IRS Resources for the October 2024 tax deadline are your roadmap to navigating the complexities of tax filing. Whether you’re a seasoned filer or a first-timer, understanding the resources available is crucial for a smooth and successful tax season.
This guide will delve into the essential tools, programs, and information provided by the IRS to help you meet your tax obligations with confidence.
The October 2024 deadline marks a significant shift in the tax calendar, extending the usual April filing date. This change offers taxpayers additional time to gather their financial records, prepare their returns, and seek assistance if needed. However, it’s important to note that the extended deadline doesn’t negate the importance of filing accurately and on time to avoid penalties.
Contents List
- 1 Understanding the October 2024 Tax Deadline
- 2 IRS Resources for Filing Taxes
- 3 Free Tax Preparation Assistance
- 4 Tax Filing Methods and Options
- 5 Common Tax Filing Mistakes to Avoid: IRS Resources For The October 2024 Tax Deadline
- 6 Tax Payment Options and Deadlines
- 7 Tax Audits and Appeals
- 8 Tax Credits and Deductions
- 9 Changes and Updates to Tax Laws
- 10 Contacting the IRS for Assistance
- 11 Conclusion
- 12 Helpful Answers
Understanding the October 2024 Tax Deadline
The October 2024 tax deadline marks the final day for individuals and businesses to file their tax returns and pay any outstanding taxes for the 2023 tax year. This deadline is crucial as it directly impacts your financial obligations and potential penalties.
The Importance of the October 2024 Tax Deadline
Missing the tax deadline can have significant consequences, including penalties and interest charges. The IRS imposes penalties for late filing and late payment, which can add up quickly. Additionally, late filing can impact your ability to receive refunds, potentially delaying your access to funds you are entitled to.
Consequences of Missing the October 2024 Tax Deadline
The IRS imposes penalties for late filing and late payment. The penalty for late filing is generally 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25% of the unpaid taxes.
The penalty for late payment is 0.5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the payment is late, up to a maximum of 25% of the unpaid taxes.
The IRS may also charge interest on underpayments and underpayments.
Definition of the Tax Deadline
The tax deadline refers to the final date by which taxpayers must file their tax returns and pay any outstanding taxes. The deadline is typically April 15th of the following year, but for the 2023 tax year, it has been extended to October 15, 2024.
The deadline is crucial because it sets a clear timeframe for fulfilling your tax obligations.
IRS Resources for Filing Taxes
The IRS offers a wealth of resources to assist taxpayers in understanding their tax obligations and filing their returns accurately. These resources cover various aspects of tax filing, from understanding your tax bracket to accessing online tools and getting personalized assistance.
IRS Website
The IRS website is a comprehensive online platform offering a plethora of information and tools for taxpayers.
Knowing the tax rates for each bracket is crucial for planning your finances. Tax rates for each tax bracket in 2024 can vary depending on your income level and filing status.
- Tax Information and Publications:Access a vast library of publications, guides, and articles covering various tax topics, including deductions, credits, and filing requirements.
- Forms and Instructions:Download and print various tax forms, including Form 1040, Form W-2, and Form 1099, along with detailed instructions for completing them.
- Interactive Tax Assistant (ITA):This online tool provides personalized answers to tax-related questions based on your specific situation. It guides you through different scenarios and helps you make informed decisions.
- Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS):TAS is an independent organization within the IRS that helps taxpayers resolve tax-related issues they have been unable to resolve through other IRS channels.
- IRS News and Announcements:Stay updated on the latest tax news, announcements, and changes in tax regulations through the IRS website.
IRS Publications
The IRS publishes a wide range of publications covering various tax topics. These publications provide detailed explanations, examples, and guidance on specific tax issues.
- Publication 17:This publication provides comprehensive information on the standard deduction and itemized deductions for individuals.
- Publication 529:This publication covers the topic of Miscellaneous Deductions, including expenses related to business, job hunting, and education.
- Publication 544:This publication explains the tax implications of sales and exchanges of property, including real estate and stocks.
IRS Phone Numbers
The IRS provides several phone numbers for taxpayers to reach out for assistance.
- IRS Taxpayer Assistance Center (TAC):This phone number is for general tax questions, including filing status, deductions, and credits.
- IRS Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS):This phone number is for taxpayers experiencing problems with the IRS or who have been unable to resolve their issues through other channels.
- IRS Fraud Reporting Hotline:This hotline is for reporting suspected tax fraud or identity theft.
IRS Tools and Resources
The IRS offers a variety of online tools and resources to help taxpayers navigate the tax filing process.
- Free File:This program allows taxpayers with certain income limits to file their taxes for free through participating tax preparation software providers.
- Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE):TCE provides free tax counseling and assistance to taxpayers aged 60 and older, focusing on issues related to pensions, retirement income, and Social Security.
- Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA):VITA provides free tax preparation assistance to low- to moderate-income taxpayers, persons with disabilities, and limited English speakers.
Free Tax Preparation Assistance
The IRS offers several programs that provide free tax preparation assistance to eligible taxpayers. These programs are designed to help individuals and families prepare their taxes accurately and receive all the credits and deductions they qualify for.
Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA)
The VITA program provides free tax preparation assistance to low- to moderate-income taxpayers, people with disabilities, and limited-English-speaking taxpayers.
- Eligibility:Taxpayers with an Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) of $58,000 or less in 2024 are generally eligible for VITA services.
- Services:VITA volunteers can help taxpayers prepare and e-file their federal and state tax returns, including the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), Child Tax Credit, and other credits and deductions.
- Location:VITA sites are typically located at community centers, libraries, schools, and other convenient locations. You can find a VITA site near you by using the IRS’s online locator tool.
Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE)
The TCE program provides free tax preparation assistance to taxpayers who are 60 years of age or older, with a focus on issues specific to seniors.
- Eligibility:The program is open to taxpayers of all income levels who are 60 years or older.
- Services:TCE volunteers can assist taxpayers with preparing their federal and state tax returns, including questions about pensions, retirement income, and other issues related to seniors.
- Location:TCE sites are often located at senior centers, community centers, and other locations frequented by seniors. You can find a TCE site near you by using the IRS’s online locator tool.
How to Access Free Tax Preparation Assistance
To access free tax preparation assistance through VITA or TCE, you will need to gather the following documents:
- Social Security cards for yourself and any dependents
- Photo identification
- Income documents (W-2s, 1099s, etc.)
- Other relevant tax documents (e.g., child care expenses, student loan interest)
You can then locate a VITA or TCE site near you using the IRS’s online locator tool. The tool allows you to search by zip code, city, or state. You can also search for sites that offer specific services, such as assistance with the EITC or other credits.
Tax Filing Methods and Options
The IRS offers several ways to file your taxes, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. You can choose the method that best suits your needs and preferences.
Filing Methods
- Online Filing:Filing your taxes online is the most popular and convenient method. You can use tax preparation software or file directly through the IRS website. Online filing is typically faster, more accurate, and less prone to errors. You can also get immediate feedback on your return and receive your refund faster.
- Mail Filing:You can file your taxes by mail using paper forms. This method is suitable for those who prefer a more traditional approach or who are not comfortable using online services. However, mail filing can be time-consuming, prone to errors, and can take longer to process.
Head of household filers have specific tax brackets to consider. Tax brackets for head of household in 2024 offer different rates and thresholds compared to other filing statuses.
- Tax Professional:You can hire a tax professional, such as a certified public accountant (CPA) or an enrolled agent (EA), to prepare and file your taxes. This option is beneficial for those who have complex tax situations, need help with tax planning, or prefer to have an expert handle their taxes.
Tax bracket changes can impact your tax liability. Tax bracket changes for 2024 may adjust the income levels and tax rates, so it’s crucial to stay informed.
However, hiring a tax professional can be expensive.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Filing Methods, IRS resources for the October 2024 tax deadline
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Online Filing |
|
|
| Mail Filing |
|
|
| Tax Professional |
|
|
Common Tax Filing Mistakes to Avoid: IRS Resources For The October 2024 Tax Deadline
Making mistakes on your tax return can lead to delays, penalties, and even audits. It’s important to be aware of common errors and take steps to avoid them.
Deductions
Deductions can reduce your taxable income, resulting in lower tax liability. However, claiming incorrect or ineligible deductions is a common mistake.
- Claiming deductions for ineligible expenses:Ensure that you only claim deductions for expenses that meet the IRS’s requirements. For example, if you are claiming a home office deduction, you must meet specific criteria regarding the use of the space.
- Overstating deductions:Double-check your documentation and calculations to ensure that you are not overstating your deductions.
- Missing deductions:Many taxpayers overlook potential deductions. Review your expenses carefully to identify any eligible deductions you may have missed.
Credits
Tax credits can directly reduce your tax liability, offering a dollar-for-dollar reduction.
The highest tax bracket in 2024 is a significant factor to consider when planning your finances. What is the highest tax bracket in 2024? provides details about the top bracket and how it affects high-income earners.
- Claiming credits for which you are not eligible:Only claim credits for which you meet the eligibility requirements. For example, the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) has specific income and other requirements.
- Failing to claim all eligible credits:Many taxpayers miss out on valuable tax credits. Research and explore available credits for which you may qualify, such as the Child Tax Credit or the American Opportunity Tax Credit.
Filing Status
Your filing status determines your tax bracket and other tax-related benefits.
- Choosing the wrong filing status:Selecting the incorrect filing status can lead to overpayment or underpayment of taxes. Carefully consider your circumstances and choose the appropriate filing status.
- Failing to update your filing status:If your marital status or dependents change throughout the year, ensure you update your filing status accordingly.
Other Common Mistakes
- Failing to file on time:Missing the tax deadline can result in penalties. Plan ahead and file your taxes well before the deadline.
- Providing inaccurate information:Double-check all information on your tax return, including your Social Security number, income, and deductions.
- Not keeping adequate records:Maintain organized records of all income and expenses throughout the year. This will make tax preparation easier and help you avoid errors.
Tax Payment Options and Deadlines
Paying your taxes is a crucial part of your financial responsibility as a citizen. Understanding the different payment options available and the consequences of late payments is essential for avoiding unnecessary penalties and maintaining a good standing with the IRS.
Payment Options
The IRS offers several convenient payment methods for your tax obligations. Here are some common options:
- Direct Pay:This online service allows you to make payments directly from your checking or savings account. It’s free, secure, and available 24/7. You can access it through the IRS website.
- Electronic Funds Withdrawal:When e-filing your taxes with tax preparation software or through a tax professional, you can choose to pay electronically via electronic funds withdrawal. This method transfers the payment directly from your bank account to the IRS.
- Debit Card, Credit Card, or Digital Wallet:You can use a debit card, credit card, or digital wallet to pay your taxes through a third-party payment processor. This option may incur a fee, so it’s important to check the charges before proceeding.
- Check or Money Order:You can send a check or money order payable to the U.S. Treasury, along with your tax return. Make sure to include your name, address, Social Security number, tax year, and the relevant tax form number on the check or money order.
If you need more time to file your taxes, filing extensions are available. Tax filing extensions for October 2024 can give you additional time to gather your documents and file accurately.
- Cash:You can pay your taxes in cash at one of the IRS’s authorized payment locations, such as retail stores or banks. Be sure to obtain a payment confirmation from the location.
Late Payment Consequences
Failing to pay your taxes on time can result in significant penalties and interest charges. The IRS assesses penalties for late payment based on the amount owed and the length of the delay. Additionally, you may face interest charges on the unpaid amount.
The penalty for late payment is typically 0.5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the taxes are late, up to a maximum penalty of 25%.
Payment Deadlines
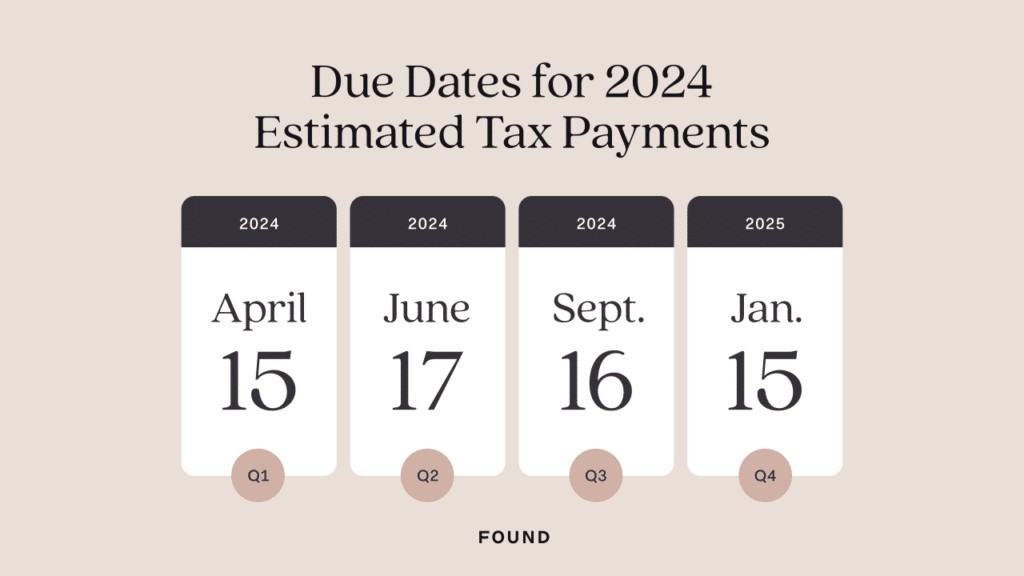
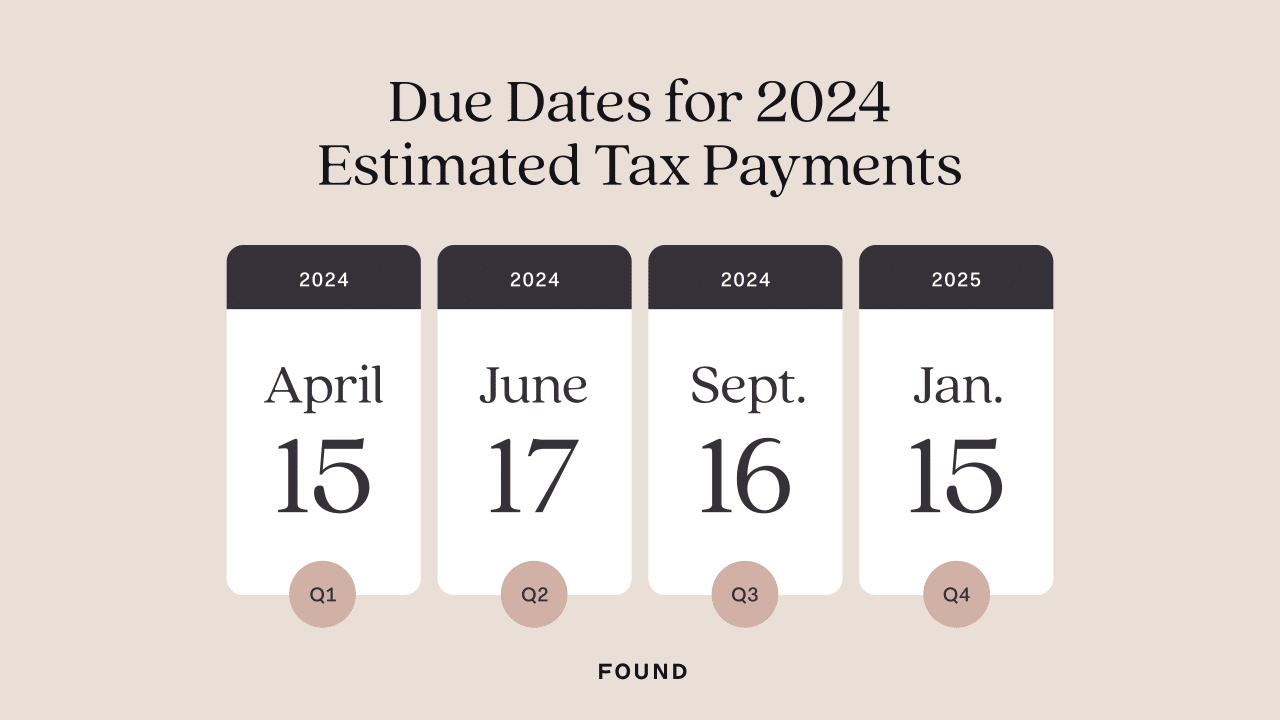
The deadline for paying your taxes is typically April 15th of each year. However, if April 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. For the 2024 tax year, the deadline is October 15th, 2024, as April 15th falls on a Sunday.
The Seahawks had a tough game this week, and their comeback attempt fell short. Rapid Reactions: Seahawks Comeback Falls Short In Week 5 Loss offers insights into the game and what’s next for the team.
- Filing Deadline:The filing deadline is the date by which you must submit your tax return. For most taxpayers, this is April 15th. However, if you are self-employed or operate a small business, you may have until October 15th to file your return.
Lewandowski’s impressive hat trick helped Barcelona secure a victory. First-half hat trick for Lewandowski as Barcelona top ahead of provides a recap of the exciting match and highlights the player’s performance.
- Payment Deadline:The payment deadline is the date by which you must pay your taxes. This is generally the same as the filing deadline, unless you have an extension. If you file for an extension, you have until October 15th to file your return but still need to pay your taxes by April 15th.
Tax Audits and Appeals
The IRS may select your tax return for an audit to ensure that the information reported is accurate and that you have paid the correct amount of taxes. This process is a routine part of tax administration and aims to maintain the integrity of the tax system.
Missing the October 2024 tax deadline can result in penalties. Tax penalties for missing the October 2024 deadline can be substantial, so it’s important to file on time or seek an extension.
Understanding the Audit Process
An audit involves the IRS reviewing your tax return and related documents to verify the accuracy of the information reported. The IRS can conduct audits through various methods, including correspondence audits, office audits, and field audits.
- Correspondence auditsare the most common type of audit. The IRS will send you a letter requesting additional information or documentation. You can respond to the request through mail or online.
- Office auditsinvolve meeting with an IRS agent at an IRS office to discuss your tax return. These audits are typically conducted for more complex issues or when additional information is required.
- Field auditsare conducted at your home or business and are generally reserved for the most complex or high-risk cases.
Preparing for an Audit
It is crucial to be prepared for an audit if selected.
Tax brackets are a key part of the U.S. tax system, and understanding them is essential for both individuals and businesses. Tax brackets for 2024 in the United States outline the various income levels and corresponding tax rates.
- Gather all relevant documentation, including tax returns, receipts, bank statements, and any other supporting documents that may be required. This will help you respond to the IRS’s inquiries accurately and efficiently.
- Stay organized. Maintain a system for tracking all your tax-related documents and information. This will make it easier to locate necessary information during an audit.
- Be cooperative. Respond to the IRS’s inquiries promptly and accurately. Avoid being evasive or confrontational, as this could escalate the situation.
- Seek professional helpif you feel overwhelmed or uncertain about the audit process. A tax professional can provide guidance and support throughout the process.
Appealing an Audit Decision
If you disagree with the IRS’s audit findings, you can appeal the decision.
If you’re filing as a single individual, understanding the specific tax brackets for your situation is essential. Tax brackets for single filers in 2024 are different from other filing statuses, so it’s important to be aware of them.
- Understand your appeal rights. You have the right to appeal an audit decision if you believe it is incorrect. The IRS provides detailed information on the appeal process on its website.
- File a formal appeal. If you choose to appeal, you must file a formal appeal with the IRS within the designated timeframe. You can do this online or by mail.
- Prepare your appeal. This involves gathering all relevant documentation and evidence to support your case. You may need to provide additional information or explanations to justify your position.
- Represent yourself or hire a tax professional. You can represent yourself during the appeal process, but it is often advisable to hire a tax professional, especially if the case is complex.
Tax Credits and Deductions
Tax credits and deductions can significantly reduce your tax liability. They offer various benefits to taxpayers based on their individual circumstances. Understanding these benefits and how to claim them can save you money.
Understanding how tax brackets affect your income is vital for financial planning. How will tax brackets affect my 2024 income? can help you make informed decisions about your income and expenses.
Tax Credits
Tax credits are direct reductions in your tax liability, dollar for dollar. They are more valuable than deductions, as they directly reduce the amount of taxes you owe.
For example, if you qualify for a $1,000 tax credit, your tax liability will be reduced by $1,000.
Here are some common tax credits:
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC):This credit is available to low- and moderate-income working individuals and families. The amount of the credit depends on your income and family size. The EITC can be claimed by eligible taxpayers even if they do not have a filing obligation.
- Child Tax Credit:This credit provides a tax break for families with qualifying children under 17 years old. The credit amount is $2,000 per child, and it is partially refundable, meaning you may receive some of it back even if you owe no taxes.
- American Opportunity Tax Credit:This credit helps pay for the first four years of college. The credit is worth up to $2,500 per eligible student and is phased out based on income.
- Premium Tax Credit:This credit helps offset the cost of health insurance purchased through the Marketplace. The amount of the credit depends on your income and the cost of your health insurance plan.
Tax Deductions
Tax deductions reduce your taxable income, which in turn lowers your tax liability.
For example, if you have a $10,000 deduction, your taxable income will be reduced by $10,000, potentially resulting in lower taxes.
Deductions are categorized based on their purpose:
Itemized Deductions
These deductions are listed on Schedule A of Form 1040. You can choose to itemize your deductions or take the standard deduction, whichever is more beneficial to you.
- Medical Expenses:You can deduct medical expenses exceeding 7.5% of your adjusted gross income (AGI). This deduction can help offset the cost of medical bills, prescription drugs, and other healthcare expenses.
- State and Local Taxes (SALT):You can deduct up to $10,000 in state and local taxes, including property taxes, income taxes, and sales taxes. This deduction is subject to limitations, and you may need to choose between deducting state and local taxes or taking the standard deduction.
- Home Mortgage Interest:You can deduct interest paid on up to $750,000 of qualified home mortgage debt. This deduction can help reduce the cost of homeownership.
- Charitable Contributions:You can deduct cash contributions to qualified charities up to 60% of your AGI. This deduction can help support charitable organizations and reduce your tax liability.
Above-the-Line Deductions
These deductions are taken directly from your gross income to arrive at your adjusted gross income (AGI). They are not subject to the itemized deduction limitations.
- Student Loan Interest:You can deduct up to $2,500 in interest paid on student loans. This deduction can help offset the cost of student loans.
- IRA Contributions:You can deduct contributions to traditional IRAs, subject to income limitations. This deduction can help reduce your tax liability and save for retirement.
- Health Savings Account (HSA) Contributions:You can deduct contributions to an HSA if you have a high-deductible health insurance plan. This deduction can help reduce your tax liability and save for future healthcare expenses.
Other Deductions
These deductions are not categorized as itemized or above-the-line deductions.
- Moving Expenses:You can deduct moving expenses if you meet certain requirements, such as moving for a new job or for a distance of at least 50 miles. This deduction can help offset the cost of moving.
- Job-Related Expenses:You can deduct certain job-related expenses, such as expenses for uniforms, supplies, and travel. This deduction can help reduce your tax liability.
Changes and Updates to Tax Laws
The tax landscape is constantly evolving, with new laws and regulations being introduced regularly. These changes can significantly impact your tax obligations and filing requirements. It is crucial to stay informed about the latest tax updates to ensure you are filing accurately and avoid potential penalties.The IRS website is an excellent resource for staying updated on tax law changes.
You can find information on new legislation, guidance, and publications that can help you understand how these changes affect your tax situation.
Changes in Tax Brackets and Rates
Tax brackets and rates can change from year to year, affecting the amount of taxes you owe. These changes are usually based on factors such as inflation and economic conditions. For example, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 reduced tax rates for many individuals and businesses.
To get a clear picture of your tax situation, using a tax bracket calculator is a great tool. Tax bracket calculator for 2024 can help you estimate your tax liability and make informed financial decisions.
It is essential to check the current tax brackets and rates for the relevant tax year to determine your tax liability accurately.
Changes in Deductions and Credits
The availability and amount of deductions and credits can also change over time. These changes can affect your tax refund or tax liability. For instance, the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021 expanded the Child Tax Credit and provided additional tax credits for individuals and families.
Staying updated on changes to deductions and credits can help you maximize your tax savings.
Changes in Filing Requirements
The IRS may update filing requirements from time to time, such as changes to income thresholds for certain deductions or credits. For example, the Affordable Care Act introduced the individual mandate, requiring most individuals to have health insurance or pay a penalty.
Understanding the thresholds for each tax bracket is essential for accurate tax planning. Tax bracket thresholds for 2024 define the income levels at which you move into a higher tax bracket.
It is essential to review the latest filing requirements to ensure you meet all the necessary criteria.
Changes in Tax Payment Options
The IRS may introduce new or modify existing tax payment options. For example, the IRS offers online payment options through its website or third-party payment processors. Staying informed about these changes can help you choose the most convenient and cost-effective payment method.
Changes in Audit Procedures
The IRS may also update its audit procedures. For example, the IRS may implement new technologies or strategies for conducting audits. Staying informed about these changes can help you understand what to expect during an audit and prepare accordingly.
Staying Informed about Current Tax Legislation
The IRS website is the primary source for staying informed about tax law changes. You can find information on new legislation, guidance, and publications. The IRS also offers various resources, such as tax guides, publications, and videos, to help you understand the latest tax updates.You can also subscribe to the IRS’s email updates or follow their social media accounts for the latest news and announcements.
Additionally, consider consulting a tax professional who can provide personalized advice on how tax law changes affect your situation.
The October 2024 tax deadline is fast approaching for businesses. October 2024 tax deadline for businesses is a crucial date to remember, and filing on time can help avoid penalties.
Contacting the IRS for Assistance
The IRS offers various ways to contact them for assistance with tax-related matters. You can reach out to them by phone, mail, or online. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and it’s important to choose the most suitable one based on your needs and preferences.
It’s important to understand how tax brackets work, especially as we head into 2024. Understanding tax brackets for 2024 can help you make informed financial decisions and potentially save money.
Contacting the IRS by Phone
Calling the IRS is the quickest way to get immediate assistance. You can reach the IRS by calling their toll-free number, which is available 24/7. The IRS also offers specialized phone lines for specific topics, such as tax credits, deductions, or payment options.
- The IRS toll-free number is 1-800-829-1040.
- The IRS also offers specialized phone lines for specific topics, such as tax credits, deductions, or payment options. For example, you can call 1-800-TAX-FORM (1-800-829-3676)to get information about specific tax forms or publications.
- You can also find the phone numbers for specific IRS offices on the IRS website.
Contacting the IRS by Mail
If you need to send a letter or document to the IRS, you can mail it to the address listed on the IRS website. It is important to note that it may take several weeks for the IRS to receive and process your mail.
- The IRS address for general correspondence is Internal Revenue Service, P.O. Box 7004, Ogden, UT 84201-7004.
- For specific tax forms or publications, you can find the mailing address on the IRS website.
- You can also find the mailing address for specific IRS offices on the IRS website.
Contacting the IRS Online
The IRS offers a variety of online services, including the ability to file your taxes, track your refund, and get information about your tax account. You can also use the IRS website to find answers to frequently asked questions, download tax forms and publications, and contact the IRS through their online forms.
- The IRS website is www.irs.gov.
- The IRS offers a variety of online services, including the ability to file your taxes, track your refund, and get information about your tax account.
- You can also use the IRS website to find answers to frequently asked questions, download tax forms and publications, and contact the IRS through their online forms.
Contacting the IRS Through Social Media
The IRS is also active on social media and uses these platforms to share tax information and answer questions from taxpayers. You can follow the IRS on Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube.
- The IRS Twitter account is @IRSnews.
- The IRS Facebook page is facebook.com/IRS.
- The IRS YouTube channel is youtube.com/user/IRSvideos.
Conclusion
With the October 2024 tax deadline approaching, it’s essential to utilize the wealth of resources provided by the IRS. By understanding the available options, taking advantage of free assistance programs, and filing accurately and on time, you can ensure a smooth and successful tax season.
Remember, the IRS is committed to helping taxpayers navigate the complexities of tax filing, so don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance if needed.
Helpful Answers
What if I can’t afford a tax professional?
The IRS offers free tax preparation assistance programs for eligible taxpayers. These programs provide free tax preparation services, ensuring you get your taxes done correctly and receive all the credits and deductions you qualify for.
What if I can’t afford to pay my taxes by the deadline?
The IRS offers payment options for taxpayers who can’t afford to pay their taxes in full by the deadline. These options include payment plans, short-term extensions, and offers in compromise. It’s important to contact the IRS as soon as possible if you’re facing financial difficulties to explore your options.