.
It’s important to consider these risks and choose an annuity from a financially stable insurer.
What are some factors to consider when choosing an annuity?
Factors to consider include the insurer’s financial stability, the annuity’s terms and conditions, and the available payment options. It’s crucial to compare different annuity products and choose one that aligns with your individual needs and goals.









