Is Annuity Income Taxable 2024? This is a question that many people ask, especially as they approach retirement. Annuities are financial products that provide a stream of income for a set period of time, and understanding how they are taxed is crucial for planning your finances.
The taxability of annuity payments can vary depending on the type of annuity and how it is structured, making it essential to consult with a financial advisor to ensure you are making informed decisions.
Annuities can be a valuable tool for retirement planning, offering a guaranteed stream of income that can help you meet your financial needs in your later years. However, the tax implications of annuity payments can be complex, and it is important to understand how they are taxed to make informed financial decisions.
This guide will explore the taxability of annuity income in 2024, providing a comprehensive overview of the rules and regulations that apply.
To truly grasp the mechanics of annuities, understanding the underlying calculations is crucial. Annuity Equation 2024 provides a glimpse into the mathematical formulas that drive these financial products.
Contents List
Annuity Income: A Comprehensive Guide to Tax Implications in 2024: Is Annuity Income Taxable 2024
Annuities are financial products that provide a stream of income payments for a specified period or for life. They are often used as a way to generate retirement income, protect against longevity risk, or provide financial security for beneficiaries. Annuities come in various forms, each with its own unique features and tax implications.
Understanding the taxability of annuity income is crucial for individuals considering or already receiving annuity payments, as it can significantly impact their overall tax burden.
Types of Annuities
Annuities can be broadly classified into two main types: fixed annuities and variable annuities.
- Fixed annuitiesprovide a guaranteed rate of return, typically in the form of a fixed interest rate. The income payments are predictable and generally lower than those offered by variable annuities.
- Variable annuitiesinvest in a portfolio of securities, such as stocks and bonds. The income payments are not guaranteed and can fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying investments. These annuities offer the potential for higher returns, but also carry greater risk.
Within these two main types, there are various sub-types of annuities, each with its own unique characteristics and tax implications. It is important to carefully consider the specific features and tax implications of any annuity before making a decision.
Annuities are a common topic of discussion when it comes to retirement planning. Annuity Is 2024 provides a basic overview. Annuity Is A Voluntary Retirement Vehicle 2024 clarifies their role in retirement planning.
General Taxability of Annuity Payments
Generally, annuity payments are considered taxable income. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) classifies annuity payments as ordinary income, which means they are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. However, the specific tax treatment of annuity payments can vary depending on the type of annuity and the circumstances surrounding the payments.
Tax Treatment of Different Annuity Types
The taxability of annuity income depends on the type of annuity and the specific terms of the contract. Here are some examples of different annuity types and their respective tax implications:
- Traditional IRA annuities:These annuities are funded with pre-tax dollars, meaning that the income payments are taxed as ordinary income in retirement.
- Roth IRA annuities:These annuities are funded with after-tax dollars, meaning that the income payments are tax-free in retirement.
- Deferred annuities:These annuities are typically purchased with after-tax dollars, but the income payments are taxed as ordinary income when they are received.
- Immediate annuities:These annuities begin making payments immediately after purchase. The income payments are taxed as ordinary income, but a portion of the payments may be tax-free, depending on the exclusion ratio.
Taxable Portion of Annuity Payments
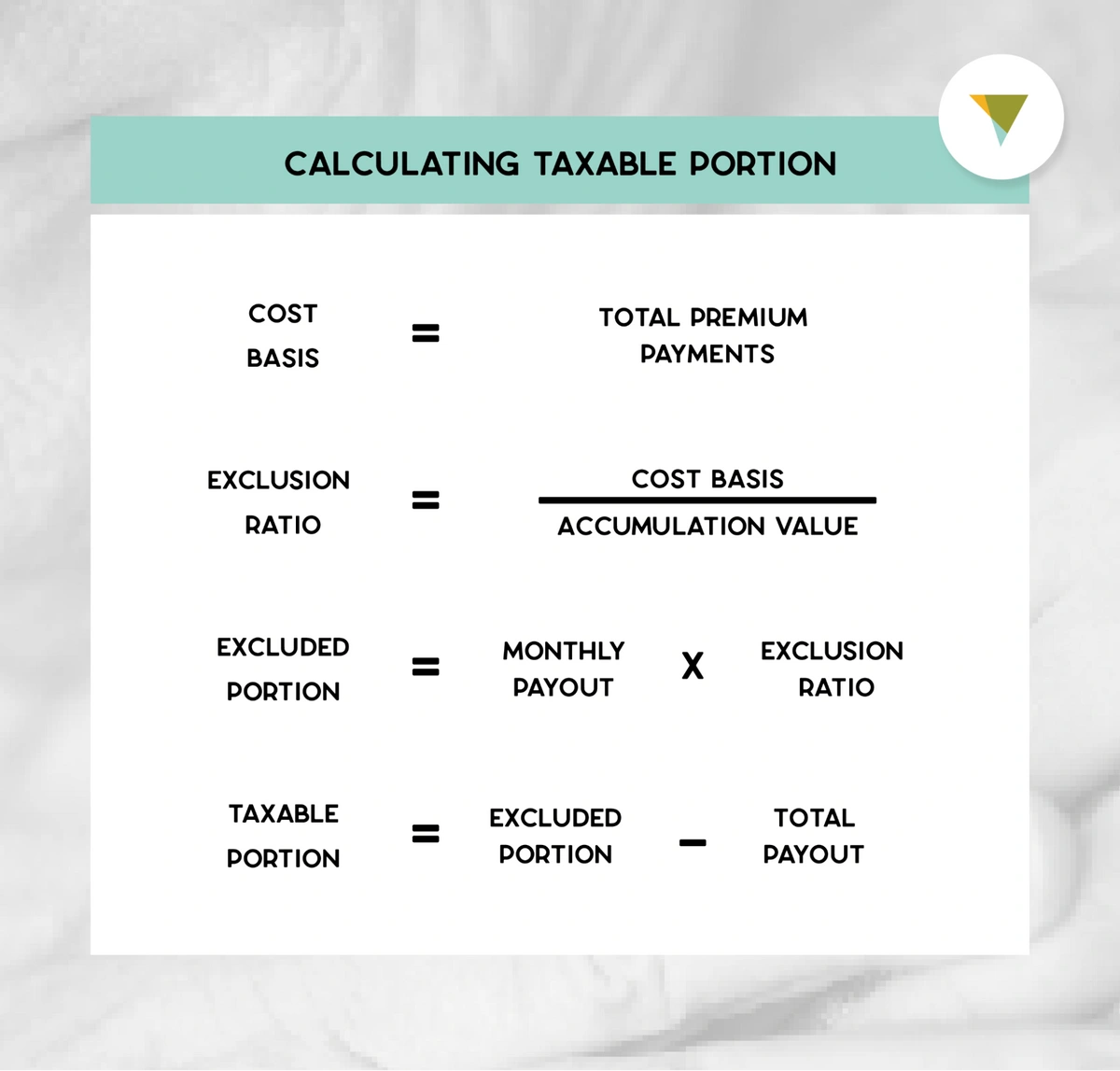
The taxable portion of annuity payments is determined using the “exclusion ratio.” This ratio represents the proportion of each annuity payment that represents a return of your original investment (which is not taxable) and the proportion that represents interest or earnings (which is taxable).
The exclusion ratio is calculated as follows:Exclusion Ratio = Original Investment / Expected Total Payments
While annuities can be valuable, it’s important to understand their nature. Is Annuity Bond 2024 sheds light on the relationship between annuities and bonds. Annuity Health Insurance 2024 explores the potential connection between annuities and health insurance, which might be relevant for your overall financial planning.
For example, if you invested $100,000 in an annuity that is expected to pay you $150,000 over your lifetime, your exclusion ratio would be 100,000 / 150,000 = 0.67. This means that 67% of each annuity payment would be considered a return of your original investment and would be tax-free, while the remaining 33% would be considered taxable income.
The exclusion ratio remains constant throughout the annuity period. However, the amount of taxable income in each payment will vary based on the payment amount and the exclusion ratio.
Taxable vs. Non-Taxable Annuity Payments
As mentioned, a portion of each annuity payment is generally considered a return of your original investment and is not taxable. This is known as the “cost basis” of the annuity. The remaining portion of the payment represents interest or earnings and is considered taxable income.
When planning for the future, understanding how annuities work with trusts is important. Annuity Beneficiary Is A Trust 2024 provides insights into this aspect. Annuity Gator 2024 is another resource that can help you understand the intricacies of annuities.
- Taxable portion:This represents the portion of each annuity payment that is considered interest or earnings and is subject to income tax.
- Non-taxable portion:This represents the portion of each annuity payment that is considered a return of your original investment and is not subject to income tax.
For example, if you receive an annuity payment of $1,000 and your exclusion ratio is 0.67, then $670 (0.67 x $1,000) would be considered non-taxable, and $330 (0.33 x $1,000) would be considered taxable income.
The tax treatment of annuity payments can have a significant impact on your overall income taxes. It is important to understand the tax implications of your annuity payments and to plan accordingly to minimize your tax burden.
If you’re wondering if you can still work while receiving an annuity, Can You Receive Annuity And Still Work 2024 provides answers. An Annuity Is 2024 offers a deeper understanding of how annuities work.
Tax Implications of Annuity Withdrawals, Is Annuity Income Taxable 2024
Withdrawing money from an annuity before reaching the annuity period can have tax consequences. The tax treatment of withdrawals depends on the type of annuity and the specific terms of the contract.
If you’re considering an annuity, it’s essential to understand how it works. The Is Annuity Certain 2024 article provides a clear explanation. To help you make an informed decision, you can use an Annuity Calculator Uk 2024 to see how different scenarios might play out.
- Traditional IRA annuities:Withdrawals before age 59 1/2 are generally subject to a 10% penalty, as well as ordinary income tax.
- Roth IRA annuities:Withdrawals before age 59 1/2 are tax-free and penalty-free, as long as the funds have been in the account for at least five years.
- Deferred annuities:Withdrawals before the annuity period may be subject to a surrender charge, as well as ordinary income tax.
- Immediate annuities:Withdrawals before the annuity period are generally subject to ordinary income tax, and may also be subject to a surrender charge.
It is important to carefully consider the tax implications of withdrawing money from an annuity before reaching the annuity period. You should consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to understand the potential tax consequences and to develop a plan that minimizes your tax burden.
Outcome Summary
Understanding the taxability of annuity income is crucial for anyone considering this financial product. By understanding the rules and regulations that apply, you can make informed decisions about your retirement planning and minimize your tax burden. Remember, seeking professional financial advice is always recommended to ensure you are making the best choices for your individual circumstances.
Android app development is becoming increasingly specialized. Android app development for specific industries in 2024 is tailoring solutions to meet the unique needs of various sectors. If you’re looking for reliable information about annuities, Is Annuity Gator Legit 2024 is a resource worth exploring.
Key Questions Answered
How do I calculate the exclusion ratio for my annuity payments?
The exclusion ratio is calculated by dividing the investment in the annuity by the expected total payments. For example, if you invested $100,000 in an annuity and are expected to receive $200,000 in payments, your exclusion ratio would be 50%.
This means that 50% of each annuity payment is considered non-taxable, and the remaining 50% is taxable.
What are the tax consequences of withdrawing money from an annuity early?
The metaverse is gaining momentum, and Android app development is playing a key role. Android app development for the metaverse in 2024 is exploring new frontiers, and it’s crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest security measures. Android WebView 202 security updates are essential for protecting user data and ensuring a secure experience.
Withdrawing money from an annuity before reaching the annuity period can result in taxes and penalties. The tax treatment of withdrawals depends on the type of annuity and the age of the annuitant. Generally, withdrawals before age 59 1/2 are subject to a 10% penalty, in addition to ordinary income tax.
Consult a financial advisor to understand the specific tax implications for your situation.
Can I use an annuity to reduce my tax liability?
Yes, annuities can be used as part of a tax planning strategy. By strategically structuring your annuity, you may be able to reduce your overall tax liability. For example, you can choose an annuity that provides a guaranteed stream of income for life, which can help you minimize your tax burden in retirement.









