When Are Taxes Due In October 2023? Navigating the tax landscape can be tricky, especially with various deadlines looming. October presents a unique set of tax filing and payment obligations, making it crucial to stay informed. Whether you’re an individual or a business owner, understanding the key deadlines and potential extensions is vital to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of tax deadlines in October 2023, covering federal, state, and local taxes, as well as potential extensions and exceptions.
From individual income tax returns to estimated tax payments, sales tax, and payroll tax, we’ll break down the specific dates and provide insights into the relevant regulations. We’ll also explore common tax mistakes to avoid and offer valuable tax planning strategies to help you minimize your tax liability and maximize your financial well-being.
Contents List
- 1 Tax Filing Deadlines in October 2023: When Are Taxes Due In October 2023
- 2 Quarterly Estimated Taxes
- 3 Extension of Time to File
- 4 Tax Payments in October 2023
- 5 Tax Audit Season
- 6 Common Tax Mistakes
- 6.1 Missing the Deadline
- 6.2 Inaccurate Reporting of Income
- 6.3 Incorrect Deductions and Credits
- 6.4 Errors in Filing Status
- 6.5 Failing to Keep Adequate Records
- 6.6 Ignoring Changes in Tax Laws
- 6.7 Failing to File an Extension
- 6.8 Ignoring Notices from the IRS
- 6.9 Overlooking the Impact of Life Events
- 6.10 Relying Solely on Free Online Tax Preparation Services
- 7 Tax Planning Strategies
- 8 Tax Resources and Support
- 9 State Tax Deadlines
- 10 Tax Changes and Updates
- 11 Impact of Inflation on Taxes
- 12 Tax Filing Software
- 13 Tax Tips for Specific Groups
- 14 Taxation and the Economy
- 15 Final Review
- 16 FAQ Overview
Tax Filing Deadlines in October 2023: When Are Taxes Due In October 2023
October is a crucial month for tax filers, with various deadlines for federal, state, and local taxes. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of these deadlines, helping you stay on top of your tax obligations.
Federal Tax Deadlines
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sets deadlines for filing various federal taxes. These deadlines can vary depending on the type of tax and the filing status.
Individual Income Tax
The filing deadline for individual income tax returns in October 2023 is October 15, 2023, for those who filed for an extension. If you didn’t file for an extension, the original deadline was April 18,
2023. Here’s a breakdown of the filing deadlines for various filing statuses
| Filing Status | Filing Deadline |
|---|---|
| Single | October 15, 2023 |
| Married Filing Jointly | October 15, 2023 |
| Head of Household | October 15, 2023 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | October 15, 2023 |
| Married Filing Separately | October 15, 2023 |
Corporate Income Tax
The filing deadline for corporate income tax returns in October 2023 depends on the corporation’s fiscal year end. For corporations with a fiscal year ending September 30, 2023, the filing deadline is October 15, 2023. For corporations with different fiscal year ends, the filing deadline is typically the 15th day of the fourth month after the end of their fiscal year.
For example, a corporation with a fiscal year ending December 31, 2023, would have a filing deadline of April 15, 2024.
Estimated Taxes
The payment deadline for estimated taxes in October 2023 is October 17, 2023. This deadline applies to individuals, corporations, and other entities required to pay estimated taxes.Estimated taxes are payments made throughout the year to cover your tax liability. The frequency of estimated tax payments depends on your income and tax situation.
Whether you’re planning a big purchase or just curious about current market trends, it’s helpful to know the Mortgage Rates October 2023. Rates fluctuate, so it’s always a good idea to check the latest information before making any major financial decisions.
You may be required to make quarterly payments, or you may be able to pay in a lump sum.
Keep track of important dates and events with the October 2023 Calendar. From holidays to deadlines, this resource can help you stay organized and on top of your schedule.
“Failure to pay estimated taxes on time can result in penalties. These penalties can be substantial, so it’s important to make sure you’re paying your estimated taxes on time.”
State Tax Deadlines
State tax deadlines can vary significantly, so it’s important to check with your state’s tax agency for specific information.
Individual Income Tax
The filing deadline for individual income tax returns in October 2023 for most states is October 15, 2023, for those who filed for an extension. Some states may have different deadlines or extensions, so it’s essential to check with your state’s tax agency.Here’s a table summarizing the specific dates for each state, highlighting any states with unique deadlines or extensions:
| State | Filing Deadline | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| California | October 15, 2023 | For taxpayers who filed for an extension. |
| New York | October 15, 2023 | For taxpayers who filed for an extension. |
| Texas | October 15, 2023 | For taxpayers who filed for an extension. |
| Florida | No state income tax | N/A |
Corporate Income Tax
The filing deadline for corporate income tax returns in October 2023 for most states is October 15, 2023, for corporations with a fiscal year ending September 30, 2023. Some states may have different deadlines or extensions, so it’s essential to check with your state’s tax agency.Here’s a table summarizing the specific dates for each state, considering the potential impact of fiscal year ends:
| State | Filing Deadline | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| California | October 15, 2023 | For corporations with a fiscal year ending September 30, 2023. |
| New York | October 15, 2023 | For corporations with a fiscal year ending September 30, 2023. |
| Texas | October 15, 2023 | For corporations with a fiscal year ending September 30, 2023. |
| Florida | No state corporate income tax | N/A |
Sales Tax
The payment deadline for sales tax in October 2023 can vary significantly based on state and local regulations. It’s essential to check with your state’s tax agency and your local municipality for specific deadlines.Here’s a table summarizing the specific dates for different states, highlighting any states with unique deadlines or extensions:
| State | Filing Deadline | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| California | October 20, 2023 | For businesses with a monthly filing requirement. |
| New York | October 20, 2023 | For businesses with a monthly filing requirement. |
| Texas | October 20, 2023 | For businesses with a monthly filing requirement. |
| Florida | October 20, 2023 | For businesses with a monthly filing requirement. |
Other Tax Deadlines
In addition to federal and state taxes, there are other tax deadlines to be aware of in October 2023.
Payroll Tax
The filing deadlines for payroll tax in October 2023 can vary depending on the type of payroll tax. Here’s a table summarizing the specific dates for different payroll tax types, highlighting any unique deadlines or extensions:
| Payroll Tax Type | Filing Deadline | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Income Tax Withholding | October 15, 2023 | For employers who file quarterly. |
| Social Security and Medicare Taxes | October 15, 2023 | For employers who file quarterly. |
| Unemployment Taxes | October 15, 2023 | For employers who file quarterly. |
Property Tax
The payment deadlines for property tax in October 2023 can vary significantly based on local regulations. It’s essential to check with your local tax assessor’s office for specific deadlines.Here’s a table summarizing the specific dates for different jurisdictions, highlighting any unique deadlines or extensions:
| Jurisdiction | Filing Deadline | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| City of Los Angeles | October 1, 2023 | For property owners who pay their taxes in installments. |
| County of San Diego | October 15, 2023 | For property owners who pay their taxes in installments. |
| State of Texas | October 31, 2023 | For property owners who pay their taxes in installments. |
Potential Extensions and Exceptions
Taxpayers may be eligible for an extension to file their taxes. However, it’s important to note that an extension only grants additional time to file, not to pay. Taxes are still due on the original deadline.
“Taxpayers who are unable to meet the filing deadline may be eligible for an extension. However, it is important to note that an extension only grants additional time to file, not to pay. Taxes are still due on the original deadline.”
Here are some potential exceptions to tax deadlines in October 2023:* Natural disasters:Taxpayers who have been affected by a natural disaster may be eligible for an extension.
When you’re ready to upgrade your ride, explore the Best Lease Deals October 2023. You might find some great deals on popular models that fit your budget and lifestyle.
Military service
Taxpayers who are serving in the military may be eligible for an extension.
Overseas duty
Taxpayers who are living and working overseas may be eligible for an extension.
If you’re considering investing in a Certificate of Deposit (CD), take a look at the CD Rates October 2023 to find the best options. CD rates are often influenced by broader economic factors, so it’s wise to stay informed about current trends.
Disability
Taxpayers who are disabled may be eligible for an extension.
Resources and Additional Information
For taxpayers seeking information on tax deadlines in October 2023, there are numerous resources available. Here are some helpful links:* Internal Revenue Service (IRS):[https://www.irs.gov/](https://www.irs.gov/)
State Tax Agencies
[https://www.taxadmin.org/](https://www.taxadmin.org/)
Tax Software Providers
[https://www.intuit.com/](https://www.intuit.com/), [https://www.turbotax.com/](https://www.turbotax.com/)
Accounting Firms
[https://www.aicpa.org/](https://www.aicpa.org/)For additional guidance on specific tax-related issues or assistance with tax preparation, consider these resources:* Tax Articles and Blog Posts:[https://www.irs.gov/newsroom/](https://www.irs.gov/newsroom/), [https://www.forbes.com/](https://www.forbes.com/)
Online Tax Tools
[https://www.irs.gov/individuals/free-tax-preparation](https://www.irs.gov/individuals/free-tax-preparation), [https://www.taxact.com/](https://www.taxact.com/)
Quarterly Estimated Taxes
Quarterly estimated taxes are payments made throughout the year to cover your tax liability. This applies to individuals and businesses who don’t have enough taxes withheld from their income, or those who have significant income from sources not subject to withholding.
Taxpayers Required to Pay Quarterly Estimated Taxes
Paying quarterly estimated taxes is usually required for individuals and businesses whose income is not subject to withholding.
- Self-Employed Individuals:Freelancers, independent contractors, and other self-employed individuals generally have to pay quarterly estimated taxes. Their income isn’t subject to withholding like regular employees.
- Small Business Owners:Small business owners, especially those with significant income, are typically required to pay quarterly estimated taxes. This includes sole proprietorships, partnerships, and S corporations.
- Other Taxpayers:Individuals with significant income from investments, royalties, or other sources that aren’t subject to withholding may also be required to pay quarterly estimated taxes.
Calculating Quarterly Estimated Taxes
The most common method for calculating quarterly estimated taxes is based on your projected annual income.
- Form 1040-ES:The IRS provides Form 1040-ES (Estimated Tax for Individuals) to help you calculate your quarterly payments. This form guides you through the process based on your income and deductions.
- Simple Example:Let’s say you expect to earn $50,000 in a year, and your tax bracket is 12%. You would estimate your annual tax liability as $6,000 ($50,000 x 0.12). To calculate your quarterly payments, you would divide this by four, resulting in a quarterly payment of $1,500.
Quarterly Estimated Tax Due Dates in October 2023
Here are the due dates for quarterly estimated tax payments in October 2023:
| Payment Period | Due Date |
|---|---|
April 15
|
June 15, 2023 |
June 16
|
September 15, 2023 |
| September 16
With the Tax Deadline 2023 approaching, you might be looking for ways to manage your finances. Understanding the October Extension Tax Deadline 2023 can help you plan accordingly. It’s important to stay organized and informed about deadlines to avoid penalties.
|
January 15, 2024 |
December 16
|
April 15, 2024 |
Note:If any of these dates fall on a weekend or holiday, the due date is shifted to the next business day. Late payments can result in penalties.
Additional Information
- Safe Harbor Rule:The “safe harbor” rule allows you to avoid penalties if you pay at least 90% of your current year’s tax liability or 100% of your previous year’s tax liability (if your previous year’s income was at least $150,000 for single filers or $300,000 for joint filers).
This rule provides some flexibility, but it’s important to understand the specific requirements.
- Resources:For more information on quarterly estimated taxes, you can visit the IRS website (www.irs.gov) or consult with a tax professional.
Extension of Time to File
If you need more time to file your federal income tax return, you can request an extension of time to file. This gives you an additional six months to file your return, but it does not give you an extension to pay your taxes.
Implications of an Extension on the Payment Deadline
An extension of time to file does not extend the time to pay your taxes. You still have to pay your taxes by the original due date, even if you have filed for an extension. If you do not pay your taxes by the original due date, you may be subject to penalties.
Penalties for Late Filing and Late Payment
The IRS may impose penalties for late filing and late payment. These penalties can be significant, so it is important to file your return and pay your taxes on time.
Late Filing Penalty
The late filing penalty is generally 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. The penalty is reduced if you have a reasonable cause for filing late.
Late Payment Penalty
The late payment penalty is generally 0.5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the payment is late, up to a maximum of 25%. The penalty is reduced if you have a reasonable cause for paying late.
The late payment penalty is generally 0.5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the payment is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
Tax Payments in October 2023

October is a crucial month for taxpayers, as it marks the deadline for various tax payments. Understanding the different payment methods and their deadlines is essential to avoid penalties and ensure timely fulfillment of your tax obligations.
Tax Payment Methods in October 2023
The IRS offers various methods for making tax payments, each with its own deadline and specific requirements. The following table Artikels the most common payment options available to taxpayers in October 2023.
| Payment Method | Deadline | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Electronic Funds Withdrawal (EFW) | October 17, 2023 | This is the fastest and most convenient way to pay taxes. You can make payments through the IRS’s online payment portal, a tax preparation software, or your bank’s website. |
| Debit Card, Credit Card, or Digital Wallet | October 17, 2023 | Third-party payment processors like Pay1040 or PayUSAtax allow you to pay taxes using debit cards, credit cards, or digital wallets like Apple Pay or Google Pay. |
| Check or Money Order | October 17, 2023 | You can mail your payment with the appropriate form to the address provided by the IRS. Make sure to include your name, address, Social Security number, the tax year, and the relevant tax form number. |
| Cash | October 17, 2023 | You can pay taxes in cash at a participating retail location, like Walmart, CVS, Walgreens, or Dollar General, using the IRS’s payment barcode. |
| IRS Direct Pay | October 17, 2023 | This free service allows you to make tax payments directly from your bank account through the IRS website. |
| Payment Arrangements | Varies | If you can’t pay your taxes in full by the deadline, you may be eligible for a payment plan or an offer in compromise. These options allow you to pay off your tax debt over time or negotiate a lower payment amount. |
Tax Audit Season
While October 2023 is not typically considered the peak of tax audit season, it’s important to understand the general timing of audits and how they might impact you. The IRS conducts audits throughout the year, but there are certain periods when they tend to increase their scrutiny.
Types of Tax Audits
The IRS conducts different types of tax audits, each with its own focus and process. Understanding the different types of audits can help you prepare for a potential review.
- Correspondence Audit:This is the most common type of audit. It involves the IRS requesting additional information or clarification about specific items on your tax return. These audits are usually conducted by mail and are often limited in scope.
- Office Audit:This type of audit requires you to visit an IRS office to discuss your tax return. It is typically more comprehensive than a correspondence audit and may involve a review of multiple items.
- Field Audit:This is the most intensive type of audit and involves an IRS agent visiting your home or business to examine your records and documentation. These audits are usually reserved for complex tax situations or those involving potential fraud.
Preparing for a Tax Audit
While you can’t always predict whether you’ll be audited, there are steps you can take to prepare and increase your chances of a smooth audit process.
- Keep Accurate Records:Maintaining detailed and organized records of all your income, expenses, deductions, and credits is crucial. The IRS expects you to be able to substantiate any claims you make on your tax return.
- Understand Your Tax Liability:Familiarize yourself with the tax laws and regulations that apply to your situation. This includes understanding your filing status, deductions, and credits. Seek professional advice if needed.
- Respond Promptly:If you receive a notice from the IRS, respond promptly and provide the requested information. Ignoring the notice could lead to further complications and penalties.
- Be Prepared for an Interview:If you are selected for an audit, be prepared to answer questions from an IRS agent. Be polite, respectful, and honest. Bring all relevant documentation to support your claims.
Common Tax Mistakes
October is a crucial month for tax filing, especially for those who need to file quarterly estimated taxes or are seeking an extension. It’s also a time when many taxpayers make common mistakes that can lead to penalties, interest, and other complications.
Understanding these mistakes and how to avoid them is essential for a smooth tax season.
Missing the Deadline
One of the most common tax mistakes is simply missing the deadline. While the official tax deadline for most taxpayers is April 15th, quarterly estimated taxes for the third quarter are due on October 17th, 2023. Missing this deadline can result in penalties, which can be substantial depending on the amount of underpayment and the length of the delay.
To avoid this mistake, set reminders well in advance of the deadline. Consider using calendar alerts, online reminders, or even a physical calendar. It’s also wise to file your taxes early, especially if you’re expecting a refund, to avoid any potential issues with delays or processing.
Inaccurate Reporting of Income
Another common mistake is reporting income inaccurately. This could include forgetting to report all income, misclassifying income types, or making errors in calculating income amounts. Accurate income reporting is crucial for determining your tax liability and ensuring that you pay the correct amount of taxes.
- Forgetting to report all income: Be sure to report all income sources, including wages, salaries, tips, interest, dividends, and capital gains. Don’t overlook income from side hustles or freelance work.
- Misclassifying income types: Ensure that you correctly categorize each income source. For example, self-employment income should be reported on Schedule C, while rental income is reported on Schedule E.
- Errors in calculating income amounts: Double-check your income calculations and ensure that all numbers are accurate. You can use tax preparation software or consult with a tax professional to help with this process.
Incorrect Deductions and Credits
Taking advantage of all eligible deductions and credits can significantly reduce your tax liability. However, claiming incorrect deductions or credits can lead to penalties and audits.
- Claiming ineligible deductions: Make sure that you meet the requirements for each deduction you claim. For example, the home office deduction has specific requirements that must be met.
- Overstating deductions: Carefully document all expenses related to deductions. Don’t overestimate expenses or claim deductions for items that don’t qualify.
- Incorrectly claiming credits: Many credits have specific eligibility requirements, such as income limitations or age restrictions. Be sure to meet these requirements before claiming any credits.
Errors in Filing Status
Choosing the correct filing status is crucial for determining your tax liability. Filing under the wrong status can result in overpaying or underpaying taxes.
The IRS offers several filing statuses, including single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, and qualifying widow(er). It’s essential to understand the requirements for each status and choose the one that applies to your circumstances. If you’re unsure, consult with a tax professional for guidance.
Failing to Keep Adequate Records
Maintaining accurate and organized financial records is essential for tax preparation. Without proper documentation, you may struggle to claim deductions or credits, and you could face penalties for inaccurate reporting.
- Keep receipts and invoices: Retain all receipts and invoices for expenses related to deductions, including medical expenses, charitable contributions, and business expenses.
- Maintain bank statements and investment records: Keep track of all bank statements, investment records, and other financial documents that may be relevant to your tax return.
- Organize your records: Create a system for organizing your tax documents, such as using folders or a digital filing system. This will make it easier to locate information when you need it.
Ignoring Changes in Tax Laws
Tax laws are constantly changing, so it’s important to stay informed about any updates that could affect your tax liability. Failing to keep up with these changes could result in errors on your tax return.
The IRS website is a valuable resource for information about tax law changes. You can also subscribe to tax newsletters or consult with a tax professional to stay informed.
Failing to File an Extension
If you can’t file your tax return by the deadline, you can request an extension. However, it’s crucial to understand that an extension only grants you more time to file your return; it does not extend the time to pay your taxes.
If you anticipate needing an extension, file Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, by the original deadline. This will give you an automatic six-month extension to file your return, but remember that taxes are still due by the original deadline.
If you owe taxes, you may still face penalties for late payment.
Ignoring Notices from the IRS
The IRS may send you notices regarding your tax return, such as a notice of underpayment or a notice of audit. Ignoring these notices can lead to serious consequences, including penalties, interest, and even legal action.
If you receive a notice from the IRS, carefully review the information and respond promptly. If you have any questions, contact the IRS directly for clarification.
Overlooking the Impact of Life Events
Life events, such as marriage, divorce, the birth of a child, or a job change, can significantly impact your tax liability. Be sure to consider these events when preparing your tax return.
For example, if you get married, you may need to file jointly, which could affect your tax bracket and deductions. Similarly, if you have a child, you may be eligible for the Child Tax Credit. Stay informed about how these events affect your taxes and consult with a tax professional if needed.
Relying Solely on Free Online Tax Preparation Services
While free online tax preparation services can be convenient, they may not be suitable for everyone. These services often have limitations and may not handle complex tax situations.
If you have a complex tax situation, such as self-employment income, investments, or multiple income sources, consider consulting with a tax professional. A qualified tax advisor can provide personalized guidance and ensure that your return is accurate and complete.
Tax Planning Strategies
Tax planning is an essential aspect of financial management, whether you’re an individual or a business. By strategically planning your tax obligations, you can maximize your savings and minimize your tax liability. This section will delve into tax planning strategies for individuals and businesses in October 2023.
If you’re looking to maximize your savings, check out the Best CD Rates October 2023 to see what offers are available. CD rates are constantly changing, so it’s important to stay informed about the latest options.
Tax Planning Strategies for Individuals
Effective tax planning can help individuals reduce their tax burden and maximize their financial well-being. Here are some strategies that can be implemented in October 2023:
- Maximize Retirement Contributions:Contributing to retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs can significantly reduce your taxable income. Consider increasing your contributions before the year’s end to take advantage of tax benefits. For example, if you’re eligible for a Roth IRA, your contributions grow tax-free and withdrawals in retirement are also tax-free.
- Harvest Tax Losses:If you have investments that have lost value, consider selling them to offset capital gains and reduce your tax liability. This strategy is known as tax-loss harvesting. For example, if you have a stock that has declined in value, you can sell it and use the loss to offset gains from other investments.
This can reduce your overall capital gains tax liability.
- Review Your Withholding:Ensure your W-4 form is up-to-date to avoid underpayment penalties. If you’ve experienced significant life changes, such as a job change, marriage, or a new child, you may need to adjust your withholdings to ensure you’re paying the correct amount of taxes throughout the year.
You can use the IRS withholding calculator to determine the appropriate amount of withholding for your situation.
- Consider Tax Credits:Explore available tax credits that can directly reduce your tax liability. The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and the Child Tax Credit are examples of credits that can provide significant tax savings for eligible individuals. For example, the EITC is a refundable tax credit for low-to-moderate-income working individuals and families.
The Child Tax Credit can provide a significant tax break for families with children.
- Make Charitable Donations:Donating to qualified charities can provide a tax deduction. If you haven’t already, consider making a donation before the year’s end to take advantage of this tax benefit. For example, if you donate $1,000 to a qualified charity, you may be able to deduct this amount from your taxable income, resulting in tax savings.
Potential Deductions and Credits for Individuals
Here is a list of potential deductions and credits that may be available to individuals in October 2023. Remember to consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.
| Category | Deduction/Credit | Description | Eligibility Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Expenses | Medical Expense Deduction | Deductible medical expenses exceeding a certain percentage of your adjusted gross income. | Medical expenses must exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income (AGI) in 2023. |
| Charitable Contributions | Cash Contribution Deduction | Deduction for cash contributions to qualified charities. | Contributions must be made to a qualified charitable organization. |
| Education Expenses | American Opportunity Tax Credit | Tax credit for qualified education expenses for the first four years of higher education. | Must be enrolled at least half-time in a qualified educational institution. |
| Homeownership | Home Mortgage Interest Deduction | Deduction for interest paid on a qualified home mortgage. | The mortgage must be on a primary residence and meet certain requirements. |
| Child Care Expenses | Child Tax Credit | Tax credit for each qualifying child under the age of 17. | Must meet certain income and residency requirements. |
Maximizing Tax Savings for Individuals
- Keep Accurate Records:Maintain detailed records of all income and expenses. This will help you accurately claim deductions and credits on your tax return. Use a system that works for you, such as a spreadsheet, a dedicated notebook, or a digital expense tracker.
It’s essential to keep receipts, invoices, and other supporting documentation for all expenses.
- Consider Tax-Advantaged Savings:Contribute to retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs to reduce your taxable income. These accounts offer tax benefits, such as tax-deferred growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement. For example, if you contribute $10,000 to a traditional IRA, this amount will be deducted from your taxable income, resulting in lower taxes.
Additionally, the earnings in the IRA will grow tax-deferred, meaning you won’t pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them in retirement.
- Consult a Tax Professional:Seek advice from a qualified tax professional to ensure you’re taking advantage of all available deductions and credits. A tax professional can help you develop a personalized tax plan and identify opportunities to maximize your tax savings.
Tax Planning Strategies for Businesses
Effective tax planning is crucial for businesses to minimize their tax liability and maximize their profitability. Here are some strategies businesses can implement in October 2023:
- Maximize Business Deductions:Businesses can deduct various expenses related to their operations, such as rent, utilities, salaries, and supplies. Review your business expenses and ensure you’re claiming all eligible deductions. For example, if you’re a small business owner, you can deduct expenses related to your home office, business travel, and professional training.
It’s essential to maintain accurate records of all business expenses to support your deductions.
- Consider Tax Credits:Explore available tax credits that can directly reduce your business’s tax liability. The Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit and the Work Opportunity Tax Credit are examples of credits that can provide significant tax savings for eligible businesses. For example, the R&D Tax Credit can provide a tax credit for businesses that conduct qualified research and development activities.
Looking for a new car? October is a great time to explore lease deals. Check out the October 2023 Lease Deals to see what incentives are available. You might be surprised at the savings you can find.
The Work Opportunity Tax Credit can provide a tax credit for businesses that hire individuals from certain target groups, such as veterans, ex-felons, and long-term unemployed individuals.
- Invest in Tax-Advantaged Assets:Consider investing in assets that offer tax benefits, such as depreciable property or equipment. Depreciation allows businesses to deduct a portion of the cost of these assets over time, reducing their taxable income. For example, if you purchase a new piece of equipment for your business, you can deduct a portion of its cost each year as depreciation expense.
This can help reduce your business’s tax liability over the life of the asset.
- Explore Tax-Advantaged Financing:Consider using tax-advantaged financing options, such as Small Business Administration (SBA) loans, to fund your business operations. These loans may offer favorable interest rates and tax benefits. For example, SBA loans are designed to help small businesses obtain financing and can offer lower interest rates than traditional bank loans.
Potential Deductions and Credits for Businesses
Here is a list of potential deductions and credits that may be available to businesses in October 2023. Consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.
| Category | Deduction/Credit | Description | Eligibility Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Expenses | Business Expense Deduction | Deduction for ordinary and necessary business expenses. | Expenses must be incurred in connection with the business and meet certain requirements. |
| Research and Development | Research and Development Tax Credit | Tax credit for qualified research and development activities. | Must meet specific requirements for qualified research activities. |
| Employee Benefits | Employee Health Insurance Premium Deduction | Deduction for premiums paid for employee health insurance. | Must meet specific requirements for employer-sponsored health insurance. |
| Depreciation | Depreciation Expense Deduction | Deduction for the cost of depreciable assets over time. | Must be a tangible asset with a useful life of more than one year. |
| Investment | Investment Tax Credit | Tax credit for investments in certain types of assets. | Must meet specific requirements for qualifying investments. |
Maximizing Tax Savings for Businesses
- Track Business Expenses:Maintain accurate records of all business expenses. Use a system that works for your business, such as accounting software, a spreadsheet, or a dedicated notebook. Keep receipts, invoices, and other supporting documentation for all expenses. Accurate record-keeping will help you claim all eligible deductions and credits on your tax return.
- Consider Tax-Advantaged Investments:Invest in assets that offer tax benefits, such as depreciable property or equipment. Depreciation allows businesses to deduct a portion of the cost of these assets over time, reducing their taxable income. For example, if you purchase a new piece of equipment for your business, you can deduct a portion of its cost each year as depreciation expense.
This can help reduce your business’s tax liability over the life of the asset.
- Consult a Tax Professional:Seek advice from a qualified tax professional to ensure you’re taking advantage of all available deductions and credits. A tax professional can help you develop a personalized tax plan for your business and identify opportunities to maximize your tax savings.
Tax Resources and Support
Navigating the complexities of the tax system can be daunting, even for seasoned taxpayers. Luckily, there are numerous resources available to help individuals and businesses understand their tax obligations and make informed decisions.
Government Agencies
Government agencies play a crucial role in providing information and guidance on tax matters. Here are some key resources:
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS):The IRS is the primary federal tax agency in the United States. It offers a wealth of information on tax laws, regulations, forms, and publications. The IRS website provides a comprehensive library of resources, including online tools, calculators, and frequently asked questions (FAQs).
You can also contact the IRS by phone, mail, or through their online services.
- State Tax Departments:Each state has its own tax department that administers state income tax, sales tax, and other state-specific taxes. State tax departments provide information on state tax laws, forms, and deadlines. You can typically find their websites and contact information through the state government website.
Professional Organizations
Professional organizations dedicated to tax preparation and accounting offer valuable resources and support for taxpayers.
- American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA):The AICPA is a professional organization for certified public accountants (CPAs). The AICPA offers resources and guidance on various tax-related matters, including ethics, standards, and best practices. Their website provides access to publications, research, and educational materials.
- National Society of Accountants (NSA):The NSA is a professional organization for accountants and bookkeepers. The NSA provides resources and support for tax professionals, including continuing education, networking opportunities, and advocacy efforts. Their website offers information on tax laws, regulations, and best practices.
Online Resources
The internet has become an invaluable source of tax information. Here are some reputable online resources:
- Tax Preparation Software Websites:Tax preparation software companies like TurboTax, H&R Block, and TaxAct offer free guides, articles, and calculators on various tax topics. They also provide access to tax forms and filing instructions.
- Financial News Sites with Tax Sections:Reputable financial news sites, such as Investopedia, The Balance, and NerdWallet, often have dedicated sections on taxes. They provide articles, videos, and calculators to help you understand tax-related issues and make informed decisions.
Contact Information
| Resource | Website | Phone Number | Email Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Revenue Service (IRS) | https://www.irs.gov/ | (800) 829-1040 | [email protected] |
| American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) | https://www.aicpa.org/ | (888) 777-7077 | [email protected] |
| National Society of Accountants (NSA) | https://www.nsa.org/ | (800) 228-6722 | [email protected] |
Benefits of Seeking Professional Tax Advice
Seeking professional tax advice from a qualified tax professional can offer significant benefits, especially for individuals and businesses with complex tax situations.
- Individuals:Professional tax advice can help individuals navigate complex tax situations, such as those involving investments, real estate, or inheritance. Tax professionals can help individuals identify deductions and credits they may be eligible for, ensuring they pay the correct amount of taxes and avoid potential penalties.
- Small Businesses:Small business owners often face unique tax challenges, including choosing the right business structure, managing payroll taxes, and complying with state and federal tax regulations. Tax professionals can provide guidance on these matters, helping small businesses minimize their tax liability and maximize their profitability.
- High-Income Earners:High-income earners often face complex tax situations involving capital gains, estate planning, and charitable giving. Tax professionals can help them develop strategies to minimize their tax liability while maximizing their wealth.
State Tax Deadlines
While federal taxes have a single deadline, state income taxes have varying deadlines. This can be confusing for individuals who live in multiple states or have income from various sources. Understanding these deadlines is crucial to avoid penalties for late filing or payment.
State Tax Deadlines in October 2023
The following table Artikels the state income tax deadlines for October 2023. Please note that these deadlines may vary depending on individual circumstances, such as extensions or special circumstances. It’s always best to consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.
| State | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Alabama | April 15, 2024 |
| Alaska | April 15, 2024 |
| Arizona | April 15, 2024 |
| Arkansas | April 15, 2024 |
| California | April 15, 2024 |
| Colorado | April 15, 2024 |
| Connecticut | April 15, 2024 |
| Delaware | April 15, 2024 |
| Florida | No state income tax |
| Georgia | April 15, 2024 |
| Hawaii | April 15, 2024 |
| Idaho | April 15, 2024 |
| Illinois | April 15, 2024 |
| Indiana | April 15, 2024 |
| Iowa | April 15, 2024 |
| Kansas | April 15, 2024 |
| Kentucky | April 15, 2024 |
| Louisiana | April 15, 2024 |
| Maine | April 15, 2024 |
| Maryland | April 15, 2024 |
| Massachusetts | April 15, 2024 |
| Michigan | April 15, 2024 |
| Minnesota | April 15, 2024 |
| Mississippi | April 15, 2024 |
| Missouri | April 15, 2024 |
| Montana | April 15, 2024 |
| Nebraska | April 15, 2024 |
| Nevada | April 15, 2024 |
| New Hampshire | April 15, 2024 |
| New Jersey | April 15, 2024 |
| New Mexico | April 15, 2024 |
| New York | April 15, 2024 |
| North Carolina | April 15, 2024 |
| North Dakota | April 15, 2024 |
| Ohio | April 15, 2024 |
| Oklahoma | April 15, 2024 |
| Oregon | April 15, 2024 |
| Pennsylvania | April 15, 2024 |
| Rhode Island | April 15, 2024 |
| South Carolina | April 15, 2024 |
| South Dakota | April 15, 2024 |
| Tennessee | April 15, 2024 |
| Texas | No state income tax |
| Utah | April 15, 2024 |
| Vermont | April 15, 2024 |
| Virginia | May 1, 2024 |
| Washington | April 15, 2024 |
| West Virginia | April 15, 2024 |
| Wisconsin | April 15, 2024 |
| Wyoming | April 15, 2024 |
Unique State Tax Rules
Certain states have specific tax rules or regulations that may impact your tax obligations. For example,
“In California, residents must file an estimated tax return if their income tax liability exceeds $1,000.”
Another example is:
“In New York, residents must pay an additional tax on income earned from other states.”
It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with these unique state tax rules to ensure accurate and timely filing.
Tax Changes and Updates
The tax landscape is constantly evolving, and 2023 saw a number of significant changes that impact taxpayers. Understanding these updates is crucial for ensuring accurate tax filing and maximizing potential benefits.
Changes to Standard Deductions
The standard deduction is the amount you can deduct from your taxable income without itemizing. It varies based on your filing status and age. For 2023, the standard deduction amounts increased slightly for most filing statuses. This means that more taxpayers may find it advantageous to take the standard deduction rather than itemizing their deductions.
- Single Filers:$13,850 (increased from $12,950 in 2022)
- Married Filing Jointly:$27,700 (increased from $25,900 in 2022)
- Head of Household:$20,800 (increased from $19,400 in 2022)
- Qualifying Widow(er):$27,700 (increased from $25,900 in 2022)
- Married Filing Separately:$13,850 (increased from $12,950 in 2022)
Changes to Child Tax Credit
The Child Tax Credit is a valuable tax break for families with children. For the 2023 tax year, the maximum credit amount remains at $2,000 per qualifying child, but the income thresholds for claiming the full credit have been adjusted.
- Full Credit:The full $2,000 credit is available to families with adjusted gross income (AGI) below certain thresholds, which vary based on filing status. For example, the threshold for married filing jointly is $400, 000.
- Partial Credit:For families with AGI above the thresholds, the credit begins to phase out.
Changes to Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
The EITC is a refundable tax credit that helps low- and moderate-income working individuals and families. For 2023, the EITC has been adjusted to reflect changes in the cost of living.
- Increased Credit Amounts:The maximum EITC amount has been increased for certain income levels and filing statuses.
- Adjusted Income Thresholds:The income thresholds for eligibility have been adjusted, which may impact whether individuals qualify for the credit.
Staying Informed about Tax Developments
Staying up-to-date on tax changes is essential for taxpayers. There are a number of resources available to help you stay informed.
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS):The IRS website (www.irs.gov) is a primary source for information on tax laws, regulations, and updates.
- Tax Professionals:Consulting with a qualified tax professional can provide personalized guidance and ensure you are aware of any relevant tax changes.
- Tax News and Publications:Many reputable financial publications and websites provide regular updates on tax developments.
Impact of Inflation on Taxes
Inflation can significantly impact tax liabilities, especially for individuals and families facing rising prices. As inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, it can affect income, deductions, and tax brackets, ultimately influencing how much tax you owe.
Tax Liabilities
Inflation can impact both income tax and property tax liabilities. As prices increase, individuals may experience an increase in their income, which could push them into a higher tax bracket. This is known as “bracket creep,” where a rise in nominal income due to inflation leads to a higher tax burden.
For example, if your salary increases from $50,000 to $55,000 due to inflation, you might find yourself in a higher tax bracket, leading to a larger tax bill. Additionally, inflation can affect property taxes as rising property values lead to higher assessments, resulting in increased property tax liabilities.
Tax Planning
To mitigate the negative effects of inflation on taxes, individuals can employ various tax planning strategies. One strategy is to adjust investment strategies, potentially shifting investments towards tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs to reduce taxable income. Adjusting tax withholdings is another strategy.
Increasing withholdings can help avoid a large tax bill at the end of the year, especially if you anticipate a higher income due to inflation. For example, if you expect a salary increase due to inflation, you could increase your withholding to avoid being surprised by a larger tax bill come tax season.
Deductions and Credits
Inflation can affect the value of specific deductions and credits. The standard deduction, mortgage interest deduction, and charitable contribution deduction may lose some of their value due to inflation. For example, a $1,000 charitable contribution may have a lower tax benefit in a year with high inflation compared to a year with lower inflation.
Similarly, tax credits like the Child Tax Credit or the Earned Income Tax Credit may also be affected by inflation, as their value may not keep pace with rising prices.
Tax Brackets
Inflation can lead to changes in tax brackets due to the phenomenon of “bracket creep.” As inflation pushes your income higher, you might find yourself moving into a higher tax bracket, even though your purchasing power may not have significantly increased.
For instance, if your salary increases from $70,000 to $75,000 due to inflation, you could be pushed into a higher tax bracket, resulting in a larger tax bill. This can happen even though your real income (adjusted for inflation) may not have increased substantially.
Tax Filing Software
Tax filing software has revolutionized how individuals prepare and file their taxes. These programs offer user-friendly interfaces, guidance through complex tax forms, and the convenience of e-filing. With numerous options available, choosing the right tax filing software can be a daunting task.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of popular tax filing software options, factors to consider when making your choice, and recommendations based on your specific needs.
Comparison of Popular Tax Filing Software
Here’s a comparison of five popular tax filing software options, highlighting their features, pricing, and user feedback:
| Software Name | Features | Pricing | User Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| TurboTax | Supports various tax forms, deductions, credits, federal and state filing, e-filing, audit support, and live tax advice. | Pricing varies based on filing needs, ranging from free for simple returns to premium tiers with additional features and support. | Generally positive reviews, praising its user-friendliness, comprehensive features, and helpful guidance. However, some users complain about the cost and occasional technical issues. |
| H&R Block | Offers similar features to TurboTax, including support for various tax forms, deductions, credits, federal and state filing, e-filing, and audit support. | Pricing structure is similar to TurboTax, with free options for simple returns and premium tiers for more complex situations. | User reviews are generally positive, highlighting its ease of use, accuracy, and helpful customer support. Some users note that it can be expensive for advanced features. |
| TaxAct | Provides a comprehensive suite of features, including support for various tax forms, deductions, credits, federal and state filing, e-filing, and audit support. | TaxAct offers a more affordable pricing structure compared to TurboTax and H&R Block, with options for free, basic, and premium tiers. | User reviews are generally positive, praising its affordability and comprehensive features. Some users mention occasional technical issues and limited customer support. |
| FreeTaxUSA | A free option for simple federal and state returns, offering support for basic tax forms, deductions, and credits. | Free for federal and state returns for simple tax situations. Paid options are available for additional features and support. | User reviews are generally positive, highlighting its affordability and ease of use for simple returns. Some users note that it lacks advanced features and support for complex situations. |
| Credit Karma Tax | A free option for federal and state returns, offering support for various tax forms, deductions, and credits. | Completely free for federal and state returns, with no paid tiers or additional features. | User reviews are generally positive, praising its free service and user-friendly interface. Some users note that it lacks advanced features and support for complex situations. |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Tax Filing Software
When selecting tax filing software, consider these factors:
- Ease of Use:The software should be intuitive and easy to navigate, even for those with limited tax knowledge. Look for features like clear instructions, helpful prompts, and a user-friendly interface.
- Accuracy:The software should accurately calculate your taxes and ensure you receive the maximum deductions and credits you’re eligible for. Look for features like built-in tax calculators, error checks, and IRS compliance.
- Features:Choose software that supports the tax forms, deductions, and credits you need to file your return. Consider features like support for various income types, dependents, and tax situations.
- Customer Support:Look for software that offers reliable customer support through various channels, such as phone, email, and online chat. This is crucial for resolving any technical issues or questions you may have.
- Data Security:Your personal and financial information is sensitive, so choose software that uses robust security measures to protect your data. Look for features like encryption, two-factor authentication, and compliance with industry standards.
- Price:Tax filing software comes in various price ranges, from free options for simple returns to premium tiers with additional features and support. Choose a software that fits your budget and filing needs.
Recommendations for Choosing Tax Filing Software
Here are some recommendations based on individual needs and circumstances:
- For simple tax situations (e.g., single filers with no dependents, basic income):FreeTaxUSA or Credit Karma Tax are excellent choices due to their affordability and ease of use. These options are suitable for individuals with straightforward tax situations.
- For moderate tax situations (e.g., families with children, self-employed individuals):TurboTax or H&R Block offer a good balance of features and support for a reasonable price. These options are suitable for individuals with more complex tax situations.
- For complex tax situations (e.g., business owners, investors, those with multiple income sources):TurboTax or H&R Block’s premium tiers provide comprehensive features, expert support, and audit protection. These options are suitable for individuals with complex financial situations.
Tax Tips for Specific Groups
Understanding your specific tax situation is crucial for minimizing your tax liability and maximizing your financial well-being. This section provides tailored tax tips for different groups, including small business owners, freelancers, retirees, and students.
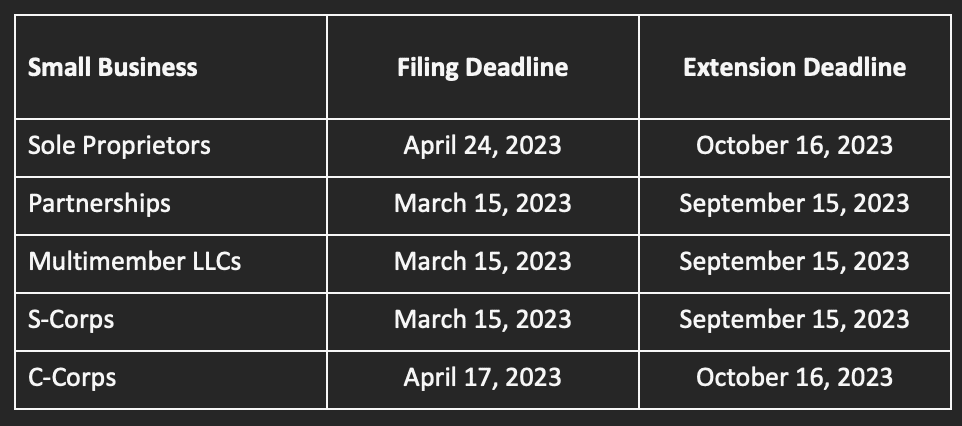
Small Business Owners
Small business owners face a unique set of tax challenges, but understanding the specific deductions and credits available to them can significantly minimize their tax burden.
- Deductions for Business Expenses: Small business owners can deduct a wide range of expenses incurred in running their business, including rent, utilities, salaries, supplies, and marketing costs. Keeping accurate records of all business expenses is crucial for claiming these deductions. For example, a small business owner can deduct the cost of renting office space, purchasing office supplies, and paying for advertising.
- Tax Credits Available to Small Businesses: The government offers various tax credits to encourage small business growth and job creation. These credits can offset a portion of the business owner’s tax liability, potentially resulting in a tax refund. For example, the Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC) provides a tax credit for hiring individuals from certain disadvantaged groups.
- Choosing the Right Business Structure: The choice of business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, etc.) can have significant tax implications. Each structure has its own rules for reporting income and expenses, as well as its own tax liabilities. Consulting with a tax professional is essential to determine the most suitable structure for your specific business needs.
October is a busy month for financial deadlines. The IRS October Deadline 2023 is a key date to remember for anyone who filed for an extension on their taxes. Make sure you’re prepared to meet your obligations by checking the calendar and understanding the specific requirements.
- Estimating and Paying Quarterly Taxes: Small business owners are generally required to estimate and pay their taxes quarterly through IRS Form 1040-ES. Failure to make timely payments can result in penalties. It is crucial to accurately estimate your income and expenses to avoid underpayment penalties.
Using an online tax calculator or consulting with a tax professional can help you determine the appropriate quarterly tax payments.
- Understanding the Difference Between Business and Personal Income: It is essential to separate business income and expenses from personal income and expenses. Mixing personal and business funds can lead to complications and penalties. Maintaining separate bank accounts for business and personal finances is a good practice.
- Key Tax Forms for Small Business Owners: Small business owners are responsible for filing various tax forms, including Schedule C (Profit or Loss From Business), Form 1040 (U.S. Individual Income Tax Return), and Form 1065 (U.S. Return of Partnership Income). It is crucial to understand the requirements for each form and file them accurately and on time.
Common Deductions for Small Business Owners
| Deduction | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Home Office Deduction | Deduct a portion of your home expenses if you use a part of your home exclusively for business purposes. | Rent, mortgage interest, utilities, insurance, repairs, and depreciation. |
| Business Expenses | Expenses directly related to your business operations. | Advertising, supplies, travel, salaries, rent, and utilities. |
| Depreciation | Deduct the cost of business assets over their useful life. | Computers, equipment, vehicles, and furniture. |
| Health Insurance Premiums | Deduct premiums paid for health insurance for yourself and your family if you are self-employed. | Individual and family health insurance premiums. |
| Retirement Contributions | Deduct contributions to retirement plans, such as a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k). | Contributions to a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k). |
“Small business owners often face a unique set of tax challenges. It’s crucial to understand the specific deductions and credits available to them to minimize their tax liability.”
Freelancers, When Are Taxes Due In October 2023
Freelancers have the flexibility of setting their own hours and rates, but they also have the responsibility of managing their own taxes. Understanding the key tax considerations for freelancers can help them optimize their tax situation.
- Reporting Income and Expenses: Freelancers are required to report their income and expenses on Schedule C of Form 1040. It is crucial to keep accurate records of all income and expenses, including receipts, invoices, and bank statements. This will help you determine your net income and ensure you claim all eligible deductions.
- Deductions for Home Office Expenses: Freelancers who use a portion of their home exclusively for business purposes can claim the home office deduction. This deduction allows you to deduct a portion of your home expenses, such as rent, mortgage interest, utilities, and insurance, based on the percentage of your home used for business purposes.
- Estimating and Paying Self-Employment Taxes: Freelancers are responsible for paying self-employment taxes, which include Social Security and Medicare taxes. These taxes are calculated on your net self-employment income and are paid quarterly through IRS Form 1040-ES. It is important to estimate your income and expenses accurately to avoid underpayment penalties.
- Choosing the Right Tax Filing Status: Freelancers can choose their tax filing status, such as single, married filing jointly, or head of household. The chosen status can affect your tax liability, so it is important to choose the status that results in the lowest tax burden.
- Understanding the Difference Between 1099-NEC and 1099-MISC Forms: Freelancers typically receive Form 1099-NEC (Nonemployee Compensation) or Form 1099-MISC (Miscellaneous Income) from clients who pay them for their services. It is important to understand the difference between these forms and report your income accurately. Form 1099-NEC is used to report payments for services, while Form 1099-MISC is used to report other types of payments, such as rent or royalties.
Comparison of 1099-NEC and 1099-MISC Forms
| Form | Purpose | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|
| 1099-NEC | Reports payments for services performed by an independent contractor. | Used for payments for services, including freelance work, consulting, and contract labor. |
| 1099-MISC | Reports miscellaneous income payments, including rent, royalties, and prizes. | Used for payments other than services, such as rent, royalties, prizes, and payments to attorneys. |
“Freelancers have the flexibility of setting their own hours and rates, but they also have the responsibility of managing their own taxes.”
Taxation and the Economy
Taxes are a fundamental aspect of any modern economy, playing a crucial role in shaping economic activity, funding public services, and influencing the distribution of wealth. Understanding the intricate relationship between taxation and the economy is essential for informed decision-making and effective policy formulation.
Tax Policies and Economic Growth
Tax policies have a significant impact on economic growth by influencing investment, consumption, and labor supply. For example, lower corporate tax rates can incentivize businesses to invest and expand, leading to job creation and increased economic output. Similarly, tax breaks for research and development can encourage innovation and technological advancements, contributing to long-term economic growth.
However, tax policies can also have unintended consequences. For example, high marginal tax rates can discourage work and investment, leading to a decrease in economic activity.
Taxation and Government Spending
The relationship between taxation and government spending is complex and multifaceted. Taxes provide the revenue that governments use to finance public services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and defense. Government spending, in turn, can stimulate economic activity, create jobs, and improve the overall quality of life.
However, excessive government spending can lead to higher taxes, which can stifle economic growth. The optimal balance between taxation and government spending is a subject of ongoing debate among economists and policymakers.
Taxation and Income Inequality
Taxation plays a vital role in addressing income inequality by redistributing wealth from higher-income earners to lower-income earners through progressive tax systems. This involves imposing higher tax rates on higher incomes, which can help reduce the gap between the rich and the poor.
However, the effectiveness of taxation in reducing income inequality depends on various factors, including the design of the tax system, the level of government spending on social programs, and the overall economic environment.
Taxation and Economic Stability
Taxation can contribute to economic stability by providing a buffer against economic shocks. For example, during a recession, governments can use tax cuts or increased spending to stimulate economic activity. However, excessive reliance on fiscal policy, such as tax cuts or increased spending, can lead to higher government debt and inflation.
Therefore, policymakers must carefully consider the potential impact of tax policies on economic stability.
Taxation and International Competitiveness
Tax policies can also influence a country’s international competitiveness. For example, low corporate tax rates can attract foreign investment and create jobs, while high tax rates can make a country less attractive to businesses. The level of taxation can also affect the cost of doing business and the profitability of companies, impacting their ability to compete in the global marketplace.
Final Review
Staying organized, understanding the rules, and utilizing available resources are key to navigating tax obligations successfully. Remember, tax deadlines are often unforgiving, so plan ahead, seek professional advice when needed, and stay informed about any changes in tax laws or regulations.
By taking proactive steps, you can ensure a smoother tax experience and avoid any unpleasant surprises.
FAQ Overview
What happens if I miss a tax deadline?
Missing a tax deadline can result in penalties, including late filing penalties and late payment penalties. The amount of the penalty can vary depending on the type of tax, the amount owed, and the length of the delay. It’s important to file on time or request an extension if necessary.
Can I get an extension for filing my taxes?
Yes, you can request an extension to file your taxes, but it’s important to note that this only extends the filing deadline, not the payment deadline. You’ll still need to pay any taxes owed by the original deadline.
What if I owe taxes but can’t afford to pay them?
If you can’t afford to pay your taxes in full, you may be able to set up a payment plan with the IRS. You can also explore other options, such as an Offer in Compromise (OIC), which allows you to settle your tax debt for a lower amount.