Is Annuity Death Benefit Taxable 2024? This question often arises when individuals consider annuities as part of their estate planning. Annuities, known for their guaranteed income streams, can provide financial security throughout retirement. However, understanding the tax implications of annuity death benefits is crucial for beneficiaries to avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
Curious about the concept of an annuity due? Annuity Due Is 2024 explains this financial concept and its implications for your investments.
This guide delves into the complex world of annuity death benefits and their tax treatment in 2024. We’ll explore different types of annuities, the calculation of death benefits, and the specific tax rules that apply. We’ll also examine factors like the beneficiary’s relationship to the annuitant and the annuity’s purchase date, which can influence taxability.
The Android WebView 202 is a powerful tool for businesses. It allows you to integrate web content into your Android apps, providing a seamless user experience.
Finally, we’ll discuss strategies to minimize tax liability and provide practical advice for reporting and documentation.
Contents List
Understanding Annuity Death Benefits
Annuity death benefits are a crucial aspect of annuity contracts, offering financial protection to beneficiaries upon the annuitant’s passing. These benefits can provide a source of income or a lump sum payment to help cover expenses and ensure financial stability for loved ones.
Looking to develop an app for a specific industry? Android app development for specific industries in 2024 is a great way to target a niche market and stand out from the competition.
Understanding the intricacies of annuity death benefits, including their tax implications, is essential for both annuitants and beneficiaries.
Types of Annuities and Death Benefit Features
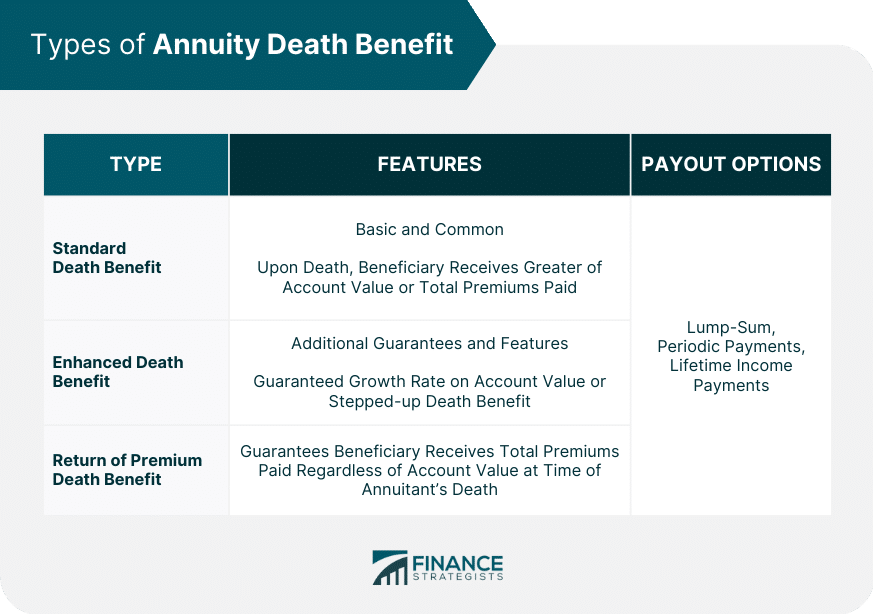
Annuities are financial products that provide a stream of income payments, typically for a specified period or for life. Different annuity types offer varying death benefit features, influencing the amount and taxability of the benefits received by beneficiaries.
Want to learn more about the Android WebView 202 and how it compares to previous versions? This new version boasts significant performance improvements and enhanced security features.
- Fixed Annuities:These annuities guarantee a fixed interest rate and a fixed payment amount. Death benefits are typically the greater of the premium paid or the account value at the time of death.
- Variable Annuities:Variable annuities offer growth potential but do not guarantee a specific return. Death benefits are usually based on the account value at the time of death, which can fluctuate depending on market performance.
- Indexed Annuities:These annuities link returns to a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. Death benefits are often calculated based on the account value at the time of death, which may be subject to a minimum guarantee.
Calculating Death Benefits
The calculation of death benefits varies depending on the type of annuity and its specific terms. Here’s a general overview of common methods:
- Guaranteed Minimum Death Benefit:Some annuities provide a guaranteed minimum death benefit, regardless of the account value at the time of death. This ensures beneficiaries receive a specific amount, even if the account value has declined.
- Account Value at Death:For many annuities, the death benefit is equal to the account value at the time of death. This means the beneficiary receives the full accumulated value of the annuity.
- Multiple of Premium:Certain annuities offer a death benefit equal to a multiple of the premium paid, such as two or three times the premium. This provides a guaranteed minimum benefit for beneficiaries.
Common Death Benefit Scenarios, Is Annuity Death Benefit Taxable 2024
Here are some common examples of how annuity death benefits may be distributed:
- Lump Sum Payment:The beneficiary may receive a lump sum payment representing the entire death benefit amount.
- Income Payments:The death benefit may be used to purchase a new annuity that provides income payments to the beneficiary for a specific period or for life.
- Combination of Payments:The beneficiary may receive a portion of the death benefit as a lump sum and the remaining balance as income payments.
Tax Implications of Annuity Death Benefits: Is Annuity Death Benefit Taxable 2024
The tax treatment of annuity death benefits can vary depending on several factors, including the type of annuity, the beneficiary’s relationship to the annuitant, and the annuitant’s age and health status. Understanding these tax implications is crucial for beneficiaries to avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
General Tax Treatment of Death Benefits
In general, death benefits received from life insurance policies are not subject to federal income tax. However, death benefits from annuities are typically taxable as ordinary income. This is because annuity payments are considered to be a return of the annuitant’s investment, and the death benefit is treated as a continuation of those payments.
The Snapdragon 2024 is expected to be released soon. Keep an eye out for updates on its release date and pricing.
Tax Rules for Annuity Death Benefits in 2024
The specific tax rules governing annuity death benefits in 2024 are subject to change, so it’s important to consult with a tax professional for up-to-date information. However, some general principles apply:
- Exclusion of Premiums:Beneficiaries are generally allowed to exclude the portion of the death benefit that represents the premiums paid by the annuitant from their taxable income.
- Taxable Earnings:The remaining portion of the death benefit, representing accumulated earnings, is taxable as ordinary income.
- Tax Basis:The annuitant’s tax basis in the annuity, which represents the amount of premiums paid, is used to determine the taxable portion of the death benefit.
Tax Treatment for Different Annuity Types
The tax treatment of death benefits can differ depending on the type of annuity:
- Fixed Annuities:Death benefits from fixed annuities are typically taxed as ordinary income, with the portion representing accumulated earnings subject to taxation.
- Variable Annuities:Death benefits from variable annuities are also taxed as ordinary income, but the taxable amount may be subject to fluctuations based on market performance.
- Indexed Annuities:The tax treatment of death benefits from indexed annuities depends on the specific terms of the contract. Some indexed annuities may offer tax-deferred growth, while others may have a portion of the death benefit taxed as ordinary income.
Factors Influencing Taxability
Several factors can influence the taxability of annuity death benefits. Understanding these factors is crucial for beneficiaries to accurately assess their potential tax liability.
Looking for a way to create unique and expressive avatars? Dollify 2024 offers a fun and easy way to customize your digital self. With its vast array of options, you can create an avatar that truly reflects your personality.
Beneficiary’s Relationship to the Annuitant
The beneficiary’s relationship to the annuitant can impact the tax treatment of death benefits. For example, if the beneficiary is the annuitant’s spouse, the death benefit may be eligible for certain tax advantages. However, if the beneficiary is a non-spouse, such as a child or friend, the death benefit may be subject to full taxation.
Thinking about building an app for your business? Android app development for the enterprise is a great way to reach your target audience and streamline your operations.
Annuitants Age and Health Status
The annuitant’s age and health status can also influence taxability. If the annuitant dies before reaching a certain age or before a specified period, the death benefit may be subject to different tax rules. Additionally, if the annuitant is terminally ill, certain tax benefits may apply to the death benefit.
Want to learn more about the Android WebView 202 API changes ? These updates offer developers new ways to interact with web content, improving the functionality of their apps.
Annuity’s Purchase Date
The annuity’s purchase date can also affect tax implications. Annuities purchased before a certain date may be subject to different tax rules than those purchased after that date. It’s essential to consult with a tax professional to determine the specific tax rules that apply to the annuity in question.
Curious about the future of avatar creation? Dollify 2024 is pushing the boundaries with new features and advancements. Get ready for even more personalized and expressive avatars.
Avoiding or Minimizing Taxes
While annuity death benefits are typically taxable, beneficiaries can take steps to minimize their tax liability. Understanding these strategies is crucial for maximizing the value of the inheritance.
Wondering about the differences between an annuity and a 401k? Is Annuity Better Than 401k 2024 explores the pros and cons of each retirement savings option.
Strategies for Minimizing Tax Liability
Here are some strategies for beneficiaries to reduce their tax burden on annuity death benefits:
- Maximize the Exclusion of Premiums:Ensure that the beneficiary accurately excludes the portion of the death benefit representing the premiums paid by the annuitant from their taxable income.
- Consider Income Payments:If the beneficiary is in a lower tax bracket than the annuitant, receiving the death benefit as income payments may be advantageous, as the payments would be taxed at the beneficiary’s lower rate.
- Time Payments for Lower Tax Brackets:By strategically timing the receipt of payments, beneficiaries can potentially minimize their tax liability by receiving the payments in years when they are in a lower tax bracket.
Estate Planning Techniques for Tax Reduction
Estate planning techniques can also help reduce taxes on annuity death benefits:
- Irrevocable Life Insurance Trusts (ILITs):Establishing an ILIT can allow the death benefit to pass to beneficiaries outside of the estate, potentially reducing estate taxes.
- Charitable Remainder Trusts (CRTs):CRTs can provide income to beneficiaries for a specific period, with the remaining assets going to charity. This can help reduce both income and estate taxes.
Using Trusts to Receive Annuity Death Benefits
Trusts can play a crucial role in minimizing taxes on annuity death benefits. For example, a beneficiary could receive the death benefit through a trust, allowing for more flexible distribution and tax planning options.
- Revocable Living Trusts:These trusts allow the grantor to maintain control over the assets during their lifetime and can provide tax benefits upon death.
- Irrevocable Trusts:These trusts are established with the intention of transferring assets permanently, often for estate planning purposes.
Tax Reporting and Documentation
Accurate tax reporting is essential for beneficiaries receiving annuity death benefits. Understanding the required forms and documentation is crucial for compliance with tax regulations.
Need to find the best deals and discounts on the Glovo app ? Check out their promotions section for exclusive offers and savings on your next delivery.
Required Tax Forms
| Form | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Form 1040 | Used to report income and calculate tax liability. |
| Schedule B | Used to report interest and dividend income, including annuity payments. |
| Form 1099-R | Issued by the annuity provider to report distributions from the annuity. |
| Form 5498 | Used to report the value of IRAs, pensions, and other retirement plans, including annuities. |
Essential Documents for Tax Filing
Here’s a checklist of essential documents needed for tax filing purposes:
- Annuity contract
- Form 1099-R
- Death certificate of the annuitant
- Beneficiary designation form
- Any other relevant documentation, such as estate planning documents or trust agreements.
Reporting Annuity Death Benefits on Income Tax Returns
Beneficiaries must report annuity death benefits on their income tax returns. The amount of the death benefit that is taxable will depend on the factors discussed earlier, such as the type of annuity, the beneficiary’s relationship to the annuitant, and the annuitant’s age and health status.
Need help managing your tasks? Google Tasks 2024 is a powerful tool for businesses to stay organized and on top of their to-do lists.
- Report on Form 1040:The taxable portion of the death benefit is reported on Form 1040, typically on Schedule B.
- Include Form 1099-R:The Form 1099-R received from the annuity provider should be included with the tax return to support the reported income.
- Consult a Tax Professional:It’s recommended to consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate reporting and minimize tax liability.
Examples and Case Studies
Understanding the tax implications of annuity death benefits is crucial for beneficiaries to make informed financial decisions. Real-world examples and case studies can illustrate how these benefits are taxed in various situations.
Want to know how to use the Glovo app to get your groceries delivered right to your doorstep? It’s a breeze! Simply open the app, choose your preferred store, select your items, and checkout. Glovo will take care of the rest, delivering your groceries fresh and fast.
Annuity Death Benefit Scenarios and Tax Implications
| Scenario | Annuity Type | Death Benefit | Taxable Amount | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| John purchased a fixed annuity with a death benefit equal to the account value at death. He dies with an account value of $200,000. The premiums paid were $100,000. | Fixed Annuity | $200,000 | $100,000 | The $100,000 premium paid is excluded from taxable income, and the remaining $100,000 is taxed as ordinary income. |
| Mary purchased a variable annuity with a death benefit equal to the account value at death. She dies with an account value of $150,000. The premiums paid were $100,000. | Variable Annuity | $150,000 | $50,000 | The $100,000 premium paid is excluded from taxable income, and the remaining $50,000 is taxed as ordinary income. |
| David purchased an indexed annuity with a guaranteed minimum death benefit of $120,000. He dies with an account value of $100,000. The premiums paid were $80,000. | Indexed Annuity | $120,000 | $40,000 | The $80,000 premium paid is excluded from taxable income, and the remaining $40,000 is taxed as ordinary income. |
Real-World Examples of Annuity Death Benefit Taxation
- Spouse as Beneficiary:When a spouse inherits an annuity death benefit, they may be eligible for certain tax advantages, such as a stepped-up basis, which can reduce their tax liability.
- Non-Spouse Beneficiary:If the beneficiary is a non-spouse, such as a child or friend, the death benefit may be subject to full taxation. The beneficiary will need to report the taxable portion of the death benefit on their income tax return.
- Annuity Purchased Before 1987:Annuities purchased before 1987 may be subject to different tax rules. For example, the death benefit may be excluded from taxable income if the annuitant lived for at least 10 years after purchasing the annuity.
Tax Disputes and Legal Challenges
There are several common tax disputes and legal challenges related to annuity death benefits. For example, beneficiaries may dispute the taxability of the death benefit or the amount of the taxable portion. These disputes can be complex and may require legal expertise to resolve.
Thinking about getting a new foldable phone? Check out the latest Snapdragon 2024 processor designed specifically for these devices. It’s packed with features to give you the best possible experience, including improved performance and battery life.
Closure
Navigating the tax implications of annuity death benefits can be challenging, but understanding the intricacies of this topic is essential for beneficiaries. By understanding the tax rules, exploring strategies for minimizing tax liability, and utilizing proper documentation, beneficiaries can ensure that the legacy left by the annuitant is maximized and enjoyed as intended.
If you’re in the market for a new laptop, consider a model with the latest Snapdragon 2024 processor. It’s designed to deliver incredible performance and battery life, making it perfect for productivity and entertainment.
FAQ Resource
What happens if the beneficiary is not a spouse or direct descendant?
The tax treatment of annuity death benefits may differ depending on the beneficiary’s relationship to the annuitant. For example, if the beneficiary is a friend or charity, the death benefit may be considered taxable income. It’s essential to consult with a tax professional to determine the specific tax implications in such cases.
Are there any tax advantages to choosing a specific type of annuity?
Yes, the tax treatment of death benefits can vary depending on the type of annuity. For example, a fixed annuity typically offers more predictable tax implications compared to a variable annuity. It’s crucial to carefully consider the tax implications of different annuity types during the selection process.
What documentation should beneficiaries keep for tax purposes?
Beneficiaries should maintain thorough documentation related to the annuity, including the annuity contract, death benefit statements, and any tax forms received. This documentation will be essential for accurate tax reporting and potential audits.









