When Are Taxes Due In October sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. October is a critical month for tax obligations, as it marks the deadline for several important tax filings and payments.
This guide will delve into the most common tax deadlines in October, providing clarity and insights for taxpayers of all levels.
From estimated tax payments to extension requests, this guide will cover a wide range of tax obligations that may be due in October. We’ll explore individual income tax, business income tax, payroll tax, sales tax, and property tax, providing a comprehensive overview of the tax landscape during this crucial month.
Contents List
- 1 October Tax Deadlines: When Are Taxes Due In October
- 2 Estimated Taxes
- 3 Quarterly Taxes
- 4 4. Extension Deadlines
- 5 State Taxes
- 6 6. Penalties and Interest
- 7 Tax Tips and Strategies
- 8 Filing Methods
- 9 Tax Audit Considerations
- 10 Year-End Tax Planning
- 11 Ultimate Conclusion
- 12 FAQ Explained
October Tax Deadlines: When Are Taxes Due In October
October is a crucial month for tax obligations, marking the deadline for several important tax filings and payments. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the most common tax deadlines in October, covering individual income tax, business income tax, payroll tax, sales tax, and property tax obligations.
We’ll also discuss the implications of missing deadlines and provide practical tips for managing your tax obligations effectively.
Estimated Tax Payments
Estimated tax payments are required for individuals and businesses who anticipate owing taxes but do not have sufficient withholding from their income. The IRS requires taxpayers to make estimated tax payments on a quarterly basis, with the fourth and final payment due on October 17th.
The estimated tax payment schedule is as follows:
- April 15th: First quarter
- June 15th: Second quarter
- September 15th: Third quarter
- October 17th: Fourth quarter
Taxpayers who fail to make timely estimated tax payments may face penalties. The penalty for underpayment is calculated based on the difference between the amount of tax owed and the amount of tax paid through withholding and estimated payments. The penalty rate is generally 0.5% of the underpayment for each month or part of a month that the underpayment remains unpaid.
Extension Requests
Taxpayers can request an extension of time to file their tax return, but this does not extend the deadline for paying taxes. The extension deadline for filing federal income tax returns is generally October 15th. However, this deadline may be subject to change based on the calendar year.
For example, in 2023, the deadline for filing was extended to October 16th.
- The extension request must be filed on IRS Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.
- While the extension allows more time to file, it does not extend the deadline for paying taxes.
- Taxpayers must still estimate their tax liability and pay the estimated amount by the original due date.
- Failing to pay the estimated tax liability by the original due date may result in penalties.
State Tax Deadlines
State tax deadlines vary depending on the state. It is crucial for taxpayers to be aware of their state’s tax deadlines, as they may differ from federal deadlines. Many states align their deadlines with the federal deadlines, so the state income tax return filing deadline is also typically October 15th.
However, some states have different deadlines. For example, California’s deadline for filing state income tax returns is generally April 15th.
Individual Income Tax
Individuals may have remaining tax obligations in October, such as estimated tax payments or adjustments to previous filings. For example, if an individual’s income changes during the year, they may need to adjust their estimated tax payments to ensure they are paying the correct amount of tax.
Individuals may also need to make adjustments to their previous filings if they receive certain tax credits or deductions after filing their return.
Curious about the current CD rates in October 2023? You can find a comprehensive overview of CD Rates October 2023 to see how they compare.
Business Income Tax
Businesses have various tax obligations, including corporate income tax, partnership tax, and estimated payments. Businesses must file their corporate income tax returns and partnership tax returns by the due date, which is typically March 15th for corporations and April 15th for partnerships.
However, businesses may also have to make estimated tax payments throughout the year. The fourth and final estimated tax payment for businesses is due on October 17th.
Payroll Tax
Payroll tax obligations include federal and state withholdings. Employers are required to withhold federal income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax from their employees’ wages. They must also pay matching Social Security and Medicare taxes. Employers are generally required to deposit payroll taxes with the IRS on a monthly or semi-weekly basis, depending on their payroll tax liability.
The deadline for depositing payroll taxes varies depending on the deposit schedule.
October is a great time to find some great deals on leases. Check out the October 2023 Lease Deals to see what’s available.
Sales Tax
Sales tax obligations are typically due monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the state and the business’s sales volume. Some states may require businesses to file and pay sales tax in October. For example, California requires businesses to file and pay sales tax on a monthly basis.
Businesses should check with their state’s tax agency to determine their specific sales tax filing requirements.
Property Tax
Property tax payments are typically due annually. However, some jurisdictions may require property taxes to be paid in installments. Taxpayers should consult with their local tax assessor to determine their property tax payment schedule.
Table of Key Tax Deadlines in October
| Deadline Date | Tax Obligation | Who is Affected | Forms |
|---|---|---|---|
| October 17th | Estimated Tax Payments (Fourth Quarter) | Individuals and Businesses | IRS Form 1040-ES (Individuals) or IRS Form 1040-ES (Businesses) |
| October 15th | Federal Income Tax Return Filing Extension | Individuals and Businesses | IRS Form 4868 |
Estimated Taxes
Estimated taxes are payments you make throughout the year to cover your tax liability. They are typically required for individuals who have income that is not subject to withholding, such as self-employment income, investment income, or income from a side hustle.
Paying estimated taxes ensures that you avoid penalties for underpayment at the end of the tax year.
Estimated Tax Payments in October
The due dates for estimated tax payments in October depend on whether you are a quarterly or monthly filer. The following table Artikels the specific due dates for both types of filers:
| Payment Due Date | Tax Year | Filer Type |
|---|---|---|
| October 17, 2023 | 2023 | Quarterly |
| October 17, 2023 | 2023 | Monthly |
Penalties for Late Estimated Tax Payments
If you fail to pay your estimated taxes on time, you may be subject to penalties. The penalty rate for late estimated tax payments is typically calculated as an annual interest rate on the underpayment amount. The penalty applies only to the underpayment amount, not the entire tax liability.
The penalty for underpayment of estimated taxes is calculated as an annual interest rate on the underpayment amount.
There are some exceptions to the penalty, such as if you are experiencing a hardship or if you have a reasonable cause for not paying on time. It’s best to consult with a tax professional to determine if you qualify for any exceptions.
Methods for Paying Estimated Taxes
There are several different methods you can use to pay your estimated taxes. Some of the most common methods include:
- Online payment options:You can pay your estimated taxes online through the IRS website or through a third-party payment service. This is a convenient and secure way to make payments. You will need your Social Security number, bank account information, and the amount of your payment.
- Mailing checks or money orders:You can also mail your estimated tax payments to the IRS. You will need to make your check or money order payable to the U.S. Treasury and include your name, address, Social Security number, and the tax year for which the payment is being made.
The address to mail your payment can be found on the IRS website.
- Direct debit from a bank account:You can set up direct debit from your bank account to pay your estimated taxes. This method allows you to make your payments automatically on the due date. You will need to provide your bank account information to the IRS.
Looking for a great deal on a lease? October is a great time to find some amazing offers. Check out the Best Lease Deals October 2023 to see what’s available.
Example Scenario
Let’s say that you are self-employed and expect to have a taxable income of $100,000 for the year. You have already paid $20,000 in estimated taxes for the year. Your estimated tax liability is $25,000. This means you need to pay an additional $5,000 in estimated taxes by October 17, 2023.
Your estimated tax liability is calculated by multiplying your estimated taxable income by the applicable tax rate.
Quarterly Taxes
Quarterly taxes are payments made by individuals and businesses to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) throughout the year, rather than waiting to pay in a lump sum at the end of the tax year. These payments are an estimate of your annual tax liability, and they help to avoid a large tax bill at the end of the year.
The IRS has some important deadlines in October. Make sure you’re aware of the IRS October Deadline 2023 to avoid any issues.
Quarterly Tax Deadlines in October
Quarterly tax payments are due on specific dates throughout the year. The deadline for the third quarter of the tax year is typically September 15. However, if September 15 falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is shifted to the next business day.
In 2023, September 15 falls on a Friday, so the deadline for the third quarter is September 15.The deadline for the fourth quarter of the tax year is typically January 15. However, if January 15 falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is shifted to the next business day.
In 2024, January 15 falls on a Monday, so the deadline for the fourth quarter is January 15.
Who Pays Quarterly Taxes?
Individuals and businesses are required to pay quarterly taxes if they meet certain criteria.
Individuals
- Individuals who are self-employed or operate a small business and expect to owe at least $1,000 in taxes.
- Individuals who have income from sources other than wages, such as investments or rental properties, and expect to owe at least $1,000 in taxes.
- Individuals who have significant tax liability from previous years and are at risk of owing a large amount of taxes in the current year.
Businesses
- Businesses that are organized as corporations, partnerships, or LLCs.
- Businesses that have significant income and expect to owe a large amount of taxes.
- Businesses that are required to pay estimated taxes by state or local laws.
Examples of Businesses and Individuals Who Pay Quarterly Taxes
Individuals
- Freelancers who earn income from various clients and projects.
- Real estate investors who receive rental income.
- Independent contractors who provide services to businesses.
- Individuals who have a significant amount of income from investments, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds.
Businesses
- Small businesses that operate as sole proprietorships, partnerships, or LLCs.
- Large corporations with substantial revenue and profits.
- Businesses that operate in industries with high tax liabilities, such as financial services, technology, and manufacturing.
4. Extension Deadlines
Tax extensions can be a lifesaver for individuals and businesses alike, providing extra time to gather information, complete calculations, and file your returns. Understanding the different types of extensions available and the process for filing them is crucial to avoid potential penalties.
4.1. Common Tax Extensions in October
October is a month where several tax extension deadlines fall. Understanding these deadlines and their implications is vital for both individuals and businesses.
- Individual income tax extensions: If you are unable to file your individual income tax return by the regular April 15th deadline, you can request an extension. This extension will give you an additional six months to file your return, pushing the deadline to October 15th.
To be eligible for this extension, you must file Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. The extension only applies to filing the return, not to paying the taxes owed. You still need to pay any taxes due by the original April 15th deadline to avoid penalties.
- Business tax extensions: Businesses also have the option to file for extensions on various tax returns. For instance, corporations filing Form 1120, U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return, or partnerships filing Form 1065, U.S. Return of Partnership Income, can request an extension.
These extensions also typically grant an additional six months to file, extending the deadline to October 15th. However, the extension does not apply to paying taxes owed, which must be paid by the original deadline to avoid penalties. The forms used for these extensions are Form 7004, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns.
- Other relevant extensions: In addition to individual and business income tax extensions, there are other relevant extensions that might fall in October. For example, if you have property taxes due, the deadline might fall in October, depending on your location. Similarly, estate taxes also have specific deadlines, which can sometimes fall in October.
It is important to check the specific deadlines for your jurisdiction to avoid penalties.
4.2. Filing for a Tax Extension
Filing for a tax extension is a relatively straightforward process. However, it’s crucial to understand the requirements and deadlines to ensure you are compliant.
The tax deadline for 2023 is approaching! Make sure you’re prepared by checking out the Tax Deadline 2023 information.
- Forms required: The specific form used for filing a tax extension depends on the type of tax return being extended. For example, Form 4868 is used for individual income tax extensions, while Form 7004 is used for business tax extensions.
- Information needed: When filing for an extension, you need to provide certain information, including your name, Social Security number, address, and the tax year for which you are requesting an extension. You also need to indicate the type of tax return being extended.
Are you thinking about buying a home? Keep an eye on the latest Mortgage Rates October 2023 to see how they’re fluctuating.
- Submission methods: You can file for a tax extension online, by mail, or by fax. The IRS offers online filing options through its website or through third-party tax preparation software. If you choose to file by mail, you can download the necessary forms from the IRS website.
- Deadline for filing: The deadline for filing a tax extension is typically the same as the original filing deadline for the tax return. For example, the deadline for filing an individual income tax extension is October 15th.
4.3. Consequences of Filing vs. Not Filing an Extension
Understanding the consequences of filing or not filing a tax extension is crucial to make informed decisions.
- Consequences of filing an extension:
- Impact on payment deadline: Filing an extension only extends the deadline for filing your tax return. It does not extend the deadline for paying the taxes owed. You must still pay any taxes due by the original filing deadline, even if you file an extension.
- Potential penalties: While filing an extension can help you avoid late filing penalties, it does not guarantee that you will avoid all penalties. You may still be subject to penalties for late payment if you do not pay the taxes owed by the original deadline.
- Benefits of filing an extension: Filing an extension gives you extra time to gather information, complete calculations, and file your return without incurring late filing penalties. This can be particularly helpful if you are facing complex tax situations or have limited time to prepare your return.
If you’re looking for the best CD rates in October 2023, you’ve come to the right place. Check out the latest Best CD Rates October 2023 to find the best deals for your savings.
- Consequences of not filing an extension:
- Late filing penalties: If you fail to file your tax return by the original deadline, you may be subject to late filing penalties. These penalties are typically calculated as a percentage of the unpaid taxes owed.
- Interest charges: If you do not pay your taxes by the original deadline, you will be charged interest on the unpaid amount. Interest is calculated based on the federal short-term rate.
- Potential legal issues: Failing to file your taxes on time can lead to serious legal consequences, including fines, penalties, and even imprisonment in extreme cases.
State Taxes
While federal taxes have a set deadline, state tax deadlines can vary widely. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring timely payment and avoiding penalties. This section explores state tax deadlines in October, including a comparison with federal deadlines, a list of states with October deadlines, and a guide to determining state tax deadlines based on your location.
Comparison of Federal and State Tax Deadlines in October
Here’s a table comparing and contrasting federal and state tax deadlines in October, highlighting key aspects like the deadline, filing status, and potential penalties:
| Tax Type | Deadline | Relevant Filing Status | Penalty for Late Filing | Extension Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Income Tax | October 17, 2023 (for individuals) | Individuals, businesses | 0.5% of the unpaid tax per month or part of a month that the tax is late, up to a maximum of 25% of the unpaid tax. | Yes, up to six months. |
| State Income Tax (varies by state) | October 17, 2023 (for some states) | Individuals, businesses | Varies by state, but typically includes penalties for late filing and late payment. | Yes, but the deadline and eligibility criteria vary by state. |
States with October Tax Deadlines
Here are five states with specific tax deadlines that fall in October:
-
California
- Tax Deadline: October 17, 2023
- Type of Tax: Income Tax
- Description: Tax on income earned in California.
-
Massachusetts
- Tax Deadline: October 17, 2023
- Type of Tax: Income Tax
- Description: Tax on income earned in Massachusetts.
-
New Jersey
- Tax Deadline: October 17, 2023
- Type of Tax: Income Tax
- Description: Tax on income earned in New Jersey.
-
New York
- Tax Deadline: October 17, 2023
- Type of Tax: Income Tax
- Description: Tax on income earned in New York.
-
Oregon
- Tax Deadline: October 17, 2023
- Type of Tax: Income Tax
- Description: Tax on income earned in Oregon.
Determining State Tax Deadlines Based on Location
To determine your state tax deadlines, follow these steps:
-
Using a State Tax Website
Each state has a dedicated tax website. Navigate to your state’s tax website, usually found by searching for “[State Name] tax department” or “[State Name] tax website.” Look for sections like “Tax Deadlines,” “Filing Dates,” or “Important Dates.” These sections typically provide a calendar of tax deadlines, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and other relevant deadlines.
-
Contacting the State Tax Department
If you cannot find the information online, contact your state’s tax department directly. You can find their phone number and email address on their website or through a general internet search. They can provide specific deadline information for your location and tax situation.
-
Utilizing Online Tax Preparation Software
Online tax preparation software, such as TurboTax, H&R Block, or TaxAct, can also help determine your state tax deadlines. These platforms use your location and other relevant information to calculate the correct deadlines for your specific situation. They often include features that alert you to upcoming deadlines and provide reminders to file on time.
-
Consulting a Tax Professional
If you have a complex tax situation or are unsure about your state tax deadlines, consulting a tax professional is highly recommended. They can provide personalized advice, ensure accurate filing, and help you avoid penalties.
6. Penalties and Interest
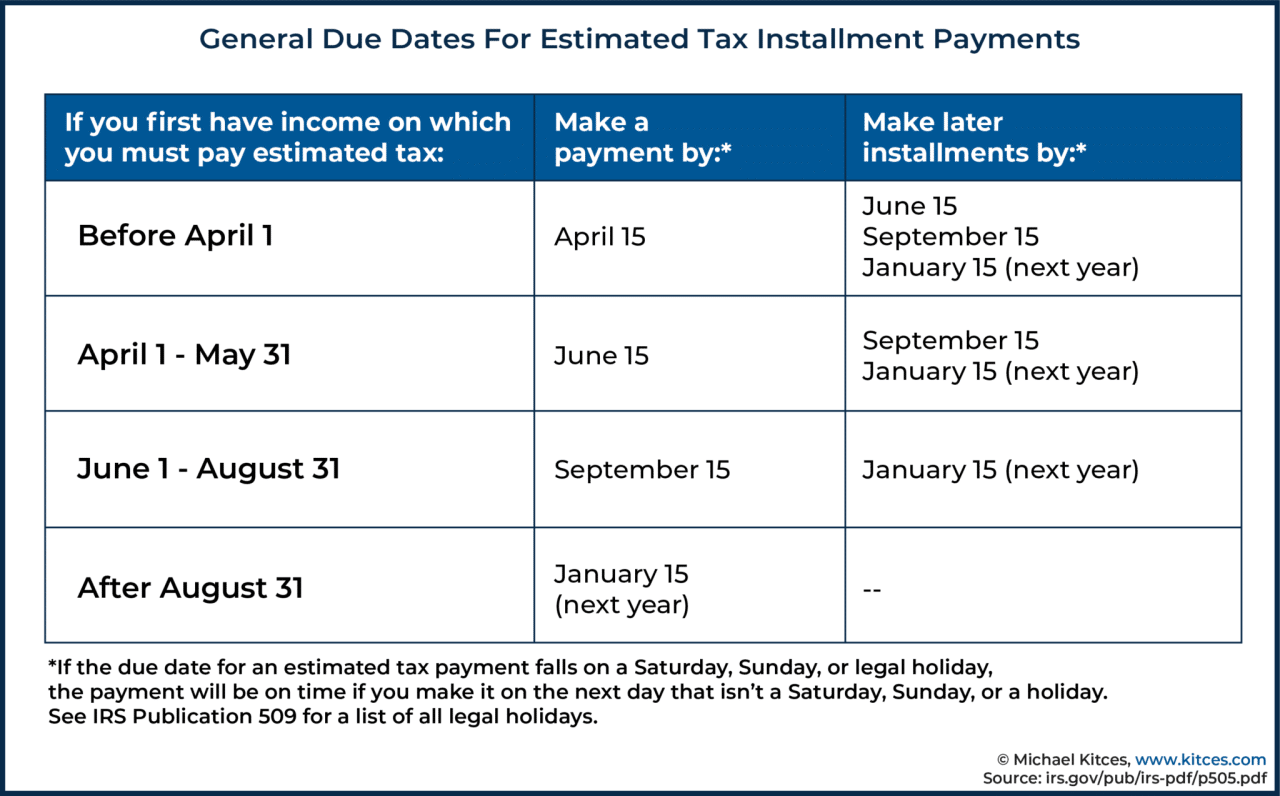
Late tax payments in October can result in penalties and interest charges. These penalties are designed to encourage timely tax compliance and ensure that the government receives its due revenue. Understanding the potential penalties and interest charges is crucial for taxpayers to avoid unnecessary financial burdens.
Penalties and Interest Rates
Penalties and interest rates for late tax payments vary depending on the type of tax. Here is a table summarizing the penalties and interest rates for different types of taxes:
| Tax Type | Penalty Rate | Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Income Tax | 0.5% of the unpaid tax for each month or part of a month that the tax is late, up to a maximum of 25% | The applicable federal short-term interest rate plus 3 percentage points |
| Property Tax | Varies by state and local jurisdiction | Varies by state and local jurisdiction |
| Sales Tax | Varies by state and local jurisdiction | Varies by state and local jurisdiction |
Factors Determining Penalty and Interest Amount
The amount of penalties and interest for late tax payments in October is determined by several factors, including:
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Amount of Unpaid Tax | The higher the unpaid tax amount, the higher the penalty and interest charges will be. |
| Duration of the Delay | The longer the delay in payment, the higher the penalty and interest charges will be. |
| Taxpayer’s History of Late Payments | Taxpayers with a history of late payments may be subject to higher penalties and interest rates. |
| Applicable Waivers or Exemptions | Certain waivers or exemptions may be available to reduce or eliminate penalties and interest charges. For example, the IRS may waive penalties for late payments if the taxpayer can demonstrate reasonable cause for the delay. |
Options to Reduce or Avoid Penalties and Interest
Taxpayers facing potential penalties for late tax payments in October have several options to reduce or avoid these charges:
- File an Amended Tax Return to Correct Errors: If the late payment is due to an error on the original tax return, filing an amended return can correct the error and reduce the amount of unpaid tax. This can help minimize penalties and interest charges.
- Request a Payment Plan: The IRS offers payment plans to taxpayers who cannot afford to pay their taxes in full. This allows taxpayers to make monthly payments over a period of time, which can help reduce the amount of penalties and interest accrued.
- Apply for a Penalty Abatement: Taxpayers can apply for a penalty abatement if they can demonstrate reasonable cause for the late payment. This may include situations like a serious illness, a natural disaster, or a death in the family. The IRS may waive penalties in these situations.
- Explore Other Options like Hardship Relief: In some cases, taxpayers may be eligible for hardship relief. This may include options like a temporary suspension of penalties and interest charges.
Tax Advisor Script
“Hi [Client Name], I understand you’re facing potential penalties for late tax payments in October. Let’s discuss this so you can understand your options. The penalties can range from 0.5% to 25% of the unpaid tax, depending on the length of the delay. Additionally, interest charges are calculated based on the applicable federal short-term interest rate. For example, if you owe $10,000 in taxes and are a month late, you could be looking at a penalty of $500, plus interest. The good news is that there are options available to reduce or avoid these penalties. We can explore filing an amended return if the late payment is due to an error, or we can apply for a payment plan if you’re unable to pay in full. We can also look into applying for a penalty abatement if there were extenuating circumstances. It’s important to act quickly, as the longer you wait, the higher the penalties and interest charges will be. Let’s discuss your specific situation and determine the best course of action for you.”
Tax Tips and Strategies
October is a crucial month for tax planning, especially if you’re self-employed or have a business. Understanding key deadlines and employing effective strategies can help you minimize tax liability and ensure compliance.
If you filed for an extension, you’ll want to be aware of the October Extension Tax Deadline 2023 to avoid any penalties.
October Tax Deadlines
This table summarizes the key tax deadlines in October:| Deadline | Description ||—|—|| October 15th | Estimated Tax Payment Deadline (Q3) || October 17th | Extension Deadline for Filing Taxes (from April 15th) || October 31st | IRS Form 1099-NEC (Non-Employee Compensation) Due |
Tax Tips and Strategies, When Are Taxes Due In October
Here are some tips and strategies for managing your tax obligations in October:
- Review your estimated tax payments:Ensure you’ve made all necessary quarterly estimated tax payments for the year. If you haven’t, you may face penalties. The IRS offers a handy tool to calculate your estimated tax payments: [https://www.irs.gov/payments/view-or-pay-your-taxes](https://www.irs.gov/payments/view-or-pay-your-taxes).
- Consider tax deductions and credits:Explore available deductions and credits that can lower your tax liability. For example, if you’re self-employed, you can deduct business expenses such as office supplies, travel, and health insurance. The IRS provides a detailed list of deductions and credits on their website: [https://www.irs.gov/taxtopics/tc502](https://www.irs.gov/taxtopics/tc502).
- File for an extension:If you need more time to file your taxes, you can file for an extension until October 17th. This will give you additional time to gather all necessary documents and complete your return. However, remember that an extension only grants you more time to file, not more time to pay.
You still need to pay your taxes by the original deadline (April 15th) to avoid penalties.
- Stay organized:Keep track of all your tax documents and receipts throughout the year. This will make it easier to file your taxes accurately and avoid any surprises come tax season.
Tax Assistance and Support
There are various resources available to assist you with your tax obligations:
- IRS website:The IRS website offers a wealth of information on taxes, including forms, publications, and FAQs. You can also use the IRS’s online tools to calculate your taxes, file electronically, and pay online.
- Tax professionals:If you’re unsure about your tax obligations or need help with filing your taxes, consider consulting a tax professional. Tax professionals can help you navigate the complexities of the tax code and ensure you’re taking advantage of all available deductions and credits.
Planning your month ahead? Take a look at the October 2023 Calendar to see what’s coming up.
- Tax preparation software:There are various tax preparation software programs available that can help you file your taxes online. These programs offer guidance and support throughout the filing process and can help you identify deductions and credits you may be eligible for.
Filing Methods
When it comes to filing your taxes in October, you have several options available to you. The method you choose will depend on your individual circumstances, preferences, and comfort level with technology. Each method comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to carefully consider your options before making a decision.
Filing Online
Filing your taxes online has become increasingly popular in recent years, thanks to its convenience, speed, and accuracy. Many online tax preparation services offer user-friendly interfaces, step-by-step guidance, and built-in error checks to help you file your taxes accurately. You can also receive your refund faster when you file electronically, as the IRS processes electronic returns much quicker than paper returns.
- Advantages:
- Convenience: You can file your taxes from the comfort of your home, at any time of day or night.
- Speed: Online tax preparation services can often complete your return in minutes.
- Accuracy: Online services typically have built-in error checks to help you avoid mistakes.
- Faster Refunds: The IRS processes electronic returns much quicker than paper returns.
- Disadvantages:
- Cost: Some online tax preparation services charge a fee, although there are many free options available, especially for simple tax returns.
- Technical Requirements: You’ll need a computer with internet access to file online.
- Security Concerns: It’s important to choose a reputable online tax preparation service and take steps to protect your personal information.
Some popular online tax preparation services include TurboTax, H&R Block, and TaxAct. These services offer a range of features, from basic tax preparation to more advanced options for self-employed individuals and small business owners. Many of these services also offer free versions for simple tax returns.
Filing by Mail
Filing your taxes by mail is a traditional method that’s still an option for many taxpayers. It involves completing a paper tax return and mailing it to the IRS. While this method is less convenient than filing online, it can be a good option for taxpayers who prefer a more hands-on approach or who don’t have access to a computer or internet connection.
- Advantages:
- No Technical Requirements: You don’t need a computer or internet access to file by mail.
- Free: Filing by mail is free, although you may need to purchase tax forms from the IRS website or your local library.
- Control: You have complete control over your tax return and can review it carefully before mailing it.
- Disadvantages:
- Time-Consuming: Filing by mail can be time-consuming, as you need to complete the forms manually and mail them to the IRS.
- Slower Refunds: The IRS processes paper returns much slower than electronic returns.
- Errors: You’re more likely to make mistakes when completing tax forms manually.
You can obtain the necessary tax forms from the IRS website or your local library. Be sure to mail your return to the correct address, as listed on the tax forms.
Filing Through a Tax Professional
Hiring a tax professional, such as a certified public accountant (CPA) or an enrolled agent (EA), can be a good option for taxpayers who have complex tax situations or who want help ensuring they’re taking advantage of all available deductions and credits.
Tax professionals can also help you navigate the tax code and avoid common mistakes.
- Advantages:
- Expertise: Tax professionals have extensive knowledge of the tax code and can help you maximize your refund or minimize your tax liability.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that a professional is handling your taxes can give you peace of mind.
- Time Savings: Tax professionals can handle all the paperwork and filing, saving you time and effort.
- Disadvantages:
- Cost: Hiring a tax professional can be expensive, especially if you have a complex tax situation.
- Limited Availability: Tax professionals can be busy during tax season, so you may need to schedule an appointment in advance.
- Lack of Control: You’ll be giving up some control over your tax return when you hire a tax professional.
Before hiring a tax professional, it’s important to ask about their fees, experience, and qualifications. You should also check their credentials with the IRS or a professional organization.
Tax Audit Considerations
While October tax deadlines may be on your mind, it’s also important to consider the possibility of a tax audit. The IRS may review your tax return, and understanding why audits happen and how to prepare can help you navigate this process.
Reasons for Tax Audits
The IRS conducts audits to ensure taxpayers are accurately reporting their income and paying the correct amount of taxes. Here are some common reasons for an audit:
- Disproportionate deductions:Claiming deductions that seem unusually high compared to your income can raise red flags.
- Errors on tax forms:Mistakes on your tax return, like incorrect Social Security numbers or mismatched information, can trigger an audit.
- Unreported income:Failing to report all income, including income from side gigs or investments, is a major reason for audits.
- Unusual transactions:Large, unusual transactions or a pattern of suspicious activity can attract the IRS’s attention.
- Matching discrepancies:The IRS compares your tax return with information from third parties like employers and banks. Any discrepancies can lead to an audit.
Preparing for a Potential Tax Audit
Being prepared for a potential audit can reduce stress and ensure you have the necessary documentation. Here’s what you can do:
- Keep accurate records:Maintain detailed records of all income, expenses, deductions, and supporting documentation. This includes receipts, bank statements, and any other relevant documents.
- Understand your tax obligations:Familiarize yourself with the tax laws and regulations that apply to your situation. This can help you avoid common mistakes that could lead to an audit.
- Be organized:Organize your tax records in a logical and accessible manner. This will make it easier to locate information if you’re audited.
- Seek professional help:If you’re unsure about any aspect of your taxes or are facing a potential audit, consider consulting a qualified tax professional. They can provide guidance and support throughout the process.
Year-End Tax Planning
October is a crucial month for tax planning, especially for individuals and businesses aiming to minimize their tax liability for the current year. This is because it provides a window to make adjustments to financial strategies and maximize tax benefits before the year ends.
Tax Planning Strategies for October
Proactive tax planning in October can significantly impact your tax burden. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Maximize Retirement Contributions:Contribute the maximum allowed to your 401(k) or IRA to reduce taxable income. Remember, contributions are tax-deductible, leading to immediate tax savings. This strategy can be especially beneficial if you anticipate being in a higher tax bracket in the future.
- Consider Tax-Loss Harvesting:This strategy involves selling losing investments to offset capital gains, reducing your overall tax liability. For example, if you have a stock that has declined in value, selling it and realizing the loss can help offset any capital gains from other investments.
- Make Charitable Donations:Charitable donations are often tax-deductible, allowing you to reduce your taxable income. Consider making larger donations in October to take advantage of this benefit.
- Review Your Withholding:Ensure your W-4 form is accurate and reflects your current financial situation. Adjust your withholdings if necessary to avoid a large tax bill or refund come tax season.
- Prepay Property Taxes:If you live in a state where property taxes are deductible, prepaying your taxes in October can create a larger deduction for the current year. This strategy is particularly relevant for individuals who expect their income to be higher in the future.
Benefits of Proactive Tax Planning
- Minimize Tax Liability:Tax planning helps identify opportunities to reduce your tax burden, ultimately saving you money.
- Increase Financial Flexibility:By reducing your tax liability, you can free up more cash flow for other financial goals.
- Avoid Penalties and Interest:Proactive tax planning can help prevent penalties and interest charges for underpayment or non-compliance.
- Optimize Your Financial Strategies:Tax planning integrates with your overall financial goals, ensuring your strategies are aligned and optimized for maximum benefit.
Ultimate Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of tax deadlines in October can be daunting, but with the right information and resources, taxpayers can confidently manage their obligations and avoid penalties. Remember, seeking professional guidance from a tax advisor is always recommended if you have any questions or require assistance.
By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure a smooth and stress-free tax experience throughout October.
FAQ Explained
What happens if I miss a tax deadline in October?
Missing a tax deadline can result in penalties and interest charges. The specific penalties and interest rates vary depending on the type of tax and the length of the delay. It’s crucial to file your taxes on time or request an extension if needed to avoid these consequences.
Can I file my taxes electronically in October?
Yes, you can file your taxes electronically in October. Many online tax preparation services offer convenient and secure options for filing your taxes online. However, it’s important to ensure that you choose a reputable and reliable service.
Are there any specific tax tips for October?
October is a good time to review your tax situation and make any necessary adjustments to your withholdings or estimated tax payments. Consider consulting with a tax advisor to ensure you are on track for the year and minimize your tax liability.











