W9 Form October 2024 for foreign entities is a crucial document for foreign entities operating in the United States. This form, required by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), serves as a vital tool for reporting tax information and ensuring compliance with US tax regulations.
While the W9 form is commonly used for US citizens and entities, foreign entities face unique challenges and considerations when filling it out.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the W9 form for foreign entities, covering everything from its purpose and key differences compared to the US citizen requirements to the specific information needed and step-by-step instructions for completion. We’ll also delve into the tax implications for foreign entities, including potential liabilities and reporting requirements.
Understanding these nuances is essential for foreign entities to navigate the complexities of US tax laws and avoid potential penalties.
Contents List
- 1 Understanding the W9 Form for Foreign Entities
- 2 Tax Implications for Foreign Entities
- 3 Common Mistakes and Solutions: W9 Form October 2024 For Foreign Entities
- 3.1 Incorrect TIN Information, W9 Form October 2024 for foreign entities
- 3.2 Missing or Incomplete Contact Information
- 3.3 Failure to Provide the Correct Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)
- 3.4 Incomplete or Inaccurate Certification
- 3.5 Lack of Proper Documentation
- 3.6 Consequences of Filing Incorrect or Incomplete W9 Forms
- 3.7 Resources and Guidance
- 4 Conclusion
- 5 Quick FAQs
Understanding the W9 Form for Foreign Entities
The W9 form is a crucial document for foreign entities operating in the United States. It serves as a means for the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to collect information necessary for tax reporting and withholding purposes. This form ensures that foreign entities comply with US tax regulations and helps the IRS track their financial activities within the country.
It’s important to comply with the W9 form requirements. Find out about the W9 Form October 2024 penalties for non-compliance to avoid any potential fines.
Key Differences Between W9 Form Requirements for US Citizens and Foreign Entities
The W9 form for foreign entities differs significantly from the form used by US citizens. These differences arise from the distinct tax obligations and reporting requirements associated with foreign entities.
If you are planning to contribute to a traditional IRA, you may want to check the IRA contribution limits for traditional IRA in 2024 to ensure you are maximizing your contributions.
- Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN):US citizens typically use their Social Security Number (SSN) as their TIN. However, foreign entities require an Employer Identification Number (EIN) to operate in the US. Obtaining an EIN is a separate process and is essential for foreign entities to comply with US tax regulations.
The W9 form has been updated for 2024. You can find out more about the W9 Form October 2024 changes and updates to ensure you are using the correct form.
- Foreign Taxpayer Identification Number (FTIN):Foreign entities are required to provide their FTIN, which is a unique identifier assigned by their home country’s tax authority. This information helps the IRS track the entity’s international tax obligations.
- Exemption from Withholding:Foreign entities may be exempt from certain US tax withholdings based on their tax treaty status. This exemption must be claimed on the W9 form and requires specific documentation.
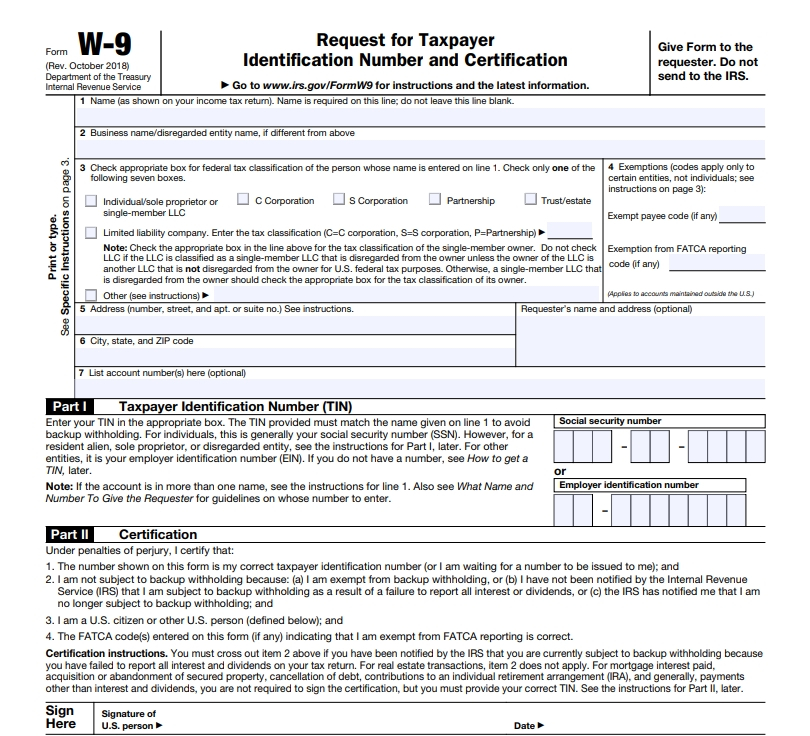
Information Required on the W9 Form for Foreign Entities
The W9 form for foreign entities requires specific information to ensure accurate tax reporting and withholding. This information helps the IRS identify the entity and its tax status.
The IRS sets a mileage rate each year for various purposes. You can find the IRS mileage rate for October 2024 on our website.
- Entity Name:This is the legal name of the foreign entity, as registered in its home country. It should match the name used for tax purposes in the US.
- EIN:This is the Employer Identification Number assigned to the foreign entity by the IRS. It serves as the primary identifier for tax purposes in the US.
- FTIN:This is the Foreign Taxpayer Identification Number assigned by the entity’s home country’s tax authority. It helps the IRS track the entity’s international tax obligations.
- Address:This is the physical address of the foreign entity in the US, if applicable. If the entity does not have a physical US address, they should provide their foreign address.
- Exemption from Withholding:This section requires the entity to indicate if they are exempt from certain US tax withholdings based on a tax treaty. They need to provide the relevant treaty article and documentation supporting their exemption.
- Certification:This section requires the authorized representative of the foreign entity to sign and date the form, certifying the accuracy of the information provided.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Fill Out the W9 Form for Foreign Entities
Filling out the W9 form correctly is crucial for foreign entities to comply with US tax regulations. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Obtain an EIN:Before filling out the W9 form, foreign entities must obtain an EIN from the IRS. This can be done online through the IRS website or by mail.
- Gather Required Information:Collect all the necessary information for the W9 form, including the entity’s legal name, EIN, FTIN, address, and tax treaty information, if applicable.
- Fill Out the Form:Complete all sections of the W9 form accurately and legibly. Use black ink or type the information.
- Sign and Date:The authorized representative of the foreign entity must sign and date the form, certifying the accuracy of the information provided.
- Submit the Form:Submit the completed W9 form to the US entity or individual requesting the information. This is typically the entity or individual making payments to the foreign entity.
Tax Implications for Foreign Entities
Foreign entities filing W9 forms in October 2024 face specific tax implications that differ from US-based entities. Understanding these implications is crucial for foreign entities to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with US tax regulations.
The IRS offers resources to help you file your taxes on time. Learn more about the IRS resources for the October 2024 tax deadline and get the support you need.
Potential Tax Liabilities and Reporting Requirements
Foreign entities filing W9 forms may be subject to various US tax liabilities, including withholding taxes, income taxes, and potentially estate and gift taxes. These liabilities are determined by the nature of the income received, the entity’s tax treaty status, and other relevant factors.
Are you a student who needs to file taxes? The October 2024 tax deadline for students is the same as the regular deadline, so make sure you file on time.
Foreign entities are required to report their US-source income on IRS Form 1040-NR, which is used to file US income tax returns by non-resident aliens and foreign entities. This form requires detailed information about the entity’s income, deductions, and credits, as well as its US tax identification number (TIN).
Businesses need to be aware of the W9 form requirements. You can learn about the W9 Form October 2024 requirements for businesses to ensure your business is in compliance.
Withholding Taxes on Payments to Foreign Entities
The US government may withhold taxes on payments made to foreign entities. The withholding rate depends on the type of income received, the entity’s tax treaty status, and the entity’s TIN.
Withholding Tax Rates
- Interest Income:The general withholding rate for interest income is 30%. However, this rate can be reduced or eliminated under certain tax treaties.
- Dividend Income:The general withholding rate for dividend income is 30%. However, this rate can be reduced or eliminated under certain tax treaties.
- Royalties:The general withholding rate for royalties is 30%. However, this rate can be reduced or eliminated under certain tax treaties.
- Other Income:The general withholding rate for other types of income, such as fees for services, is 30%. However, this rate can be reduced or eliminated under certain tax treaties.
Comparison of Tax Treatment
Foreign entities and US-based entities face different tax treatments, primarily due to their residency status.
The October 2024 tax deadline is just around the corner. Don’t wait until the last minute! You can find out how to file your taxes by the deadline with our guide on how to file taxes by the October 2024 deadline.
Differences in Tax Treatment
- Tax Residency:US-based entities are considered resident taxpayers, while foreign entities are generally considered non-resident taxpayers. This distinction impacts the types of taxes applicable to each entity.
- Tax Rates:Tax rates for foreign entities may differ from those for US-based entities, depending on the type of income and the applicable tax treaty.
- Reporting Requirements:Foreign entities have specific reporting requirements, such as filing Form 1040-NR, while US-based entities file different forms depending on their structure.
Common Mistakes and Solutions: W9 Form October 2024 For Foreign Entities
Foreign entities often encounter challenges when navigating the intricacies of the W9 form. These challenges can lead to incorrect or incomplete filings, potentially resulting in penalties and delays. This section aims to provide insights into common mistakes and offer practical solutions to ensure accurate and timely compliance.
Are you planning on donating to a charity this October? You can deduct your driving expenses, and the October 2024 mileage rate for charitable donations can help you calculate your deduction.
Incorrect TIN Information, W9 Form October 2024 for foreign entities
Foreign entities may inadvertently provide an incorrect Tax Identification Number (TIN). This could be due to using the wrong type of TIN, such as a Social Security Number instead of an Employer Identification Number (EIN), or entering an inaccurate number.
If you are self-employed, you have until October to file your taxes. The October 2024 tax deadline for self-employed individuals gives you extra time to file your taxes.
- Solution:Ensure the TIN provided on the W9 form is the correct type and accurately reflects the entity’s legal status. For example, foreign corporations generally use an EIN, which can be obtained from the IRS. Consult with a tax advisor to determine the appropriate TIN for your specific circumstances.
Partnerships need to be aware of the W9 form requirements. Learn about the W9 Form October 2024 for partnerships and ensure your partnership is in compliance.
Missing or Incomplete Contact Information
The W9 form requires accurate and complete contact information for the foreign entity. Missing or incomplete information can hinder the payer’s ability to process payments and potentially lead to delays.
Did you move in October 2024? You may be able to deduct your moving expenses, and the October 2024 mileage rate for moving expenses can help you determine the amount you can claim.
- Solution:Provide all required contact information, including the entity’s name, address, phone number, and email address. Double-check the accuracy of all information before submitting the form.
Failure to Provide the Correct Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)
Foreign entities may fail to provide the correct TIN, leading to incorrect reporting and potential penalties.
If you are a qualifying widow(er) in 2024, you may be eligible for a different tax bracket. Check out the tax brackets for qualifying widow(er)s in 2024 to see how your tax liability may be affected.
- Solution:Foreign entities should use the correct TIN based on their legal status and the requirements of the W9 form. For example, foreign corporations typically use an EIN, while foreign individuals may use their ITIN (Individual Taxpayer Identification Number) or a Social Security Number (if applicable).
Consult with a tax advisor or the IRS to determine the appropriate TIN for your specific circumstances.
Incomplete or Inaccurate Certification
The W9 form requires a certification statement from the foreign entity, confirming their tax status and the accuracy of the information provided. Missing or inaccurate information can result in delays and penalties.
- Solution:Ensure the certification statement is completed accurately and truthfully. Review the certification statement carefully and ensure all information is correct before submitting the form. Consult with a tax advisor if you have any questions or concerns about the certification statement.
It’s important to understand the standard mileage rate for your tax deductions. The standard mileage rate for October 2024 is a helpful resource to determine the amount you can deduct for your travel expenses.
Lack of Proper Documentation
Foreign entities may not have the necessary documentation to support the information provided on the W9 form. This can lead to questions from the payer and potential delays in processing payments.
Want to know what the highest tax bracket is for 2024? You can find that information and learn more about tax brackets by checking out our article on what is the highest tax bracket in 2024.
- Solution:Maintain accurate and up-to-date records of all relevant information, including the entity’s TIN, contact information, and tax status. This documentation can be helpful in addressing any inquiries from the payer and demonstrating compliance with W9 form requirements.
Consequences of Filing Incorrect or Incomplete W9 Forms
Filing an incorrect or incomplete W9 form can lead to several consequences, including:
- Penalties:The IRS may impose penalties for filing inaccurate or incomplete W9 forms. These penalties can vary depending on the severity of the error and the intent of the filer.
- Delays in Payments:Payers may delay payments if they cannot verify the information on the W9 form or if they require additional information from the foreign entity.
- Tax Reporting Errors:Incorrect W9 form information can lead to errors in tax reporting, potentially resulting in discrepancies between the payer’s and the foreign entity’s tax records.
Resources and Guidance
Foreign entities seeking assistance with W9 form compliance can utilize various resources, including:
- IRS Website:The IRS website provides comprehensive information about W9 forms, including instructions, forms, and FAQs.
- Tax Professionals:Consulting with a qualified tax advisor can provide personalized guidance on W9 form compliance and address specific questions or concerns.
Conclusion
Navigating the W9 form for foreign entities can be complex, but with careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the requirements, foreign entities can successfully fulfill their tax obligations in the US. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, foreign entities can ensure accurate and timely filing, minimizing the risk of errors and penalties.
Remember to consult with a qualified tax professional if you have any specific questions or require assistance with the W9 form.
Quick FAQs
What is the purpose of the W9 form for foreign entities?
The W9 form is used by the IRS to collect tax information from entities that are paid by US individuals or businesses. Foreign entities must complete a W9 form to provide their taxpayer identification number (TIN) and other relevant information, enabling the payer to properly report and withhold taxes on payments made to the foreign entity.
What are the consequences of filing an incorrect or incomplete W9 form?
Filing an incorrect or incomplete W9 form can lead to various consequences, including:
- Incorrect withholding of taxes, resulting in potential underpayment or overpayment of taxes.
- Delays in receiving payments due to missing or inaccurate information.
- Penalties and interest charges from the IRS for non-compliance.
Where can I find more information about the W9 form for foreign entities?
For more detailed information and guidance on the W9 form for foreign entities, you can consult the IRS website, which provides comprehensive resources and instructions. You can also seek assistance from a qualified tax professional who specializes in international tax matters.









