Open Enrollment October 2024 marks a crucial period for individuals and families to secure or adjust their health insurance coverage. This annual event offers a window of opportunity to review existing plans, explore new options, and potentially access financial assistance to make coverage more affordable.
Navigating the complexities of health insurance can be overwhelming, but understanding the process and available resources can empower you to make informed decisions that meet your unique needs.
The Open Enrollment period presents a chance to reassess your healthcare needs and explore options that align with your current health status, financial situation, and lifestyle. Whether you’re seeking a new plan, making changes to your existing coverage, or simply wanting to understand your options, this guide provides valuable information and insights to guide you through the process.
Contents List
- 1 Open Enrollment Overview
- 2 Eligibility and Enrollment Process
- 3 3. Health Insurance Plans and Options
- 4 4. Cost Considerations and Financial Assistance
- 5 5. Key Changes and Updates for 2024 in Health Insurance Regulations
- 6 Important Deadlines and Timelines
- 7 Resources and Support
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Open Enrollment
- 9 Benefits of Open Enrollment
- 10 Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
- 11 Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- 12 Health Insurance for Special Populations
- 13 Understanding Health Insurance Terminology: Open Enrollment October 2024
- 14 Tips for Making Informed Enrollment Decisions
- 15 Wrap-Up
- 16 Key Questions Answered
Open Enrollment Overview
Open Enrollment is a period when individuals and families can enroll in or change their health insurance plans. It typically occurs annually, offering a chance to review and update coverage based on changing needs and circumstances.Open Enrollment in October 2024 is a significant event for many individuals and families.
Want to know more about the woman who has captured the heart of Kansas City Chiefs star Travis Kelce? Find out all the details on the Travis Kelce Girlfriend October 2024 page.
This period provides an opportunity to assess current health insurance coverage, explore new plan options, and make adjustments to ensure appropriate protection and affordability.
Key Changes and Updates for Open Enrollment in 2024
Open Enrollment for 2024 will likely include several key changes and updates, reflecting the evolving healthcare landscape and the ongoing efforts to improve affordability and access to care.
- Changes to Plan Offerings:Health insurance companies may introduce new plans or adjust existing ones, impacting premiums, deductibles, and coverage benefits. It’s essential to carefully review plan details and compare options to find the best fit for individual needs and budgets.
- Premium Adjustments:Premiums may fluctuate based on factors like healthcare utilization trends, inflation, and government subsidies. Individuals should be prepared for potential premium changes and factor them into their budget planning.
- Expanded Coverage Options:Some states may expand their health insurance marketplace offerings, providing more choices for individuals seeking affordable coverage. This could include new plans designed to meet specific needs, such as coverage for individuals with pre-existing conditions or those seeking lower-cost options.
- Updated Eligibility Criteria:Eligibility criteria for government subsidies and financial assistance may change, impacting the affordability of health insurance for certain individuals and families. It’s crucial to review eligibility requirements and ensure accurate information is provided during the enrollment process.
Eligibility and Enrollment Process
Open Enrollment for health insurance is the annual period when individuals and families can choose or change their health insurance plans. During this time, you can enroll in a new plan, switch to a different plan, or stay with your current plan.
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for health insurance coverage during Open Enrollment, you must meet certain criteria. These criteria can vary depending on your state and the specific health insurance marketplace you are using. However, generally, you must be a U.S. citizen or legal resident, and you must not be currently enrolled in employer-sponsored health insurance.
Additionally, you must not be incarcerated.
Enrollment Process
The enrollment process for health insurance can vary slightly depending on your situation. However, the general steps are Artikeld below.
For Individuals and Families
- Determine your eligibility.The first step is to determine if you are eligible for health insurance coverage. You can do this by visiting the Health Insurance Marketplace website or contacting your state’s health insurance exchange.
- Create an account.Once you have determined your eligibility, you will need to create an account on the Health Insurance Marketplace website. This will allow you to compare plans and enroll in coverage.
- Provide your information.When creating your account, you will need to provide some basic information, such as your name, address, and Social Security number. You will also need to provide information about your income and family size.
- Compare plans.Once you have created your account, you can begin comparing health insurance plans. The Health Insurance Marketplace website provides a tool that allows you to compare plans based on factors such as cost, coverage, and provider network.
- Enroll in a plan.Once you have chosen a plan, you can enroll in coverage. You will need to provide your payment information and select your coverage start date.
- Start early.Open Enrollment is a busy time, so it is important to start the process early. This will give you ample time to compare plans and make the best decision for your needs.
- Gather your documents.Before you begin the enrollment process, gather all of your necessary documents, such as your Social Security number, income information, and any other relevant information. This will help to streamline the process.
- Use the Health Insurance Marketplace website.The Health Insurance Marketplace website is a valuable resource for finding and comparing health insurance plans. The website provides a variety of tools and resources to help you make an informed decision.
- Contact a health insurance agent or broker.If you are having trouble navigating the enrollment process, you can contact a health insurance agent or broker for assistance. They can help you understand your options and find the best plan for your needs.
3. Health Insurance Plans and Options
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re faced with a wide range of plan types, each with its own set of features and costs. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of health insurance plans available in the United States, helping you understand their key features, eligibility criteria, and cost considerations.
If you’re planning a trip to Six Flags, you’ll want to know when the Fright Fest festivities end. Check out the When Does Fright Fest End October 2024 page for all the details.
Categorize and Describe Health Insurance Plans
Understanding the different types of health insurance plans available is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage. Each plan type offers a unique combination of benefits, costs, and network restrictions.
If you’re looking for a gun show in Tulsa, you’re in luck! The Tulsa Gun Show November October 2024 is a great place to find a variety of firearms and accessories.
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): HMOs provide comprehensive coverage for healthcare services within a designated network of providers. They typically offer lower premiums than other plans, but require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who acts as your gatekeeper for referrals to specialists.
Get ready for some spooky fun at Disneyland’s iconic Haunted Mansion. For all the details on this beloved attraction, visit the The Haunted Mansion October 2024 page.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): PPOs offer greater flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to see providers both in and out of network. While in-network services are generally covered at a lower cost, out-of-network services may require higher copayments and deductibles.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): EPOs are similar to HMOs in that they require you to use providers within a specific network. However, unlike HMOs, EPOs do not typically offer out-of-network coverage, except in emergency situations.
- Point-of-Service (POS): POS plans combine features of HMOs and PPOs, allowing you to choose a PCP within the network and offering both in-network and out-of-network coverage. However, out-of-network services may require higher copayments and deductibles.
- High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): HDHPs have lower premiums than traditional plans but require you to pay a higher deductible before coverage kicks in. These plans are often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA), allowing you to save pre-tax dollars for healthcare expenses.
- Catastrophic Health Plan: Catastrophic plans are available to individuals under 30 or those who qualify for a hardship exemption. These plans have very high deductibles and only cover essential healthcare services, making them suitable for individuals who are healthy and expect minimal healthcare needs.
- Short-Term Health Insurance: Short-term plans offer temporary coverage for a limited period, typically ranging from 30 to 364 days. They may be a viable option for individuals who are between jobs or need temporary coverage for a specific reason. However, these plans are often limited in coverage and may not meet the requirements for essential health benefits.
- Medicare: Medicare is a federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities. It offers different parts, each covering specific healthcare services.
- Medicaid: Medicaid is a state-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. Eligibility requirements vary by state.
Compare and Contrast Health Insurance Plan Options
To help you understand the differences between various health insurance plans, here is a table comparing their key features, cost structures, network restrictions, and flexibility:
| Plan Type | Coverage Features | Cost Structure | Network Restrictions | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | Comprehensive coverage within network, primary care physician (PCP) required for referrals | Lower premiums, may have lower copayments and deductibles, but higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network services | Limited to network providers, no out-of-network coverage | Limited choice of providers, referrals required from PCP |
| PPO | Coverage within and outside network, no PCP requirement | Higher premiums than HMOs, lower copayments and deductibles for in-network services, higher for out-of-network services | Greater flexibility, coverage for both in-network and out-of-network services | More choice of providers, no referral requirements |
| EPO | Comprehensive coverage within network, no PCP requirement | Premiums typically lower than PPOs, limited out-of-network coverage | Limited to network providers, limited out-of-network coverage, except for emergencies | Limited choice of providers, no referral requirements |
| POS | Coverage within and outside network, PCP required for referrals | Premiums typically higher than HMOs, lower copayments and deductibles for in-network services, higher for out-of-network services | Coverage for both in-network and out-of-network services, but out-of-network services may require higher copayments and deductibles | Greater flexibility than HMOs, but less than PPOs, referrals required from PCP |
| HDHP | Comprehensive coverage, high deductible before coverage kicks in | Lower premiums than traditional plans, high deductible, lower copayments and deductibles | Coverage within and outside network, may have higher copayments and deductibles for out-of-network services | Greater flexibility than HMOs, but less than PPOs, no referral requirements |
| Catastrophic | Limited coverage for essential healthcare services | Lowest premiums, highest deductible | Coverage within and outside network, limited coverage for non-essential services | Limited flexibility, only for individuals under 30 or those with hardship exemptions |
| Short-Term | Limited coverage, may not meet requirements for essential health benefits | Variable premiums, often lower than traditional plans, limited coverage | Coverage within and outside network, limited coverage, may not cover essential health benefits | Limited flexibility, temporary coverage for a limited period |
| Medicare | Comprehensive coverage for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities | Premiums vary based on plan type and coverage, deductibles and copayments apply | Coverage within and outside network, varies based on plan type and coverage | Flexibility varies based on plan type, may require referrals from PCP |
| Medicaid | Comprehensive coverage for low-income individuals and families | No premiums, but eligibility requirements vary by state | Coverage within and outside network, varies based on state and plan type | Flexibility varies based on state and plan type, may require referrals from PCP |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Health Insurance Plan
Selecting the right health insurance plan is a crucial decision that involves considering various factors, including your personal needs, financial situation, healthcare preferences, and plan features.
- Personal Needs:
- Age: Younger individuals with good health may opt for a catastrophic plan, while older individuals with pre-existing conditions may require more comprehensive coverage.
- Health Status: Individuals with chronic conditions may need a plan with lower copayments and deductibles for specific services.
- Lifestyle: Active individuals may prioritize plans with coverage for preventive care and fitness programs.
- Family Size: Families with children may need a plan with coverage for pediatric services.
- Financial Situation:
- Income: Consider your income and budget when evaluating premium costs, deductibles, and copayments.
- Budget: Determine how much you can afford to pay for health insurance premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
- Savings: Evaluate your ability to save money for healthcare expenses, particularly for high-deductible plans.
- Healthcare Preferences:
- Choice of Providers: Research the provider networks of different plans to ensure access to your preferred doctors and hospitals.
- Access to Specialists: Consider your need for specialist care and choose a plan that provides coverage for specialists in your area.
- Hospital Preferences: Check if your preferred hospitals are included in the plan’s network.
- Plan Features:
- Coverage Limits: Understand the limitations of coverage, such as maximum out-of-pocket expenses and annual benefit limits.
- Deductibles: Evaluate the amount you need to pay out-of-pocket before coverage kicks in.
- Copayments: Consider the copayments you’ll pay for various services, such as doctor visits and prescription drugs.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: Understand the maximum amount you’ll pay for healthcare expenses in a year.
- Network Restrictions: Review the network restrictions of the plan to ensure access to providers and hospitals in your area.
- Age:Generally, older individuals tend to have higher premiums due to a greater likelihood of needing medical care.
- Location:Premiums can vary based on your geographic location, reflecting differences in healthcare costs and the availability of providers in your area.
- Health Status:Individuals with pre-existing conditions may face higher premiums. However, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions.
- Coverage Level:Choosing a plan with more comprehensive coverage, such as a gold or platinum plan, will typically result in higher premiums compared to plans with lower coverage levels, like bronze or silver plans.
- Premium Tax Credits:These tax credits are available to individuals and families with incomes below certain thresholds. The amount of the tax credit depends on your income and the cost of the plan you choose.
- Cost-Sharing Reductions:These reductions lower your out-of-pocket costs, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. Eligibility is based on income and the plan you choose.
- State-Based Programs:Many states offer additional financial assistance programs, such as subsidies or tax credits, to help residents afford health insurance.
- Choose a High-Deductible Plan with a Health Savings Account (HSA):High-deductible plans typically have lower premiums but require you to pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in. You can use an HSA to save pre-tax dollars to cover medical expenses, potentially reducing your overall healthcare costs.
- Utilize Preventive Care Services:Many health insurance plans cover preventive care services, such as screenings and vaccinations, at no cost. Taking advantage of these services can help you stay healthy and avoid costly medical treatments in the future.
- Negotiate Lower Premiums or Obtain Discounts:You may be able to negotiate lower premiums or obtain discounts by shopping around for different insurance plans, bundling insurance policies, or taking advantage of employer-sponsored programs.
- Assess your needs:Consider your health status, coverage requirements, and budget when choosing a plan.
- Explore financial assistance options:Determine your eligibility for premium tax credits, cost-sharing reductions, or state-based programs.
- Compare plans:Use online tools or contact insurance brokers to compare plans and premiums from different insurance companies.
- Consider a high-deductible plan with an HSA:This option can be beneficial if you are generally healthy and want to save money on premiums.
- Utilize preventive care services:Stay proactive about your health by taking advantage of covered preventive care services.
- Shop around for discounts:Explore potential discounts offered by insurance companies or employer-sponsored programs.
- Review your plan regularly:Make sure your plan still meets your needs and consider switching plans if necessary.
- Expansion of Essential Health Benefits:The list of essential health benefits, which all health insurance plans must cover, has been expanded to include additional services such as mental health and substance abuse treatment, as well as expanded coverage for preventive care. This expansion aims to ensure comprehensive coverage for a wider range of healthcare needs.
- Increased Coverage for Mental Health Services:The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has mandated that all health insurance plans cover a minimum number of mental health therapy sessions per year, with reduced out-of-pocket costs for individuals. This change is aimed at improving access to mental health care and reducing financial barriers to treatment.
- Changes to Premium Tax Credits:The premium tax credits, which help individuals and families afford health insurance, have been adjusted based on income and family size. This adjustment aims to ensure that more individuals and families can access affordable health insurance.
- Expansion of Telehealth Coverage:Many health insurance plans have expanded coverage for telehealth services, recognizing the growing importance of virtual healthcare delivery. This change aims to improve access to healthcare for individuals in rural areas or with limited mobility.
- Increased Transparency in Healthcare Costs:The federal government has implemented measures to increase transparency in healthcare costs, providing individuals with more information about the cost of medical services and prescription drugs. This change empowers consumers to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
- Premium Adjustments:The changes to premium tax credits and the expansion of essential health benefits may lead to adjustments in insurance premiums. Some individuals may see a decrease in their premiums, while others may see an increase. It is important to carefully review the available plans and their costs during Open Enrollment.
- Deductibles and Co-pays:The expansion of coverage for mental health services and other essential health benefits may lead to changes in deductibles and co-pays for these services. It is crucial to understand these changes and how they might affect out-of-pocket expenses.
- Improved Access to Mental Health Services:The increased coverage for mental health services will likely improve access to care for individuals with mental health conditions. This change aims to address the growing need for mental health services and reduce the stigma associated with seeking help.
- Expanded Telehealth Options:The expansion of telehealth coverage will make it easier for individuals in rural areas or with limited mobility to access healthcare services. This change aims to improve access to care for those who might otherwise have difficulty accessing traditional healthcare settings.
- Expanded Coverage Options:The expansion of essential health benefits and the changes to premium tax credits may lead to a wider range of health insurance plans available to individuals and families. This increased choice will allow individuals to find plans that best meet their individual needs and budgets.
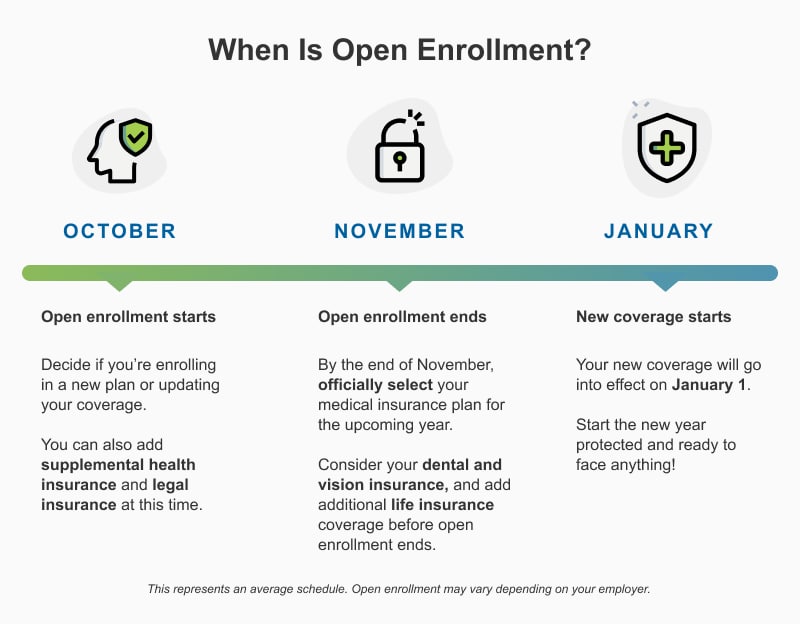
- November 1st:Open Enrollment begins. You can start shopping for plans and comparing options.
- December 15th:Deadline to enroll in a plan and have coverage start on January 1st of the following year.
- January 15th:Open Enrollment ends. If you miss this deadline, you can only enroll in a plan if you qualify for a Special Enrollment Period due to a qualifying life event, such as getting married, having a baby, or losing your job.
- February 1st:If you enrolled in a plan by December 15th, your coverage will begin.
- HealthCare.gov:The official website for the Affordable Care Act (ACA) provides detailed information on Open Enrollment, eligibility, plans, and financial assistance.
- State Health Insurance Marketplaces:Each state has its own marketplace website where you can compare plans, enroll, and get assistance. You can find your state’s marketplace website on HealthCare.gov.
- Your Employer’s Human Resources Department:If you receive health insurance through your employer, their HR department can provide information about your plan options and enrollment procedures.
- Independent Insurance Brokers:These professionals can help you compare plans and navigate the enrollment process. You can find an independent broker through the National Association of Health Underwriters (NAHU).
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS):CMS is the federal agency that oversees the ACA. You can contact them for general information about Open Enrollment and the ACA. Phone: 1-800-MEDICARE (1-800-633-4227)
- The National Association of Health Underwriters (NAHU):NAHU is a professional association for insurance brokers. You can find a local NAHU broker who can provide personalized advice and support. Website: www.nahu.org
- The National Council on Aging (NCOA):NCOA offers resources and support for older adults, including information on Medicare and other health insurance programs. Website: www.ncoa.org
- Your State’s Department of Insurance:Each state has a department of insurance that regulates health insurance plans and can provide information about your rights and responsibilities. You can find your state’s department of insurance website on the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) website.
For a truly magical experience, consider attending the Candlelight Processional October 2024. This heartwarming event combines storytelling, music, and the beauty of candlelight.
- Enroll in a Navigators Program:Navigators are trained professionals who can provide free, unbiased assistance with Open Enrollment. They can help you understand your options, compare plans, and enroll in the right coverage for you. You can find a Navigator near you on HealthCare.gov.
- Schedule an Appointment with a Certified Application Counselor (CAC):CACs are trained professionals who can help you apply for financial assistance and enroll in a health insurance plan. You can find a CAC near you on HealthCare.gov.
- Reach Out to Your State’s Health Insurance Marketplace:Most state marketplaces have call centers and online chat services that can provide assistance with enrollment and other questions.
- Who is eligible to enroll in a health insurance plan during Open Enrollment?Individuals who are employed, self-employed, or unemployed and meet certain income requirements are generally eligible.
- I’m a student; am I eligible for Open Enrollment?Students may be eligible if they are not covered under a parent’s plan and meet specific income requirements.
- I’m a retiree; can I enroll in a health plan during Open Enrollment?Retirees are typically eligible to enroll in Medicare, a federal health insurance program for individuals 65 years and older or those with certain disabilities.
- My spouse is employed; can I enroll in their health plan?You may be eligible to enroll in your spouse’s health plan if you are their dependent.
- When does Open Enrollment begin and end?The Open Enrollment period typically runs from November 1st to January 15th of each year.
- What happens if I miss the Open Enrollment deadline?If you miss the Open Enrollment deadline, you may only be able to enroll in a plan during a Special Enrollment Period due to a qualifying life event, such as a job loss, marriage, or birth of a child.
- What types of health insurance plans are available during Open Enrollment?There are various plan types available, including Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs). Each plan type has its own network of healthcare providers, coverage options, and costs.
- How do I compare different health insurance plans?You can compare plans based on factors such as monthly premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coverage for specific services.
- What factors should I consider when choosing a health insurance plan?Consider your healthcare needs, budget, and preferred healthcare providers when selecting a plan.
- How do I enroll in a health insurance plan during Open Enrollment?You can enroll online, by phone, or through an insurance agent.
- What information do I need to provide when enrolling in a health insurance plan?You will need to provide personal information, such as your Social Security number, date of birth, and contact information.
- What happens after I enroll in a health insurance plan?Once you enroll, you will receive a confirmation of your coverage and information about your plan benefits and costs.
- Are there any changes to health insurance regulations for the upcoming Open Enrollment period?It is important to stay informed about any changes to regulations that may affect your coverage or costs. You can find information about changes on the website of the Health Insurance Marketplace or consult with an insurance agent.
- Wider Range of Plans and Providers:During Open Enrollment, you have access to a wider variety of health insurance plans and providers, allowing you to compare options and choose the one that best aligns with your healthcare needs and financial situation.
- Potential for Lower Premiums:Insurance companies often offer competitive premiums during Open Enrollment to attract new customers. By comparing plans, you may find a more affordable option than what you could get outside of this period.
- Access to Better Plans:Open Enrollment is the time to explore new plans with enhanced benefits or lower deductibles, allowing you to potentially improve your coverage without increasing your premium.
- Financial Protection:Health insurance safeguards you from unexpected medical expenses, preventing financial strain due to accidents or illnesses. Gaps in coverage can leave you vulnerable to significant out-of-pocket costs.
- Access to Essential Healthcare:Continuous coverage ensures you have access to preventive care, routine checkups, and necessary medical treatments without facing financial barriers.
- Pre-Existing Conditions:Individuals with pre-existing conditions may face higher premiums or limited coverage options if they have gaps in coverage. Continuous coverage helps maintain your access to necessary healthcare services and avoids potential coverage limitations.
- Crucial in Unexpected Situations:Continuous coverage is particularly vital in situations like accidents or unexpected illnesses. It provides peace of mind knowing you have financial protection and access to necessary medical care when you need it most.
- Limited Options:Outside of Open Enrollment, your options for enrolling in health insurance are limited, potentially restricting your choices to plans with higher premiums or fewer benefits.
- Higher Costs:You may face higher premiums or limited coverage options if you enroll outside of Open Enrollment. Insurance companies may charge higher rates for individuals who choose to enroll outside of the designated period.
- Potential for a Penalty:Depending on your circumstances, you may be subject to a penalty for not having health insurance coverage. This penalty can be a significant financial burden.
- Waiting Period:There may be a waiting period before your coverage becomes effective if you enroll outside of Open Enrollment. This means you’ll have to pay out-of-pocket for any medical expenses incurred during this period.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs typically provide coverage through a network of doctors and hospitals. You will need to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network who will act as your main point of contact for healthcare. Referrals are often required to see specialists.
Lakeith Stanfield is a talented actor known for his roles in films like “Get Out” and “Atlanta.” You can learn more about his career and upcoming projects on the Lakeith Stanfield page.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to see doctors and hospitals outside the network, though you will usually pay higher out-of-pocket costs. You do not need a PCP with a PPO.
- Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs): EPOs are similar to HMOs but with a wider network of providers. They usually have lower premiums than HMOs but higher out-of-pocket costs.
- Point of Service (POS): POS plans combine features of HMOs and PPOs, offering a network of providers and the ability to see providers outside the network. You may need a referral to see specialists.
- High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs): HDHPs have lower premiums but higher deductibles than traditional plans. They are often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA), which allows you to save pre-tax dollars for healthcare expenses.
- Review Plan Options: Your employer will provide information about the available health insurance plans, including details on premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coverage.
- Choose a Plan: Based on your needs and budget, you will select the health insurance plan that best suits you.
- Complete Enrollment Forms: You will need to complete enrollment forms, providing personal information and selecting your coverage options.
- Submit Enrollment Forms: You will submit the completed enrollment forms to your employer or the designated enrollment agency.
- Confirmation of Enrollment: Once your enrollment is processed, you will receive confirmation of your coverage.
- You must not be covered by another health insurance plan, such as Medicare or Medicaid.
- You cannot be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return.
- Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income.
- Earnings on HSA funds grow tax-free.
- Withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
- Lower Out-of-Pocket Costs:By saving money in an HSA, you can cover your deductible and other out-of-pocket expenses without using your own funds.
- Financial Security:An HSA provides a dedicated source of funds for healthcare expenses, offering financial security in case of unexpected medical bills.
- Long-Term Savings:Unused HSA funds roll over year after year, allowing you to save for future healthcare needs.
- Doctor’s visits
- Prescription drugs
- Hospital stays
- Dental and vision care
- Non-Medical Expenses:Using HSA funds for non-medical expenses is generally not allowed. If you use HSA funds for non-medical expenses, you will be subject to a 20% penalty, plus you will have to pay taxes on the amount withdrawn.
- High-Deductible Health Plan Requirement:To be eligible for an HSA, you must be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). This means you will have a higher deductible than traditional health insurance plans.
- Potential Penalties for Non-Medical Spending:Using HSA funds for non-medical expenses can result in penalties and taxes.
- Risk of Losing Funds:If you don’t use your HSA funds within a certain timeframe, you may be subject to a penalty.
- Eligibility:Ensure you meet the eligibility requirements, such as being enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) and not being covered by another health insurance plan.
- Contribution Limits:Check the annual contribution limits, as these can change each year.
- Investment Options:Consider the investment options offered by the HSA provider. You can invest your HSA funds in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
- Fees:Compare the fees charged by different HSA providers. Some providers charge annual fees, while others charge transaction fees.
- Medicare Part A: Covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facilities, hospice care, and some home health services.
- Medicare Part B: Covers doctor’s visits, outpatient care, medical equipment, and preventive services.
- Medicare Part C: Also known as Medicare Advantage, offered by private insurance companies and combines coverage from Part A and Part B. It may include additional benefits, such as vision and dental care.
- Medicare Part D: Covers prescription drugs.
- ACA Marketplace: Individuals can shop for health insurance plans through the ACA Marketplace, where they can find plans that meet their needs and budget.
- State-based Marketplaces: Some states have their own marketplaces that offer health insurance plans to individuals and families.
- Medicaid: A government-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. Eligibility requirements vary by state.
- Medicaid: Provides health insurance coverage to low-income individuals with disabilities.
- Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI): Provides benefits to individuals with disabilities who have paid Social Security taxes for a certain period of time.
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI): Provides financial assistance to low-income individuals with disabilities.
- Premium:The monthly payment you make to your insurance company for your health insurance plan.
- Deductible:The amount you pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services before your insurance starts covering costs. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, you would need to pay the first $1,000 of your healthcare expenses before your insurance begins to cover the remaining costs.
- Co-pay:A fixed amount you pay for a specific healthcare service, like a doctor’s visit or prescription. Co-pays are usually a small amount, such as $20 or $30, and are often paid at the time of service.
- Co-insurance:A percentage of the cost of a healthcare service that you are responsible for paying after your deductible is met. For instance, if your co-insurance is 20%, you would pay 20% of the cost of your healthcare services after your deductible is met.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum:The maximum amount you will pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services in a year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance company will cover 100% of your remaining healthcare costs for the rest of the year.
- Formulary:A list of prescription drugs covered by your health insurance plan. Not all drugs are covered by every plan, so it’s important to check the formulary before choosing a plan.
- Network:A group of healthcare providers, such as doctors, hospitals, and pharmacies, that have agreed to provide services at discounted rates to members of a specific health insurance plan. It’s important to ensure your preferred doctors and hospitals are in your plan’s network to avoid higher costs.
If you’re planning a trip to Disneyland, be sure to check out the The Haunted Mansion Cast October 2024 to see who’s bringing the spooky charm to the classic ride this season.
- Health Savings Account (HSA):A tax-advantaged savings account that allows you to save pre-tax dollars for healthcare expenses. HSAs are often paired with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) and can offer significant tax benefits.
- Flexible Spending Account (FSA):A tax-advantaged account that allows you to save pre-tax dollars for eligible healthcare expenses and dependent care expenses. FSAs are often offered through employers and can help you save money on healthcare costs.
- Enroll in a new health insurance plan.
- Change your existing plan.
- Drop your coverage.
- Review Your Current Plan:Start by reviewing your current health insurance plan. Consider your coverage, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket expenses. Think about how well your current plan meets your needs.
- Gather Information:Research different health insurance plans available to you. Consider factors like cost, coverage, provider networks, and prescription drug formularies.
- Compare Plans:Use online tools or contact insurance brokers to compare different plans side-by-side. Pay attention to premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Consider Your Needs:Think about your health history, expected medical expenses, and any specific health conditions you have. Choose a plan that best suits your individual needs.
- Enroll Online or by Phone:Once you’ve selected a plan, enroll online through your insurance company’s website or by calling their customer service line.
- Your Insurance Company’s Website:Most insurance companies have detailed information about their plans on their websites. You can often find plan summaries, coverage details, and cost breakdowns.
- Online Comparison Tools:Several websites allow you to compare health insurance plans side-by-side. These tools can help you filter plans based on your needs and budget.
- Insurance Brokers:Licensed insurance brokers can provide personalized advice and help you find the best plan for your situation.
- Your Employer’s Human Resources Department:If you have employer-sponsored health insurance, your HR department can provide information about plan options and enrollment procedures.
- Premiums:The monthly cost you pay for your health insurance plan.
- Deductibles:The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in.
- Co-pays:The fixed amount you pay for specific medical services, like doctor visits or prescriptions.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum:The maximum amount you’ll pay out-of-pocket for medical expenses in a given year.
- Provider Network:The list of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers covered by your plan.
- Prescription Drug Formulary:The list of prescription drugs covered by your plan.
- Coverage Details:Understand the specific benefits and limitations of each plan. Consider what services are covered and what services may require pre-authorization.
- Healthcare.gov:The official website for the Affordable Care Act (ACA) provides information about health insurance plans, eligibility, and enrollment procedures.
- Your State Insurance Department:Each state has a department that regulates insurance companies. You can contact your state insurance department for information about health insurance plans and consumer protection.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC):The NAIC provides resources and information about insurance regulations and consumer protection.
4. Cost Considerations and Financial Assistance
Understanding the cost of health insurance and exploring available financial assistance options are crucial for making informed decisions during Open Enrollment. This section will guide you through the factors influencing premiums, the financial assistance programs available, strategies for managing costs, and a concise guide for understanding your health insurance expenses.
4.1. Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums are determined by various factors, including your age, location, health status, and the level of coverage you choose.
4.2. Available Financial Assistance Programs
Several financial assistance programs are available to help individuals afford health insurance.
4.3. Strategies for Managing Health Insurance Costs
There are several strategies you can employ to manage your health insurance costs.
4.4. Guide for Understanding and Managing Health Insurance Costs
Here is a concise guide for individuals seeking to understand and manage their health insurance costs:
5. Key Changes and Updates for 2024 in Health Insurance Regulations
The year 2024 brings significant changes to health insurance regulations, impacting individuals and families across the nation. These changes aim to improve access to healthcare, enhance affordability, and address evolving healthcare needs. Understanding these updates is crucial for making informed decisions during Open Enrollment.
Major Changes in Health Insurance Regulations for 2024
This section will Artikel the key changes in health insurance regulations for 2024, providing a clear understanding of their nature and scope.
If you’re curious about the stars who brought the spooky fun of the 2003 “Haunted Mansion” to life, you can check out the Cast Of Haunted Mansion 2003 for a nostalgic look at the film’s talented ensemble.
Impact of Changes on Individuals and Families
The changes in health insurance regulations for 2024 will have a direct impact on individuals and families in various ways.
Financial Implications
Access to Care
Choice and Options
Resources for Staying Informed
Staying informed about the latest developments in health insurance regulations is crucial for making informed decisions during Open Enrollment. Here are some reliable resources:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| [Link to Government Website] | Official website for health insurance regulations and updates. |
| [Link to Health Insurance Publication] | A publication dedicated to providing news and analysis of health insurance regulations. |
| [Link to Reputable News Source] | A trusted news source that covers health insurance regulations and updates. |
Important Deadlines and Timelines
Open Enrollment is a crucial period for making important decisions about your health insurance coverage for the upcoming year. It’s essential to be aware of the key deadlines and timelines associated with this process to ensure you have the coverage you need without facing any penalties.
Open Enrollment Period, Open Enrollment October 2024
The Open Enrollment period for health insurance plans offered through the Health Insurance Marketplace is typically from November 1st to January 15th. During this period, you can enroll in a new health insurance plan, change your existing plan, or drop your coverage altogether.
The Haunted Mansion has a talented cast of actors bringing the spooky characters to life. Check out the The Haunted Mansion Cast October 2024 page for more information.
It’s crucial to remember that these deadlines are subject to change each year.
Key Deadlines and Timelines
Here is a calendar that summarizes important dates to keep in mind during Open Enrollment:
Consequences of Missing Deadlines
Missing the Open Enrollment deadline can have serious consequences. You may be required to pay a penalty for not having health insurance, or you may not be able to enroll in a plan until the next Open Enrollment period.
Resources and Support
Navigating Open Enrollment can be a bit overwhelming, but you don’t have to do it alone! There are many resources available to help you understand your options and make the best choices for your health insurance needs. We’ve compiled a list of reliable resources and support organizations that can provide guidance and assistance throughout the process.
Reliable Resources for Open Enrollment Information
You can find comprehensive information about Open Enrollment on various websites and platforms:
Contact Information for Support Organizations and Agencies
Here are some organizations that can offer personalized assistance and advice:
Accessing Personalized Assistance and Advice
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Open Enrollment
This section addresses common questions individuals may have about Open Enrollment, including eligibility, deadlines, plan options, the enrollment process, and changes to coverage.
Eligibility
Eligibility for Open Enrollment is determined by various factors, including employment status, income level, and residency.
Deadlines
The Open Enrollment period has specific start and end dates. It is crucial to understand these deadlines to avoid missing out on coverage.
Plan Options
During Open Enrollment, you have the opportunity to choose a health insurance plan that best suits your needs and budget.
Enrollment Process
The enrollment process involves several steps, from choosing a plan to completing the necessary paperwork.
Changes to Coverage
Changes to health insurance regulations can impact your coverage options and costs.
Get ready for some exciting tennis action at the Swiss Indoors Basel. For all the details on this prestigious tournament, visit the Swiss Indoors Basel October 2024 page.
Benefits of Open Enrollment
Open Enrollment is a crucial period for securing health insurance coverage. It’s the time when you can choose a plan that best suits your needs and budget, ensuring you have access to essential healthcare services throughout the year.
The new “Haunted Mansion” movie is out, and you can check out what critics are saying on Haunted Mansion October 2024 Rotten Tomatoes. See if it’s worth a trip to the theater.
Advantages of Enrolling During Open Enrollment
Enrolling during Open Enrollment offers significant advantages compared to enrolling outside of this period. Here’s why:
Importance of Continuous Health Insurance Coverage
Maintaining continuous health insurance coverage is crucial for several reasons:
Consequences of Not Enrolling During Open Enrollment
Failing to enroll during Open Enrollment can have significant consequences:
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
If you are employed, your employer may offer health insurance as a benefit. This can be a valuable resource, offering coverage at potentially lower costs than individual plans.
Options for Obtaining Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Your employer may offer various health insurance plans, including:
Enrollment Process for Employer-Sponsored Plans
The enrollment process for employer-sponsored plans typically involves the following steps:
Comparison of Employer-Sponsored and Individual Plans
Here is a comparison of employer-sponsored and individual plans:
| Feature | Employer-Sponsored Plans | Individual Plans |
|---|---|---|
| Premiums | Often lower due to group discounts | Typically higher due to individual rates |
| Deductibles | May vary depending on the plan | May vary depending on the plan |
| Coverage | Can vary depending on the plan | Can vary depending on the plan |
| Enrollment Period | Usually during an annual open enrollment period | Typically available year-round |
| Eligibility | Limited to employees and their dependents | Available to anyone |
Employer-sponsored plans can be a valuable option for obtaining affordable health insurance, but it is important to carefully review your options and choose the plan that best meets your needs.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged savings account that allows individuals to save money for healthcare expenses. HSAs are designed to complement high-deductible health insurance plans (HDHPs), offering a way to manage healthcare costs more effectively.
HSA Eligibility Requirements
To be eligible to open an HSA, you must be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) and meet the following requirements:
HSA Tax Advantages
Contributing to an HSA offers several tax advantages:
Benefits of Using an HSA
HSAs offer several potential benefits for managing healthcare expenses:
Using an HSA to Manage Healthcare Expenses
You can use your HSA to pay for eligible medical expenses, such as:
Limitations on HSA Use
While HSAs offer tax advantages, there are limitations on their use:
HSA Drawbacks
While HSAs offer significant benefits, there are potential drawbacks to consider:
Comparing HSAs, FSAs, and HRAs
| Feature | HSA | FSA | HRA ||—|—|—|—|| Eligibility | Must be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) | Offered by employers | Offered by employers || Contribution Limit | Set by the government annually | Set by the employer | Set by the employer || Tax Advantages | Contributions are tax-deductible; withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free | Contributions are pre-tax; withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free | Contributions are not tax-deductible; withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free || Rollover | Unused funds roll over year after year | Funds typically do not roll over | Funds typically do not roll over || Ownership | Account is owned by the individual | Account is owned by the employer | Account is owned by the employer || Use for Non-Medical Expenses | Generally not allowed | Generally not allowed | Generally not allowed |
Calling all skiers and snowboarders! Get ready for the season’s opening at A Basin. Check out the A Basin Opening Day October 2024 page for all the details.
Opening an HSA
If you are eligible for an HSA and are looking for a way to manage your healthcare expenses more effectively, opening an HSA is a good option. You can open an HSA through a bank, credit union, or other financial institution.
Looking for a festive way to celebrate Halloween? The Woburn Halloween Parade October 2024 promises to be a fun-filled event with costumes, candy, and community spirit.
Example of HSA Use
Imagine you are a young professional with a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) and a family to support. You decide to open an HSA to save for potential healthcare expenses. You contribute the maximum amount allowed each year and use the funds to pay for doctor’s visits, prescription drugs, and other eligible medical expenses.
By saving money in your HSA, you are able to manage your healthcare costs effectively and avoid using your own funds for these expenses.
Health Insurance for Special Populations
Navigating the health insurance landscape can be complex, especially for individuals with unique needs or circumstances. This section focuses on health insurance options for specific groups, including seniors and individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Get ready for some spine-tingling fun at Turtle Back Zoo! Their annual Halloween festivities are a great time for families, and you can find out all the details on the Turtle Back Zoo Halloween October 2024 page.
Health Insurance for Seniors
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with certain disabilities.
Medicare is funded through payroll taxes and premiums. Individuals can choose different Medicare plans based on their needs and budget.
Health Insurance for Individuals with Pre-existing Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer, may face challenges in obtaining affordable health insurance. However, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions.
Individuals with pre-existing conditions should carefully consider their options and compare plans to find the best coverage at an affordable price.
Health Insurance for Individuals with Disabilities
Individuals with disabilities may qualify for additional health insurance options and benefits.
Individuals with disabilities should explore all available resources to ensure they have access to appropriate health insurance coverage.
Understanding Health Insurance Terminology: Open Enrollment October 2024
Navigating the world of health insurance can be overwhelming, especially with the numerous terms and concepts involved. Understanding these terms is crucial for making informed decisions about your health coverage and ensuring you have the right plan to meet your needs.
Key Terms and Definitions
This section defines common health insurance terms to help you better understand your coverage and make informed choices.
Significance of Understanding Health Insurance Terminology
Comprehending these terms is crucial for making informed decisions about your health insurance plan. For instance, knowing your deductible and co-pay amounts can help you estimate the costs of healthcare services. Understanding the concept of a formulary can help you choose a plan that covers the medications you need.
By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you can ensure you have the right health insurance coverage to meet your individual needs and budget.
Tips for Making Informed Enrollment Decisions
Making smart choices during Open Enrollment can save you money and ensure you have the health insurance coverage you need. Understanding the process and exploring your options is key. Here’s a guide to help you make informed decisions:
Understanding the Enrollment Process
Open Enrollment is a specific period each year when you can change your health insurance plan. It’s important to review your current plan and consider your needs for the upcoming year. During Open Enrollment, you can:
Step-by-Step Enrollment Guide
The enrollment process is usually straightforward, but it’s helpful to understand the steps involved:
Gathering Information About Plan Options
There are various ways to gather information about different plan options:
Key Factors to Consider When Evaluating Plan Options
When evaluating different health insurance plans, consider these key factors:
Comparing Plan Options
Here’s a table comparing different plan options and their features:
| Plan Type | Premium | Deductible | Co-pays | Out-of-Pocket Maximum | Provider Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) | Lower | Higher | Lower | Lower | Wide |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | Higher | Lower | Higher | Higher | Wide |
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | Lower | Lower | Lower | Lower | Narrow |
Note: This is a simplified example. Actual plan features and costs may vary.
Reading the Fine Print
Always read the fine print of any health insurance plan you’re considering. Pay close attention to the terms and conditions, especially regarding coverage limitations, exclusions, and pre-authorization requirements.
Looking for a fun way to celebrate Halloween in Woburn? The Woburn Halloween Parade October 2024 is a great option, offering costumes, candy, and community spirit.
Seeking Professional Advice
If you’re unsure about the best plan option for you, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice. Insurance brokers, financial advisors, or healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance.
Resources and Support
Here are some resources that can help you make informed enrollment decisions:
Wrap-Up
Open Enrollment October 2024 is a time to prioritize your health and well-being by ensuring you have the right health insurance coverage. By understanding your options, comparing plans, and exploring financial assistance programs, you can make informed decisions that protect your health and financial security.
Remember, taking the time to review your coverage and explore new possibilities during this period can have a significant impact on your overall health and financial well-being.
Key Questions Answered
What is the deadline for Open Enrollment?
The Open Enrollment period for health insurance typically runs from November 1st to January 15th each year. It’s essential to meet the deadline to avoid potential penalties or gaps in coverage.
How do I know if I qualify for financial assistance?
To determine your eligibility for financial assistance, you can use the Health Insurance Marketplace website or contact a certified application counselor. Income levels and household size are key factors in determining eligibility.
What are the main differences between HMO and PPO plans?
HMO plans typically offer lower premiums but require you to stay within a specific network of providers. PPO plans generally have higher premiums but offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
Can I change my health insurance plan during Open Enrollment?
Yes, you can change your health insurance plan during Open Enrollment. This is a good opportunity to review your existing coverage and consider if it still meets your needs or if there are better options available.