Roth IRA Contribution Limits 2024: Planning for retirement is a crucial aspect of financial well-being, and maximizing your savings is essential to achieving your long-term goals. Understanding the contribution limits for Roth IRAs in 2024 is a key step in this process, as it allows you to make informed decisions about your retirement savings strategy.
Roth IRAs offer a unique opportunity to save for retirement with tax-free withdrawals in the future, making them a popular choice for many individuals. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of Roth IRA contribution limits for 2024, including eligibility requirements, age-based limitations, and strategies for maximizing your contributions.
The 2024 contribution limit for Roth IRAs is $6,500 for individuals under the age of 50 and $7,500 for individuals aged 50 and over. However, it’s important to note that income eligibility requirements apply, and contributions may be phased out for individuals exceeding certain income thresholds.
This article will delve into these details, exploring the nuances of Roth IRA contribution limits and their impact on retirement planning.
Contents List
- 1 Roth IRA Contribution Limits
- 2 Who is Eligible to Contribute to a Roth IRA?
- 3 3. Contribution Limits for Different Age Groups: Roth IRA Contribution Limits 2024
- 4 Tax Benefits of Roth IRA Contributions
- 5 5. Contribution Strategies for Maximizing Retirement Savings
- 5.1 5.1. Roth IRA Contribution Limits and Tax Benefits
- 5.2 5.2. Calculating Your Optimal Roth IRA Contribution
- 5.3 5.3. Catch-Up Contributions for Individuals Aged 50 and Over
- 5.4 5.4. Dollar-Cost Averaging for Roth IRA Contributions
- 5.5 5.5. Asset Allocation for Roth IRA Investments
- 5.6 5.6. Actionable Tips for Maximizing Roth IRA Contributions
- 5.7 5.7. Impact of Roth IRA Contributions on Retirement Income Planning
- 5.8 5.8. Roth IRA vs. Traditional IRA
- 5.9 5.9. Challenges and Obstacles to Maximizing Roth IRA Contributions
- 5.10 5.10. Roth IRA Contributions and Other Retirement Savings Plans
- 6 7. Alternative Retirement Savings Options
- 7 Resources for Further Information
- 8 Epilogue
- 9 Essential FAQs
Roth IRA Contribution Limits
A Roth IRA is a retirement savings account that allows you to contribute after-tax dollars and potentially withdraw your earnings tax-free in retirement. This makes it a popular choice for many individuals, especially those who expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
Want to estimate your tax liability? A Tax Calculator can help you get a better understanding of your tax situation and make informed financial decisions.
One crucial aspect of Roth IRAs is the annual contribution limit, which determines how much you can contribute each year. Contribution limits are set by the IRS and adjusted periodically to reflect inflation and other economic factors.
Contribution Limits for 2024
The annual contribution limit for Roth IRAs in 2024 is $7,000. If you are 50 years old or older, you can contribute an additional $1,000, known as a catch-up contribution, for a total of $8,000. This limit is subject to change each year, so it’s important to check the most up-to-date information from the IRS.
The 2024 Tax Deadline is quickly approaching! Make sure you’re prepared to file your taxes on time to avoid any penalties.
Who is Eligible to Contribute to a Roth IRA?
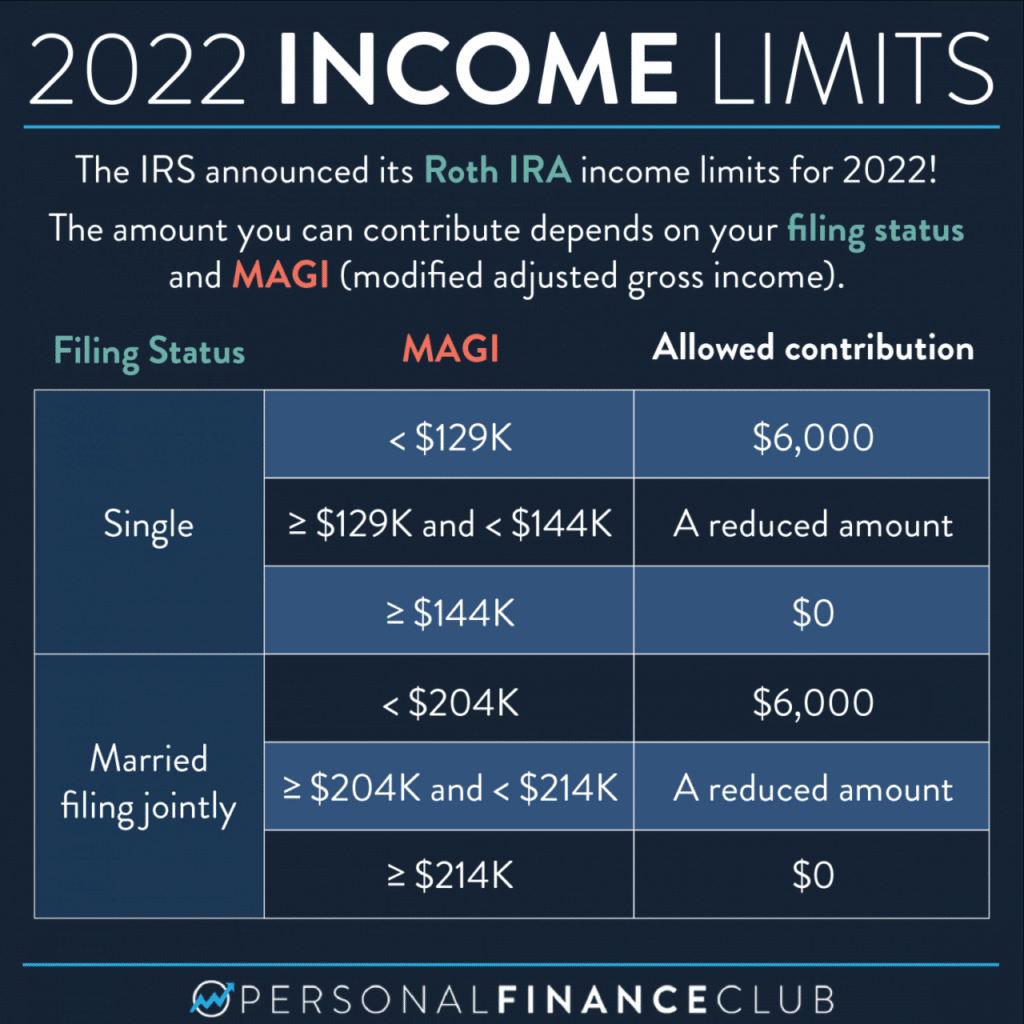
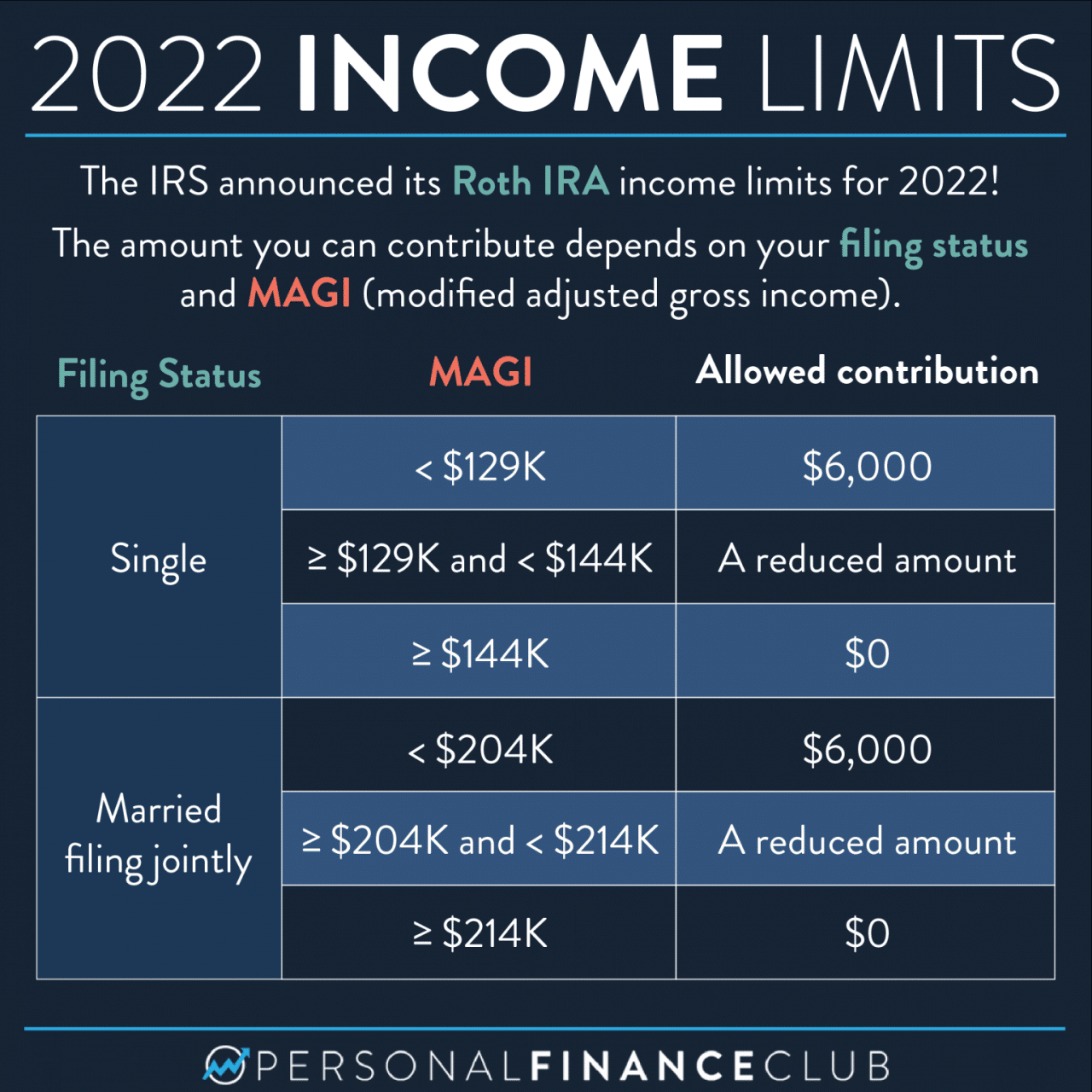
Not everyone can contribute to a Roth IRA. The IRS sets income limits for those who can contribute to a Roth IRA. If your income exceeds these limits, you may not be able to contribute to a Roth IRA or your contributions may be limited.
Income Eligibility Requirements for Roth IRA Contributions in 2024
The IRS sets income limits for those who can contribute to a Roth IRA. If your income exceeds these limits, you may not be able to contribute to a Roth IRA or your contributions may be limited. These limits are based on your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI).
Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) Thresholds
The MAGI thresholds for Roth IRA contributions in 2024 are as follows:
- Single filers: $153,000
- Married couples filing jointly: $228,000
- Head of household: $153,000
- Qualifying widow(er): $228,000
- Married filing separately: $114,000
Phase-Out of Roth IRA Contributions
If your MAGI exceeds the limits above, your Roth IRA contribution may be phased out. This means that you may not be able to contribute the full amount or you may not be able to contribute at all. The phase-out is gradual, meaning that you may be able to contribute a portion of the maximum amount.
For example, if your MAGI is slightly above the limit, you may be able to contribute a smaller amount than the maximum.
For example, if you are single and your MAGI is $155,000, you will not be able to contribute the full amount to a Roth IRA. However, you may be able to contribute a portion of the maximum amount. The specific amount you can contribute will depend on your MAGI.
3. Contribution Limits for Different Age Groups: Roth IRA Contribution Limits 2024
The contribution limits for Roth IRAs vary based on age, with higher limits available for individuals aged 50 and over. This section delves into the specific contribution limits for different age groups in 2024.
If you’re driving for work, make sure you’re using the correct 2024 Mileage Rate when claiming business expenses on your taxes.
Individual Contribution Limits for 2024
The maximum amount an individual can contribute to a Roth IRA in 2024 depends on their age.
- Individuals under the age of 50 can contribute up to $6,500 in 2024.
- Individuals aged 50 and over can contribute up to $7,500 in 2024. This additional contribution is referred to as a “catch-up contribution.”
Catch-Up Contribution Limits for Individuals Aged 50 and Over
The catch-up contribution limit for individuals aged 50 and over in 2024 is $1,000. This means that individuals in this age group can contribute an additional $1,000 on top of the regular contribution limit of $6,500, bringing their total contribution limit to $7,500.
The catch-up contribution limit is added to the regular contribution limit for individuals aged 50 and over, resulting in a total contribution limit of $7,500 in 2024.
California residents might be eligible for a California Stimulus Check in October 2024. Keep an eye out for updates on the amount and payment schedule.
Purpose and Benefits of Catch-Up Contributions
Catch-up contributions are designed to help older individuals make up for lost savings time. Individuals who started saving later in life or who experienced financial setbacks may not have had as much time to accumulate retirement savings. Catch-up contributions allow these individuals to contribute more to their retirement accounts, potentially helping them reach their retirement goals.
- The purpose of catch-up contributions is to provide older individuals with an opportunity to increase their retirement savings and bridge any savings gaps that may have accumulated over time.
- Utilizing catch-up contributions can help individuals approaching retirement accelerate their savings and potentially increase their overall retirement income.
- Catch-up contributions allow individuals to make up for lost savings time by contributing more to their retirement accounts, helping them reach their financial goals before retirement.
Tax Benefits of Roth IRA Contributions
Roth IRA contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning you’ve already paid taxes on the money you contribute. This has significant tax advantages in retirement.
Tax-Free Growth and Withdrawals, Roth IRA Contribution Limits 2024
One of the most attractive features of a Roth IRA is the potential for tax-free growth and withdrawals in retirement. This means that when you withdraw your contributions and earnings in retirement, you won’t have to pay any federal income taxes on them.
This can be a huge benefit, especially if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
For example, if you contribute $6,500 to a Roth IRA in 2024 and your account grows to $100,000 by the time you retire, you can withdraw the entire $100,000 tax-free.
Comparison of Tax Benefits with Traditional IRAs
While Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement, traditional IRAs provide tax deductions for contributions in the year you make them. This means you can lower your taxable income and potentially save on taxes in the present. However, you’ll need to pay taxes on your withdrawals in retirement.
The EV Tax Credits are having a significant impact on the auto industry in 2024. Learn about the changes and how they affect car manufacturers and consumers.
- Roth IRA:Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
- Traditional IRA:Contributions are tax-deductible, but withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
The best choice for you depends on your individual financial situation and tax bracket. If you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement, a Roth IRA may be the better option. However, if you expect to be in a lower tax bracket in retirement, a traditional IRA may be more beneficial.
5. Contribution Strategies for Maximizing Retirement Savings
Maximizing your Roth IRA contributions can significantly boost your retirement savings and potentially lead to tax-free withdrawals in the future. By understanding the contribution limits, tax benefits, and various strategies available, you can make informed decisions to optimize your retirement planning.
5.1. Roth IRA Contribution Limits and Tax Benefits
The maximum amount you can contribute to a Roth IRA in 2024 depends on your age and income. Here’s a breakdown of the contribution limits for different age groups and income levels:
| Filing Status | Age | Contribution Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Single Filer | Under 50 | $6,500 |
| 50 and Over | $7,500 | |
| Married Filing Jointly | Under 50 | $13,000 |
| 50 and Over | $15,000 | |
| Head of Household | Under 50 | $6,500 |
| 50 and Over | $7,500 |
Note:The income limits for Roth IRA contributions are subject to change and are based on your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI). For 2024, if your MAGI is above a certain threshold, you may not be able to contribute to a Roth IRA, or your contributions may be phased out.
It’s never too late to start saving for retirement! The IRA Contribution Limits for 2024 can help you plan your retirement savings strategy.
Contributing to a Roth IRA offers several tax benefits, including:* Tax-free withdrawals in retirement:Any earnings and withdrawals from your Roth IRA in retirement are tax-free, as long as you meet certain requirements, such as being at least 59 1/2 years old and having held the account for at least five years.
Knowing the Tax Brackets for 2024 is crucial for planning your income and taxes. Understanding how your income falls into different brackets can help you make informed financial choices.
Potential for tax savings
If you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement, contributing to a Roth IRA can save you money on taxes in the future.
Looking to improve the sound quality of your videos? Check out the latest information on Acoustic Foam and how it can help you elevate your audio on YouTube in 2024.
5.2. Calculating Your Optimal Roth IRA Contribution
Determining the optimal Roth IRA contribution amount involves considering your individual income, financial goals, and risk tolerance. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Estimate your income
Calculate your expected income for the current year, including salary, bonuses, and other sources of income.
2. Determine your financial goals
Define your retirement savings goals, including how much you want to accumulate and when you plan to retire.
3. Assess your expenses
Estimate your expected expenses in retirement, including housing, healthcare, travel, and entertainment.
4. Calculate your contribution capacity
Subtract your estimated expenses from your projected retirement income to determine how much you can contribute to retirement savings.
5. Factor in your risk tolerance
Consider your comfort level with market volatility and adjust your contribution amount accordingly.
Formula for Calculating Optimal Roth IRA Contribution:Optimal Contribution = (Projected Retirement Income
- Estimated Expenses) / Number of Years Until Retirement
- (Risk Tolerance Factor)
Example:* Johnis 35 years old and expects to retire at 65. His projected retirement income is $60,000 per year, and his estimated expenses are $40,000 per year. John has a moderate risk tolerance and uses a factor of 0.8.* Calculation:
- Optimal Contribution = ($60,000
- $40,000) / (65
- 35)
- 0.8 = $5,333 per year.
* John’s optimal Roth IRA contribution amount would be $5,333 per year.
5.3. Catch-Up Contributions for Individuals Aged 50 and Over
Individuals aged 50 and over can make “catch-up” contributions to their Roth IRAs in addition to the regular contribution limit. For 2024, the catch-up contribution limit is $1,000. This means that individuals aged 50 and over can contribute up to $7,500 ($6,500 regular limit + $1,000 catch-up) to their Roth IRAs in 2024.Catch-up contributions can help older individuals accelerate their retirement savings and potentially reach their financial goals faster.
However, it’s important to consider the potential impact on your overall financial situation before making catch-up contributions.
If you’re a freelancer or independent contractor, you’ll need to fill out a W9 Form to provide your tax information to the payer. This form helps the payer report your income to the IRS.
5.4. Dollar-Cost Averaging for Roth IRA Contributions
Dollar-cost averaging is a strategy that involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market fluctuations. This approach can help mitigate the risk of market volatility and potentially maximize returns over time. Example:* Sarahdecides to contribute $500 to her Roth IRA every month.
During periods of market decline, she buys more shares at a lower price, and during periods of market growth, she buys fewer shares at a higher price. This helps to average out the cost of her investments over time.Dollar-cost averaging can be implemented using automatic contributions to your Roth IRA.
When filing your taxes, you can choose to take the standard deduction or itemize your deductions. The Standard Deduction amount for 2024 is important to know when making this decision.
This ensures that you consistently invest a predetermined amount at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions.
5.5. Asset Allocation for Roth IRA Investments
Asset allocation refers to the process of distributing your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. Diversifying your Roth IRA investments across different asset classes can help reduce risk and potentially increase returns.* Stocks:Stocks represent ownership in companies and generally offer the potential for higher returns but also carry higher risk.
Bonds
Bonds represent loans to companies or governments and generally offer lower returns but also lower risk than stocks.
Real estate
Real estate investments can provide diversification and potential for appreciation but may also require significant capital and management. Investment Strategies for Optimizing Asset Allocation:* Target-date funds:These funds automatically adjust their asset allocation over time, becoming more conservative as you approach retirement.
Index funds
Wondering if you qualify for the California Stimulus Check? Make sure to review the Eligibility Requirements for October 2024.
These funds track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, and provide broad market exposure at a low cost.
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
ETFs are similar to index funds but are traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks.
5.6. Actionable Tips for Maximizing Roth IRA Contributions
Here are five actionable tips to help you maximize your Roth IRA contributions in 2024:
- Set a budget and track your spending:Allocate a portion of your income to Roth IRA contributions and track your spending to ensure you stay within your budget.
- Automate your contributions:Set up automatic contributions from your checking account to your Roth IRA to ensure consistent investing, even when you’re busy.
- Consider “catch-up” contributions if you’re 50 or older:Maximize your contributions by taking advantage of the catch-up contribution limit to accelerate your retirement savings.
- Rebalance your portfolio regularly:Review your asset allocation periodically and rebalance your portfolio to ensure your investments are aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Seek professional financial advice:Consult with a qualified financial advisor to develop a comprehensive retirement savings plan that meets your individual needs and circumstances.
5.7. Impact of Roth IRA Contributions on Retirement Income Planning
Roth IRA contributions can significantly impact your overall retirement income planning. By contributing to a Roth IRA, you can:* Avoid or reduce taxable withdrawals in retirement:Tax-free withdrawals from your Roth IRA can help reduce your tax liability in retirement and potentially increase your after-tax income.
Supplement other retirement savings plans
Roth IRA contributions can complement employer-sponsored retirement plans, such as 401(k)s and pensions, to create a diversified retirement savings strategy.
5.8. Roth IRA vs. Traditional IRA
When deciding between a Roth IRA and a traditional IRA, it’s important to consider your individual financial situation and tax implications.
| Feature | Roth IRA | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|---|
| Contribution Limits | $6,500 (under 50), $7,500 (50 and over) | $6,500 (under 50), $7,500 (50 and over) |
| Tax Implications | Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, withdrawals are tax-free in retirement | Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, withdrawals are taxed in retirement |
| Withdrawal Rules | Withdrawals are tax-free and penalty-free after age 59 1/2 and five years of account ownership | Withdrawals before age 59 1/2 are generally subject to a 10% penalty and income tax |
| Income Limits | Contribution limits may be phased out for high-income earners | No income limits for contributions |
5.9. Challenges and Obstacles to Maximizing Roth IRA Contributions
Individuals may face various challenges when trying to maximize their Roth IRA contributions, such as:* Limited income:Individuals with limited income may struggle to afford maximum contributions.
High expenses
Don’t forget about your IRA contributions! Make sure to check the IRA Limits for 2024 to ensure you’re taking advantage of all available tax benefits.
High living expenses can make it difficult to allocate funds for retirement savings.
Debt obligations
Outstanding debt, such as student loans or credit card debt, can limit the amount of money available for Roth IRA contributions. Strategies for Overcoming Challenges:* Prioritize saving:Allocate a portion of your income to Roth IRA contributions, even if it’s a small amount, and gradually increase your contributions as your financial situation improves.
Reduce expenses
Want to contribute the maximum amount to your 401k? Knowing the Max 401k Contribution for 2024 can help you plan your finances and reach your retirement goals.
Identify areas where you can cut back on spending to free up more money for retirement savings.
Consolidate debt
Consider consolidating high-interest debt to reduce monthly payments and free up more cash flow for retirement savings.
5.10. Roth IRA Contributions and Other Retirement Savings Plans
Roth IRA contributions can supplement other retirement savings plans, such as 401(k)s and employer-sponsored pensions. Having a diversified retirement savings strategy that includes both employer-sponsored plans and individual retirement accounts can help you reach your financial goals and potentially maximize your retirement income.
Example:* Janecontributes the maximum amount to her employer-sponsored 401(k) plan and also makes additional contributions to a Roth IRA. This strategy helps her maximize her retirement savings and potentially reduce her tax liability in retirement.
7. Alternative Retirement Savings Options
Beyond Roth IRAs, there are other valuable retirement savings options to consider. These options offer different features and benefits, making it crucial to understand their nuances to determine the best fit for your individual circumstances.
401(k) Plans
A 401(k) is a retirement savings plan offered by employers. It allows employees to contribute pre-tax dollars to an account that grows tax-deferred.
If you’re looking for retirement planning advice in Sarasota, consider checking out Annuity King Sarasota. They can help you secure your future.
- Types of 401(k) Plans:
- Traditional 401(k):Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income in the current year. You’ll pay taxes on the withdrawals during retirement.
- Roth 401(k):Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning you won’t pay taxes on withdrawals in retirement.
- Contribution Limits:The annual contribution limit for 401(k) plans in 2024 is $22,500 for individuals under 50 and $30,000 for those 50 and older.
- Tax Treatment:
- Traditional 401(k):Contributions are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income. Withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
- Roth 401(k):Contributions are not tax-deductible but withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
Traditional IRAs
Traditional IRAs are individual retirement accounts that allow you to contribute pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income in the current year. You’ll pay taxes on the withdrawals during retirement.
Thinking about retirement? It’s wise to check the 401k limits for 2024 to see how much you can contribute. You’ll want to maximize your contributions to get the most out of your savings.
- Contribution Limits:The annual contribution limit for traditional IRAs in 2024 is $6,500 for individuals under 50 and $7,500 for those 50 and older.
- Tax Treatment:Contributions are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income. Withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
- Deductible Contributions:Whether your contributions are deductible depends on your income and whether you are covered by an employer-sponsored retirement plan. If your income exceeds certain thresholds, you may not be able to deduct your contributions fully or at all.
Comparison of Retirement Savings Options
| Feature | Roth IRA | 401(k) | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contribution Limits (2024) | $6,500 (under 50), $7,500 (50+) | $22,500 (under 50), $30,000 (50+) | $6,500 (under 50), $7,500 (50+) |
| Tax Treatment of Contributions | Not tax-deductible | Tax-deductible (Traditional) or Not tax-deductible (Roth) | Tax-deductible |
| Tax Treatment of Withdrawals in Retirement | Tax-free | Taxed as ordinary income (Traditional) or Tax-free (Roth) | Taxed as ordinary income |
| Eligibility Requirements | No income restrictions | Offered by employers | No income restrictions (but deductibility may be limited) |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Retirement Savings Options
The best retirement savings option for you depends on your individual financial situation, income level, risk tolerance, and retirement goals. Here’s a breakdown of the advantages and disadvantages of each option:
- Roth IRA:
- Advantages:Tax-free withdrawals in retirement, potential for tax-free growth, no income restrictions, good for those expecting to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
- Disadvantages:Contributions are not tax-deductible, potentially lower tax savings in the present, may not be as beneficial for those with lower incomes who are currently in a lower tax bracket.
- 401(k):
- Advantages:Potential for employer matching contributions, tax-deductible contributions (Traditional), pre-tax growth (Traditional), higher contribution limits, good for those with stable employment.
- Disadvantages:Limited investment options, employer restrictions, potential for early withdrawal penalties, may not be available for self-employed individuals or those with no employer.
- Traditional IRA:
- Advantages:Tax-deductible contributions, potential for tax savings in the present, good for those with lower incomes or expecting to be in a lower tax bracket in retirement.
- Disadvantages:Withdrawals are taxed in retirement, deductibility may be limited based on income and employer-sponsored plan participation, potentially lower tax savings in retirement.
Resources for Further Information
This section provides resources for further information about Roth IRAs and contribution limits. These resources can provide you with more in-depth information about the intricacies of Roth IRAs and their impact on your retirement savings.
Official Government Resources
The IRS website is the official source for information about Roth IRAs. You can find detailed information about eligibility requirements, contribution limits, tax benefits, and other important details. The IRS also offers various publications and forms related to Roth IRAs.
- IRS Publication 590-A, Contributions to Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs): This publication provides comprehensive information about traditional and Roth IRAs, including contribution limits, eligibility requirements, and tax implications.
- IRS Form 5500-EZ, Annual Return of Employee Benefit Plan: This form is used to report information about employee benefit plans, including retirement plans like Roth IRAs.
Reputable Financial Institutions and Retirement Planning Resources
There are numerous financial institutions and retirement planning resources that offer valuable information about Roth IRAs. These resources can provide guidance on choosing the right retirement plan, understanding contribution strategies, and managing your retirement savings effectively.
- Vanguard: Vanguard is a well-respected investment firm that offers a wide range of retirement planning resources, including information about Roth IRAs.
- Fidelity: Fidelity is another reputable financial institution that provides comprehensive information about Roth IRAs, including contribution limits, eligibility requirements, and tax benefits.
- Schwab: Schwab is a leading financial services company that offers a variety of retirement planning resources, including information about Roth IRAs.
Consulting a Qualified Financial Advisor
Consulting with a qualified financial advisor is crucial for personalized advice regarding Roth IRAs and other retirement planning decisions. A financial advisor can help you assess your financial situation, set realistic retirement goals, and develop a customized plan to achieve your financial objectives.
Epilogue
In conclusion, Roth IRA contribution limits play a significant role in retirement planning. By understanding these limits, you can make informed decisions about your savings strategy and maximize your contributions to secure a comfortable retirement. Whether you’re just starting out or approaching retirement, taking advantage of Roth IRA contributions can help you achieve your financial goals and enjoy a more secure future.
Remember to consult with a qualified financial advisor to discuss your specific situation and develop a personalized retirement plan.
Essential FAQs
What are the tax implications of Roth IRA contributions?
Roth IRA contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning you won’t receive a tax deduction for your contributions. However, qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, providing a significant tax advantage.
How do Roth IRA contributions compare to traditional IRA contributions?
Traditional IRA contributions are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income in the year you contribute. However, withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income. Roth IRA contributions are not tax-deductible, but qualified withdrawals are tax-free. The best choice depends on your individual tax situation and financial goals.
Can I contribute to both a Roth IRA and a traditional IRA?
Yes, you can contribute to both a Roth IRA and a traditional IRA, but there are income limits that may apply. It’s important to consider the tax implications of both types of IRAs and choose the option that best aligns with your financial goals.