October 2024 tax deadline for students is approaching, and it’s crucial to understand the unique requirements and potential benefits that come with filing taxes as a student. Whether you’re working part-time, receiving scholarships, or earning income from other sources, navigating the tax landscape can feel overwhelming.
This guide aims to simplify the process, providing clarity on filing deadlines, eligibility criteria, and potential tax savings for students.
Filing taxes as a student can be a complex process, but understanding your obligations and available resources can help you maximize your tax benefits and avoid any potential penalties. This guide will walk you through the key aspects of student taxation, providing practical advice and actionable steps to ensure a smooth and successful tax filing experience.
Contents List
Understanding the Tax Deadline
The October 2024 tax deadline for students in the United States is a crucial date for filing your tax return. This deadline applies to students who are claiming certain educational tax credits and deductions, including the American Opportunity Tax Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit.
Interested in seeing how the tax brackets for 2024 compare to 2023? Our article on tax bracket changes for 2024 vs 2023 provides a detailed breakdown of the differences.
Failing to meet this deadline can result in penalties and missed opportunities for tax benefits.
Curious about how tax brackets might affect your income in 2024? You can learn more about the impact of tax brackets on your 2024 income by reading our comprehensive guide. It breaks down the changes and explains how they might impact your finances.
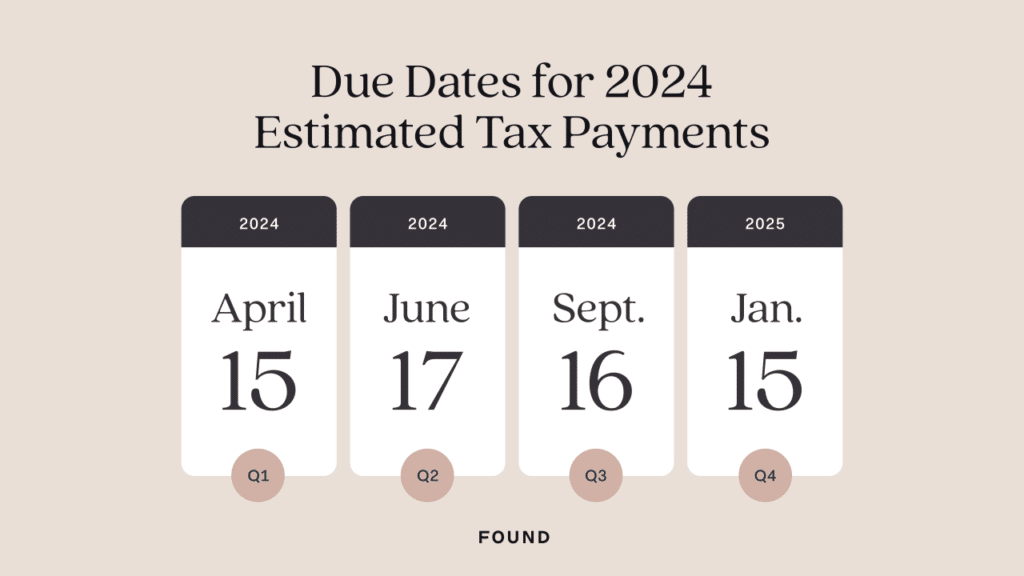
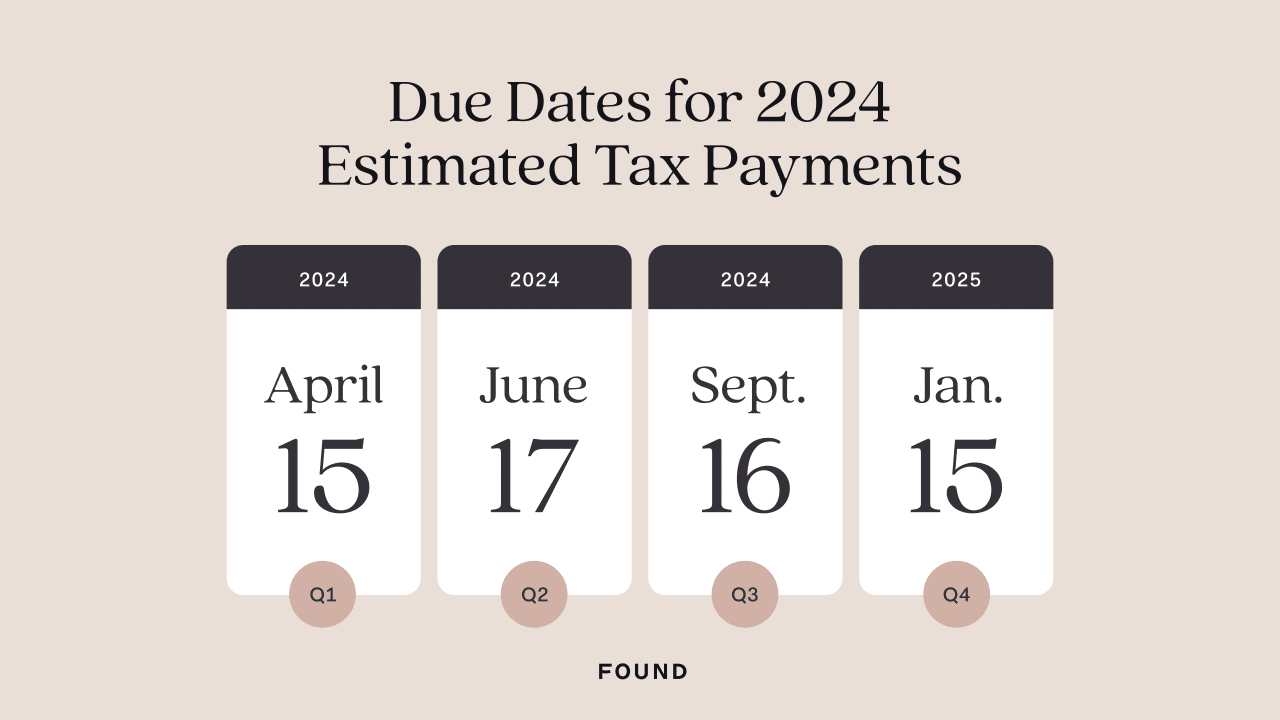
The Student Tax Deadline
The October 2024 tax deadline for students refers to the extended filing deadline for claiming certain educational tax credits and deductions. This deadline applies specifically to students who are filing for these credits and deductions, even if they don’t have any other income to report.
The general tax deadline for individuals is typically April 15th, but students who are claiming educational credits have until October 15th to file their tax return.
Implications of Missing the Deadline
Missing the October 2024 tax deadline for students can have several implications:
- Penalties:The IRS may impose penalties for late filing, which can include a percentage of the unpaid taxes or a flat fee, depending on the amount owed and the reason for the delay.
- Loss of Tax Benefits:Filing after the deadline may mean you miss out on valuable tax benefits, such as the American Opportunity Tax Credit, which can significantly reduce your tax liability.
- Impact on Future Tax Returns:Missing deadlines can create complications for future tax returns, potentially affecting your eligibility for other tax credits and deductions.
Student Tax Deadline vs. General Tax Deadline
The October 2024 tax deadline for students differs from the general tax deadline for individuals. Here’s a comparison:
| Tax Deadline | Description |
|---|---|
| General Tax Deadline | Applies to most individuals, including those with income from wages, salaries, investments, or other sources. Typically falls on April 15th. |
| Student Tax Deadline | Specifically for students claiming educational tax credits and deductions. Extended deadline of October 15th allows for additional time to file. |
Filing Requirements for Students
Not every student is required to file taxes. Whether you need to file depends on several factors, including your income level, age, and the type of income you earned. Understanding your filing requirements can help you avoid penalties and ensure you receive any tax benefits you’re eligible for.
Income Thresholds and Filing Requirements
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sets income thresholds that determine if you must file a tax return. These thresholds vary depending on your filing status and age. For example, if you are claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return, you generally don’t need to file if your income is below a certain limit.
This limit is typically higher for students under the age of 19.
Income Sources that Trigger Filing Requirements, October 2024 tax deadline for students
Many types of income can trigger a filing requirement for students. Here are some common examples:
- Wages from a part-time or summer job: If you worked during the year, you will likely have received a W-2 form from your employer. Even if your income was below the standard deduction, you may still need to file to claim certain tax credits.
- Income from self-employment: If you have a side hustle or freelance work, you will need to file taxes on your self-employment income. This includes income from platforms like Uber, Lyft, or Etsy.
- Interest or dividends: If you have savings accounts or investments that earn interest or dividends, you may need to file taxes on this income, even if it’s a small amount.
- Scholarships and grants: While scholarships and grants are generally not taxable, there are exceptions. If you received scholarships or grants that exceeded your educational expenses, you may need to report this as income.
Relevant Tax Forms for Students
Several tax forms are relevant to students, depending on their specific income sources and circumstances. Here’s a breakdown:
- Form 1040:This is the main federal income tax return form. Most students will use this form to file their taxes.
- Form W-2:This form reports your wages and withholdings from an employer. You will receive this form from any employer you worked for during the year.
- Form 1099-NEC:This form reports income from self-employment, such as freelance work or side hustles.
- Form 1099-INT:This form reports interest income from savings accounts or other investments.
- Form 1099-DIV:This form reports dividend income from investments.
- Form 1098-T:This form reports tuition payments and other educational expenses. You may need this form to claim certain education-related tax credits.
Note:If you’re unsure whether you need to file taxes or which forms to use, it’s best to consult with a tax professional.
Deductions and Credits for Students: October 2024 Tax Deadline For Students
Filing your taxes as a student can be overwhelming, but there are several deductions and credits available to help you reduce your tax burden. By understanding these tax benefits, you can maximize your tax savings and keep more of your hard-earned money.
If you’re planning to file your taxes in October 2024, make sure you’re aware of the tax filing extensions for October 2024. Our article provides information about the deadlines and requirements for filing extensions.
Deductions for Students
Deductions allow you to reduce your taxable income, which lowers your tax liability. Several deductions are specifically designed for students, including:
- Tuition and Fees Deduction:This deduction allows you to deduct up to $4,000 of qualified education expenses, including tuition, fees, and course materials. To be eligible, you must be enrolled at least half-time in a degree program at an eligible educational institution. The deduction is phased out for taxpayers with adjusted gross incomes above certain thresholds.
For example, in 2024, the deduction begins to phase out for single filers with AGIs above $80,000.
- Student Loan Interest Deduction:If you’re paying interest on student loans, you may be able to deduct up to $2,500 of that interest. This deduction is available to taxpayers who meet certain income limitations. For 2024, the deduction is phased out for single filers with AGIs above $85,000.
Credits for Students
Tax credits directly reduce your tax liability, dollar-for-dollar. Several tax credits are available for students, including:
- American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC):This credit is worth up to $2,500 per eligible student and is available for the first four years of post-secondary education. To be eligible, you must be enrolled at least half-time in a degree program at an eligible educational institution, be pursuing a degree or other recognized educational credential, and meet certain income requirements.
The credit is phased out for taxpayers with adjusted gross incomes above certain thresholds. For example, in 2024, the credit begins to phase out for single filers with AGIs above $80,000.
- Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC):This credit is worth up to $2,000 per taxpayer and is available for courses taken to acquire job skills or to pursue a degree at any level. To be eligible, you must be enrolled at least half-time in a degree program at an eligible educational institution.
The tax deadline for October 2024 is approaching. Make sure you’re prepared and know what the tax deadline is for October 2024 to avoid any penalties.
The credit is nonrefundable, meaning it can only reduce your tax liability to $0, not generate a refund.
Calculating Potential Tax Savings
To illustrate how these deductions and credits can save you money, let’s consider an example. Suppose you are a single student with an adjusted gross income of $50,000 and you paid $10,000 in tuition and fees and $1,000 in student loan interest during the year.
The tax brackets for single filers in 2024 have been adjusted. You can find a detailed explanation of the new brackets in our guide.
- Tuition and Fees Deduction:You can deduct up to $4,000 of your tuition and fees, reducing your taxable income by $4,000.
- Student Loan Interest Deduction:You can deduct up to $2,500 of your student loan interest, reducing your taxable income by $2,500.
- American Opportunity Tax Credit:Assuming you meet the eligibility requirements, you could claim the AOTC, which is worth up to $2,500. This credit directly reduces your tax liability by $2,500.
Table of Deductions and Credits
| Deduction/Credit | Eligibility Criteria | Maximum Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Tuition and Fees Deduction | Enrolled at least half-time in a degree program at an eligible educational institution | $4,000 |
| Student Loan Interest Deduction | Paying interest on student loans, meet certain income limitations | $2,500 |
| American Opportunity Tax Credit | Enrolled at least half-time in a degree program at an eligible educational institution, pursuing a degree or other recognized educational credential, meet certain income requirements | $2,500 per eligible student |
| Lifetime Learning Credit | Enrolled at least half-time in a degree program at an eligible educational institution | $2,000 per taxpayer |
Important Note:These deductions and credits are subject to certain income limitations and other eligibility requirements. Consult with a tax professional to determine your specific eligibility and maximize your tax savings.
Wondering what the highest tax bracket is in 2024? You can find out by checking out our article on the highest tax bracket in 2024. We’ve got all the details you need to know.
Filing Options for Students
When filing your taxes, you have several options available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right method depends on your individual circumstances, such as your income level, complexity of your tax situation, and personal preferences.
Want to understand how tax brackets work in 2024? We have a guide that helps you understand tax brackets for 2024 and how they impact your tax liability.
Filing Methods for Students
There are three primary ways to file your taxes:
- E-filing through tax preparation software: This is the most common and convenient method, offering features like guided assistance, error checking, and direct filing with the IRS. Popular options include TurboTax, H&R Block, and TaxAct.
- Hiring a tax professional: If your tax situation is complex, such as having multiple income sources or deductions, hiring a tax professional can be beneficial. They can provide expert advice and ensure accuracy in your filing.
- Filing by mail: This method involves using paper forms and sending them to the IRS by mail. While it’s less common, it remains an option for those who prefer a traditional approach.
Comparison of Filing Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| E-filing through tax preparation software | Convenient, fast, accurate, user-friendly, often free for simple returns | May require technical expertise, additional costs for complex returns, potential for errors if not used correctly |
| Hiring a tax professional | Expert advice, accurate filing, peace of mind, assistance with complex situations | High cost, limited access for low-income individuals, potential for conflicts of interest |
| Filing by mail | Free, no technical expertise required, traditional approach | Time-consuming, prone to errors, delayed processing, potential for lost or damaged forms |
E-filing Taxes Using Tax Preparation Software
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to file your taxes online using a popular tax preparation software:
- Choose a tax preparation software: Select a reputable software that suits your needs and budget. Consider factors like user interface, features, and pricing.
- Gather your tax documents: Collect all necessary documents, including your Social Security number, Form W-2, Form 1099-INT, and any other relevant forms.
- Create an account and start your return: Register with the software, provide your personal information, and begin filling out the tax forms.
- Answer the questions and enter your information: The software will guide you through the process, asking questions about your income, deductions, and credits.
- Review your return: Carefully check your return for accuracy and make any necessary corrections.
- E-file your return: Once you’re satisfied with your return, electronically file it with the IRS through the software.
Common Student Tax-Related Issues
Students, like everyone else, are subject to potential tax-related issues. While the tax system can seem complex, understanding common issues can help you avoid potential problems and navigate your tax obligations effectively.
Tax Audits
Tax audits are a common occurrence, and students are not exempt. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) may select students for audits for various reasons, including discrepancies in reported income, deductions, or credits.
- Incorrectly Reporting Income:Failing to report all income earned, such as wages from part-time jobs, scholarships, or grants, can lead to an audit.
- Misusing Deductions and Credits:Claiming deductions or credits for which you are not eligible can trigger an audit. For example, claiming the education tax credit for a course not related to your field of study or claiming the tuition and fees deduction for a graduate program.
- Incorrect Filing Status:Choosing the wrong filing status, such as claiming single when you are married, can result in an audit.
- Errors in Filing:Simple mistakes, like incorrect Social Security numbers or inaccurate financial information, can lead to an audit.
Last Word
While navigating the tax world can seem daunting, especially for students, remember that there are resources available to help you. By understanding your filing obligations, utilizing available deductions and credits, and choosing the appropriate filing method, you can navigate the tax process with confidence.
Remember to seek professional advice if needed and utilize the resources provided in this guide to ensure a smooth and successful tax experience.
Commonly Asked Questions
What if I miss the October 2024 tax deadline?
Missing the tax deadline can result in penalties. You may be able to file for an extension, but it’s best to file on time if possible. Contact the IRS for more information.
How do I know if I need to file taxes as a student?
If your income exceeds a certain threshold, you’re generally required to file taxes. Consult the IRS website for specific income limits.
What are some common tax deductions for students?
Students can often deduct expenses related to education, such as tuition and fees, books, and supplies.
Can I file my taxes for free?
Yes, there are free tax preparation services available for students with low to moderate incomes. Check with the IRS or your local community center for options.