Variable Annuity Non Qualified 2024 sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a world where investment choices intertwine with retirement planning. This guide delves into the intricacies of variable annuities, particularly those classified as non-qualified, highlighting their unique features and potential benefits.
Prepare to navigate a landscape where market fluctuations and tax considerations converge, shaping the future of your financial well-being.
If you’re considering a variable annuity, understanding the accumulation phase is crucial. This phase, detailed in Variable Annuity Accumulation Phase 2024 , involves your contributions growing based on the performance of the sub-accounts you choose. This growth can be impacted by market fluctuations, so understanding risk is key.
Variable annuities, unlike their fixed counterparts, allow investors to participate in the growth potential of the stock market. This flexibility comes with inherent risks, however, as the value of your investment can fluctuate. Non-qualified variable annuities, specifically, present a distinct tax treatment compared to their qualified counterparts, offering potential advantages for certain individuals.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these complexities, empowering you to make informed decisions regarding your financial future.
The Knights of Columbus offers annuities as part of their financial services. K Of C Annuity 2024 provides insights into their annuity offerings, including potential benefits and features for members.
Contents List
Variable Annuities: A Comprehensive Overview
Variable annuities are complex financial products that offer the potential for growth, but they also come with risks. They are similar to traditional fixed annuities, but they differ in how they handle investment risk and potential returns. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of variable annuities, including their characteristics, investment mechanics, and tax implications.
What are Variable Annuities?
Variable annuities are insurance contracts that offer the opportunity to invest in a range of sub-accounts, similar to mutual funds. These sub-accounts typically invest in stocks, bonds, or other assets, allowing for potential growth. However, unlike fixed annuities, which provide a guaranteed rate of return, variable annuities do not guarantee a specific return.
Annuity payments can provide a consistent income stream, and understanding the potential amount is important. Check out Annuity 300 000 2024 to get a sense of what a $300,000 annuity might generate, keeping in mind factors like interest rates and payout options can affect the final amount.
Variable Annuities vs. Traditional Fixed Annuities
The key difference between variable annuities and traditional fixed annuities lies in how they handle investment risk and returns.
C shares are a type of variable annuity that often come with higher fees but potentially higher returns. C Share Variable Annuity 2024 delves into the characteristics of these shares, including their potential benefits and drawbacks.
- Fixed Annuities:Provide a guaranteed rate of return for a specific period. This means that your investment will earn a fixed interest rate, regardless of market fluctuations. However, fixed annuities typically offer lower returns than variable annuities.
- Variable Annuities:Offer the potential for higher returns, but they also come with higher risk. The value of your investment in a variable annuity will fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying investments in the sub-accounts you choose.
How Variable Annuity Investments Work
When you purchase a variable annuity, you invest your money in sub-accounts, which are essentially mutual funds that invest in different asset classes. The value of your investment will fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying investments in the sub-accounts you choose.
To get a better grasp of how annuities work, using a calculator can be helpful. The Annuity Calculator Nerdwallet 2024 provides a user-friendly tool to estimate potential payments based on your chosen parameters.
- Sub-account Choices:Variable annuities typically offer a range of sub-accounts, allowing you to diversify your investments based on your risk tolerance and investment goals. For example, you may choose to invest in a sub-account that invests in stocks, a sub-account that invests in bonds, or a sub-account that invests in a combination of both.
- Investment Growth:Your investment in a variable annuity will grow based on the performance of the sub-accounts you choose. If the sub-accounts perform well, your investment will grow. However, if the sub-accounts perform poorly, your investment may lose value.
Examples of Sub-accounts
Variable annuities offer a variety of sub-accounts, allowing investors to tailor their portfolios to their specific needs and risk tolerances. Here are some common examples:
- Equity Sub-accounts:These sub-accounts invest in stocks, providing the potential for higher returns but also greater risk. They may focus on specific sectors, market capitalization, or investment styles.
- Fixed Income Sub-accounts:These sub-accounts invest in bonds, offering more stability and lower potential returns than equity sub-accounts. They may invest in government bonds, corporate bonds, or a combination of both.
- Balanced Sub-accounts:These sub-accounts invest in a mix of stocks and bonds, seeking to balance potential growth with risk mitigation. They may target specific asset allocation strategies, such as a 60/40 stock-to-bond ratio.
- Target-Date Funds:These sub-accounts adjust their asset allocation over time, becoming more conservative as the target date (e.g., retirement) approaches. They offer a convenient way to manage investment risk over the long term.
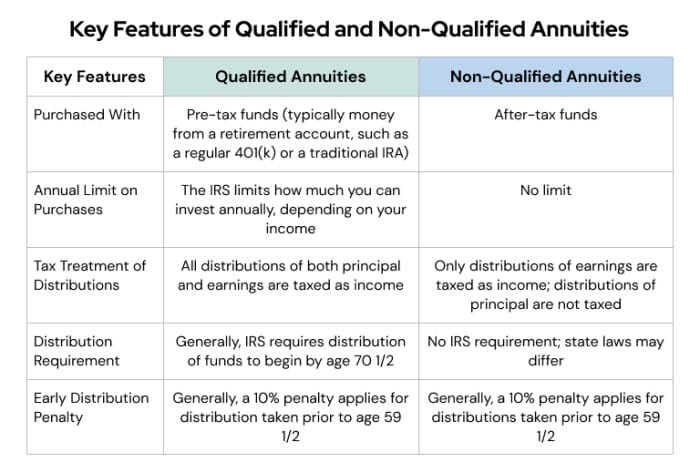
Non-Qualified Variable Annuities: Variable Annuity Non Qualified 2024
Non-qualified variable annuities are not subject to the same tax rules as qualified variable annuities. This can have significant implications for how you plan for retirement.
Tax Implications of Non-Qualified Variable Annuities
Non-qualified variable annuities are taxed differently than qualified variable annuities.
- Growth:The growth of your investment in a non-qualified variable annuity is taxed as ordinary income when you withdraw it.
- Withdrawals:Withdrawals from a non-qualified variable annuity are subject to both ordinary income tax and a 10% penalty if you withdraw the money before age 59 1/2.
Tax Treatment of Non-Qualified vs. Qualified Variable Annuities
The tax treatment of non-qualified variable annuities differs significantly from that of qualified variable annuities.
If you’re using a TI-84 calculator, you can utilize its functions to calculate annuity due payments. How To Calculate Annuity Due On Ti-84 2024 provides step-by-step instructions on using the calculator’s features to determine annuity due payments.
- Qualified Variable Annuities:These are typically purchased with pre-tax dollars and are designed to provide tax-deferred growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement. They are often used as part of a 401(k) or IRA retirement plan.
- Non-Qualified Variable Annuities:These are purchased with after-tax dollars and do not offer the same tax benefits as qualified variable annuities. The growth and withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income, and there is a 10% penalty for early withdrawals.
Potential Tax Advantages and Disadvantages
Non-qualified variable annuities can offer certain tax advantages, but they also come with disadvantages.
- Advantages:Non-qualified variable annuities can be used to shelter income from taxes, particularly in high-income years. They can also provide a way to pass wealth to heirs without incurring estate taxes.
- Disadvantages:The growth and withdrawals from non-qualified variable annuities are taxed as ordinary income, which can result in a higher tax burden than qualified variable annuities. The 10% penalty for early withdrawals can also be a significant deterrent.
Implications for Retirement Planning
Non-qualified variable annuities can play a role in retirement planning, but it is essential to consider the tax implications carefully.
For those seeking additional death benefit protection, a variable annuity with a GMIB rider can be a good option. Variable Annuity Gmib Rider 2024 explores how this rider provides a guaranteed minimum income benefit, offering peace of mind for your loved ones.
- Tax-Efficient Growth:Non-qualified variable annuities can provide a tax-efficient way to grow your wealth over the long term, but it is important to understand the tax implications of withdrawals.
- Estate Planning:Non-qualified variable annuities can be used to pass wealth to heirs without incurring estate taxes. However, it is important to consult with a tax advisor to ensure that you are maximizing the benefits of this strategy.
Variable Annuity Features in 2024
Variable annuities have evolved significantly in recent years, offering a range of features to meet the diverse needs of investors. Here is a breakdown of key features available in 2024.
Key Features of Variable Annuities
Variable annuities offer a range of features that can enhance their appeal and flexibility for investors.
- Guaranteed Minimum Death Benefit (GMDB):This feature guarantees a minimum death benefit to your beneficiaries, regardless of the performance of the underlying investments. It provides a safety net in case of market downturns.
- Living Benefits:These benefits provide income guarantees during your lifetime, even if your investment loses value. They can help to protect your retirement income from market volatility.
- Rider Options:Variable annuities often offer a variety of riders that can enhance their features and benefits. These riders may include options for guaranteed income, long-term care, or other protections.
- Withdrawal Options:Variable annuities offer different withdrawal options, allowing you to access your funds when you need them. Some options may have penalties or restrictions.
Comparison of Variable Annuity Products
Insurance companies offer a variety of variable annuity products, each with its own unique features and benefits. It is essential to compare different products carefully to find the one that best meets your needs.
- Feature Comparison:It is crucial to compare the features of different variable annuity products, including the sub-accounts offered, the fees and expenses, the guaranteed minimum death benefit, and the living benefits.
- Company Reputation:It is also important to consider the financial strength and reputation of the insurance company issuing the variable annuity. Look for companies with a strong track record of financial stability and customer service.
Table of Variable Annuity Features
The following table summarizes some key features of variable annuities and their pros and cons:
| Feature | Pros | Cons | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guaranteed Minimum Death Benefit (GMDB) | Provides a safety net for beneficiaries, guaranteeing a minimum death benefit regardless of market performance. | May come with higher fees. | The GMDB is typically a fixed percentage of the original investment, or a minimum amount. |
| Living Benefits | Provides income guarantees during your lifetime, even if your investment loses value. | May come with higher fees and restrictions on withdrawals. | Living benefits can include features like guaranteed income payments or minimum withdrawal guarantees. |
| Rider Options | Allows you to customize your annuity with additional features and benefits. | Riders can add complexity and increase costs. | Rider options may include long-term care, guaranteed income, or other protections. |
| Withdrawal Options | Provides flexibility to access your funds when you need them. | Some withdrawal options may have penalties or restrictions. | Withdrawal options may include lump-sum withdrawals, systematic withdrawals, or annuitization. |
Visual Representation of a Variable Annuity Contract
[Here you would provide a visual representation, such as a chart or diagram, illustrating the structure and components of a variable annuity contract. This would include elements like the policyholder, the insurance company, the sub-accounts, the death benefit, and the living benefits.]
Risks and Considerations
Variable annuities offer potential for growth, but they also come with risks that investors should carefully consider.
Potential Risks Associated with Variable Annuities
Variable annuities involve several risks, including market volatility and investment performance.
Variable annuities can play a role in retirement planning, offering the potential for growth alongside income guarantees. Variable Annuity For Retirement 2024 explores how variable annuities can be used to supplement your retirement savings and provide a consistent income stream.
- Market Volatility:The value of your investment in a variable annuity will fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying investments in the sub-accounts you choose. Market downturns can significantly impact the value of your investment, potentially leading to losses.
- Investment Performance:The performance of the sub-accounts you choose will directly affect the growth of your investment. If the sub-accounts perform poorly, your investment may lose value.
- Insurance Company Risk:Variable annuities are insurance contracts, and the financial strength of the issuing insurance company is essential. If the insurance company fails, your investment may be at risk.
Fees and Expenses
Variable annuities come with fees and expenses that can impact your returns.
For those who prefer quarterly payments, an annuity calculator can help you visualize the potential income stream. The Annuity Calculator Quarterly 2024 tool allows you to input your preferences and see how your annuity payments would be structured.
- Mortality and Expense Charges:These charges are used to cover the insurance company’s costs and expenses, including death benefits and administrative costs.
- Sub-account Fees:Each sub-account in a variable annuity will have its own fees and expenses, which can vary depending on the underlying investments.
- Rider Fees:If you choose to add riders to your variable annuity, you will typically pay additional fees for these features.
Insurance Company Guarantees
Insurance companies may offer guarantees in variable annuities, such as a guaranteed minimum death benefit or living benefits. However, these guarantees come with limitations.
- Limited Guarantees:Guarantees in variable annuities are typically limited to the original investment amount or a minimum death benefit. They do not guarantee a specific rate of return or protect against market losses.
- Insurance Company Risk:The guarantees in a variable annuity are only as good as the financial strength of the issuing insurance company. If the company fails, your guarantees may be at risk.
Case Study: Impact of Market Scenarios
[Here you would provide a case study illustrating the potential impact of different market scenarios on variable annuity performance. This could include examples of how the value of a variable annuity might change during periods of market growth, decline, or volatility.
You could also highlight the potential impact of different investment strategies on the overall performance of the annuity.]
Annuity payments are essentially the future value of your initial investment. Annuity Is Future Value 2024 explains how the initial lump sum, interest rates, and payment period contribute to the total future value you receive in annuity payments.
Investment Strategies
Variable annuities offer investors flexibility in choosing their investment strategies. It is crucial to consider asset allocation, diversification, and professional advice.
Investment Strategies Within a Variable Annuity
Variable annuities provide a platform for various investment strategies, tailored to different risk tolerances and financial goals.
- Growth-Oriented Strategy:This strategy emphasizes investments in stocks and other high-growth assets, aiming for potential capital appreciation over the long term. It is suitable for investors with a higher risk tolerance and a longer investment horizon.
- Income-Oriented Strategy:This strategy focuses on investments in bonds and other fixed-income securities, seeking to generate a steady stream of income. It is appropriate for investors who prioritize income over growth and have a shorter investment horizon.
- Balanced Strategy:This strategy combines elements of both growth and income, investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets. It aims to balance potential growth with risk mitigation and is suitable for investors with a moderate risk tolerance.
Asset Allocation and Diversification, Variable Annuity Non Qualified 2024
Asset allocation and diversification are crucial for managing risk and maximizing returns within a variable annuity portfolio.
- Asset Allocation:This refers to the distribution of your investment assets across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. It helps to manage risk by diversifying your investments across different asset classes.
- Diversification:This involves spreading your investments across a variety of different assets within each asset class. This helps to reduce the impact of any single investment performing poorly.
Role of Professional Financial Advice
Professional financial advice can be invaluable in managing variable annuity investments.
Calculating annuity payments can seem complex, but it’s not as daunting as it might appear. How Do You Calculate Annuity Payments 2024 breaks down the steps involved, considering factors like interest rates, the initial lump sum, and the payment period.
- Investment Strategy Development:A financial advisor can help you develop an investment strategy that aligns with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
- Asset Allocation and Diversification:An advisor can help you create a well-diversified portfolio that balances potential growth with risk mitigation.
- Monitoring and Adjustment:An advisor can monitor your investment performance and adjust your portfolio as needed to meet your evolving needs.
Comparison of Investment Options
The following table compares and contrasts different investment options available within variable annuities:
| Investment Option | Potential Returns | Risk Level | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equity Sub-accounts | High | High | Investors with a long investment horizon and a higher risk tolerance. |
| Fixed Income Sub-accounts | Moderate | Low | Investors who prioritize income and have a shorter investment horizon. |
| Balanced Sub-accounts | Moderate | Moderate | Investors with a moderate risk tolerance and a long investment horizon. |
| Target-Date Funds | Moderate | Moderate | Investors who want a convenient way to manage their investment risk over time. |
Legal and Regulatory Framework
Variable annuities are subject to a complex legal and regulatory framework, designed to protect investors and ensure fair market practices.
Winning the lottery is exciting, but understanding the annuity payment structure is important. Calculating Lottery Annuity Payments 2024 explains how these payments are calculated, considering factors like the lump sum amount and the chosen payment period.
Legal and Regulatory Framework Governing Variable Annuities
Variable annuities are regulated by both federal and state agencies.
If you’re planning for retirement with your spouse, the joint life option in an annuity can be beneficial. Learn more about this option in Annuity Joint Life Option 2024 , which explains how it ensures a consistent income stream for both of you, even if one partner passes away.
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC):The SEC regulates the sale and trading of variable annuities, ensuring that investors receive accurate and complete information about the products they are purchasing.
- State Insurance Regulators:State insurance regulators oversee the financial solvency of insurance companies issuing variable annuities, ensuring that they have the financial resources to meet their obligations to policyholders.
Disclosure Requirements for Variable Annuity Contracts
Variable annuity contracts are subject to strict disclosure requirements, ensuring that investors understand the risks and features of the products they are purchasing.
If you’re unfamiliar with annuities, understanding what they are is essential. Annuity Kya Hai 2024 provides a clear explanation of annuities, their purpose, and how they can be used for retirement planning.
- Prospectus:The prospectus provides detailed information about the variable annuity, including the investment objectives, risks, fees and expenses, and the performance of the underlying investments.
- Summary Prospectus:The summary prospectus provides a brief overview of the variable annuity, highlighting the key features and risks.
- Statement of Additional Information (SAI):The SAI provides more detailed information about the variable annuity, including the financial condition of the insurance company and the management of the sub-accounts.
Case Study: Impact of Regulatory Changes
[Here you would provide a case study illustrating the potential impact of regulatory changes on variable annuities. This could include examples of how new regulations have affected the design, features, or distribution of variable annuities. You could also discuss the potential impact of regulatory changes on the overall market for variable annuities.]
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Variable Annuity Non Qualified 2024 presents a compelling investment option for individuals seeking a blend of growth potential and tax advantages. While the inherent risks associated with market volatility cannot be ignored, careful consideration of investment strategies and professional financial advice can help mitigate potential downsides.
By understanding the nuances of non-qualified variable annuities and navigating the complexities of the financial landscape, you can position yourself for a secure and prosperous retirement.
Quick FAQs
What are the key differences between qualified and non-qualified variable annuities?
The primary distinction lies in the tax treatment. Qualified variable annuities offer tax-deferred growth, meaning earnings are not taxed until withdrawal. Non-qualified annuities, on the other hand, are subject to taxation on a yearly basis.
When it comes to annuities, the method of calculation can vary. The Annuity Method 2024 article explains the different approaches used to determine annuity payments, including the present value and future value methods.
Are there any specific tax advantages to non-qualified variable annuities?
Non-qualified annuities can offer tax advantages for individuals who are in a lower tax bracket during their working years but anticipate being in a higher tax bracket during retirement. This is because the income earned from the annuity is taxed at your current tax rate, potentially lower than your future rate.
What are the potential downsides to non-qualified variable annuities?
The main drawback is the annual taxation on earnings, which can reduce the overall growth potential compared to qualified annuities. Additionally, non-qualified annuities may not offer the same level of tax-advantaged withdrawals as qualified annuities during retirement.
Who is a non-qualified variable annuity suitable for?
Non-qualified annuities can be suitable for individuals who: 1) are in a lower tax bracket currently but anticipate a higher bracket in retirement, 2) have a high risk tolerance, and 3) are seeking a potential growth opportunity with tax flexibility.









